Abstract
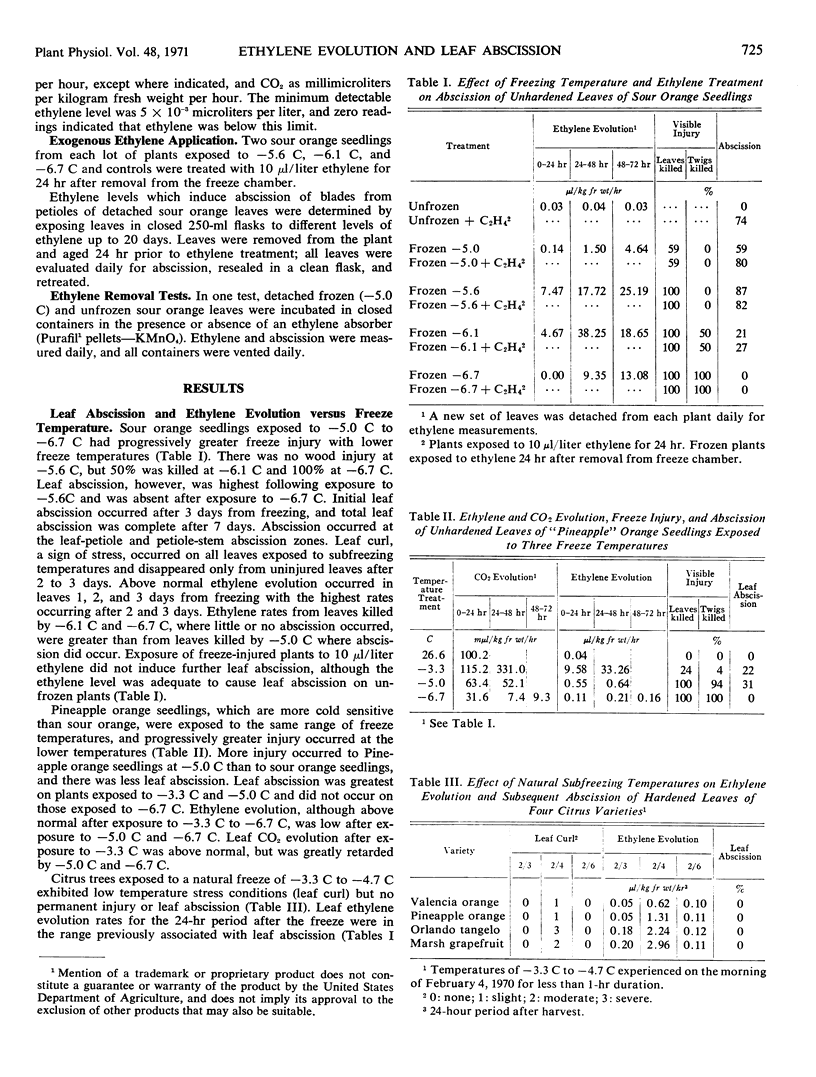
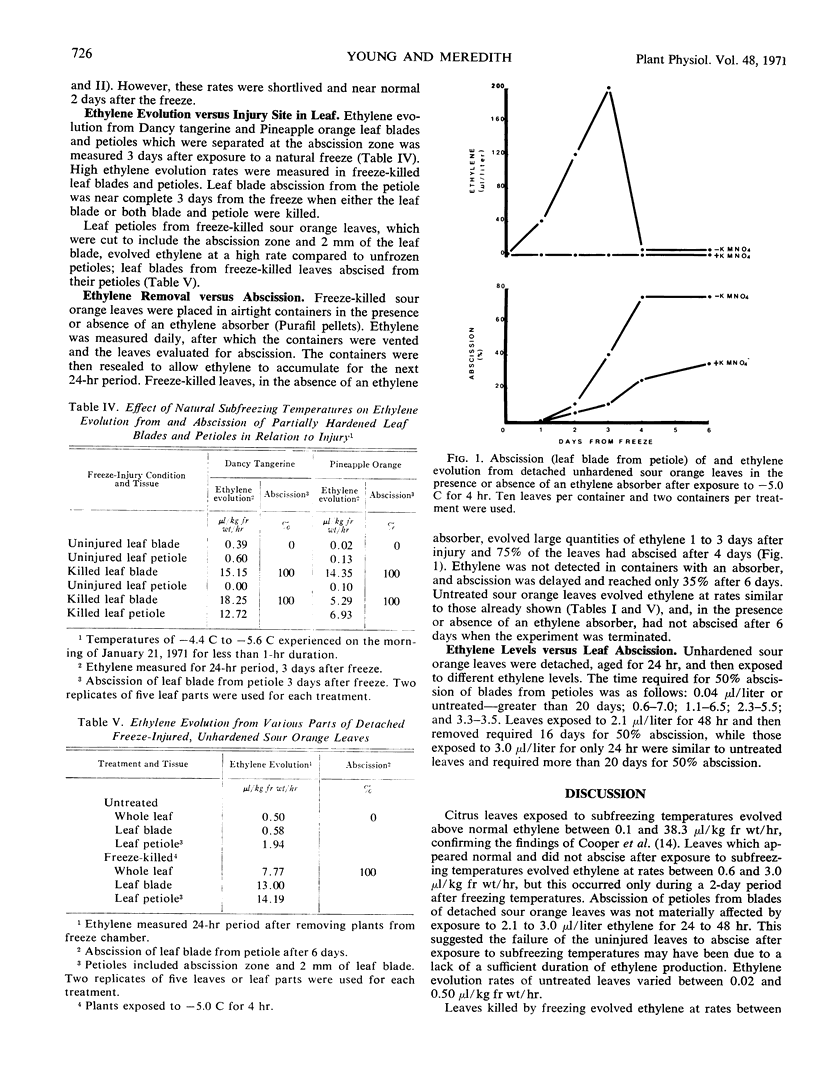
Citrus leaves exposed to subfreezing temperatures evolved ethylene at rates between 0.1 and 38.3 microliters per kilogram fresh weight per hour whereas untreated leaves evolved between 0.01 and 0.50 microliter per kilogram fresh weight per hour. Leaves not injured by freezing temperatures did not abscise, and ethylene evolution was near normal after 2 days. Freeze-injured leaves continued evolving high ethylene levels 4 or 5 days subsequent to freeze injury, and many of the freeze-killed leaves abscised. Supportive evidence suggested freeze-induced ethylene was involved in freeze-induced leaf abscission; whereas freeze-inhibited abscission was not due to a lack of ethylene but injury to other metabolic systems necessary for abscission.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles F. B. Abscission: role of cellulase. Plant Physiol. 1969 Mar;44(3):447–452. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeles F. B., Craker L. E., Leather G. R. Abscission: the phytogerontological effects of ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jan;47(1):7–9. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeles F. B., Holm R. E. Enhancement of RNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and abscission by ethylene. Plant Physiol. 1966 Oct;41(8):1337–1342. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.8.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeles F. B. Role of RNA and protein synthesis in abscission. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1577–1586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg S. P. Ethylene, plant senescence and abscission. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1503–1511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. C., Rasmussen G. K., Rogers B. J., Reece P. C., Henry W. H. Control of abscission in agricultural crops and its physiological basis. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1560–1576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm R. E., Abeles F. B. Abscission: the role of RNA synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1967 Aug;42(8):1094–1102. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.8.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Osborne D. J. Ethylene, the natural regulator of leaf abscission. Nature. 1970 Mar 14;225(5237):1019–1022. doi: 10.1038/2251019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morre D. J. Cell wall dissolution and enzyme secretion during leaf abscission. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1545–1559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster B. D. Anatomical aspects of abscission. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9 Pt B):1512–1544. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



