Abstract
According to the amyloid hypothesis for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease, beta-amyloid peptide (betaA) directly affects neurons, leading to neurodegeneration and tau phosphorylation. In rat hippocampal culture, betaA exposure activates tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (TPKI/GSK-3beta), which phosphorylates tau protein into Alzheimer disease-like forms, resulting in neuronal death. To elucidate the mechanism of betaA-induced neuronal death, we searched for substrates of TPKI/GSK-3beta in a two-hybrid system and identified pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), which converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA in mitochondria. PDH was phosphorylated and inactivated by TPKI/GSK-3beta in vitro and also in betaA-treated hippocampal cultures, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction, which would contribute to neuronal death. In cholinergic neurons, betaA impaired acetylcholine synthesis without affecting choline acetyltransferase activity, which suggests that PDH is inactivated by betaA-induced TPKI/GSK-3beta. Thus, TPKI/GSK-3beta regulates PDH and participates in energy metabolism and acetylcholine synthesis. These results suggest that TPKI/GSK-3beta plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe E., Casamenti F., Giovannelli L., Scali C., Pepeu G. Administration of amyloid beta-peptides into the medial septum of rats decreases acetylcholine release from hippocampus in vivo. Brain Res. 1994 Feb 4;636(1):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busciglio J., Lorenzo A., Yeh J., Yankner B. A. beta-amyloid fibrils induce tau phosphorylation and loss of microtubule binding. Neuron. 1995 Apr;14(4):879–888. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90232-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Maloney A. J. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1403–1403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91936-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embi N., Rylatt D. B., Cohen P. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. A rapid radiochemical method for the determination of choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1975 Feb;24(2):407–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb11895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Games D., Adams D., Alessandrini R., Barbour R., Berthelette P., Blackwell C., Carr T., Clemens J., Donaldson T., Gillespie F. Alzheimer-type neuropathology in transgenic mice overexpressing V717F beta-amyloid precursor protein. Nature. 1995 Feb 9;373(6514):523–527. doi: 10.1038/373523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy J. A., Higgins G. A. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):184–185. doi: 10.1126/science.1566067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
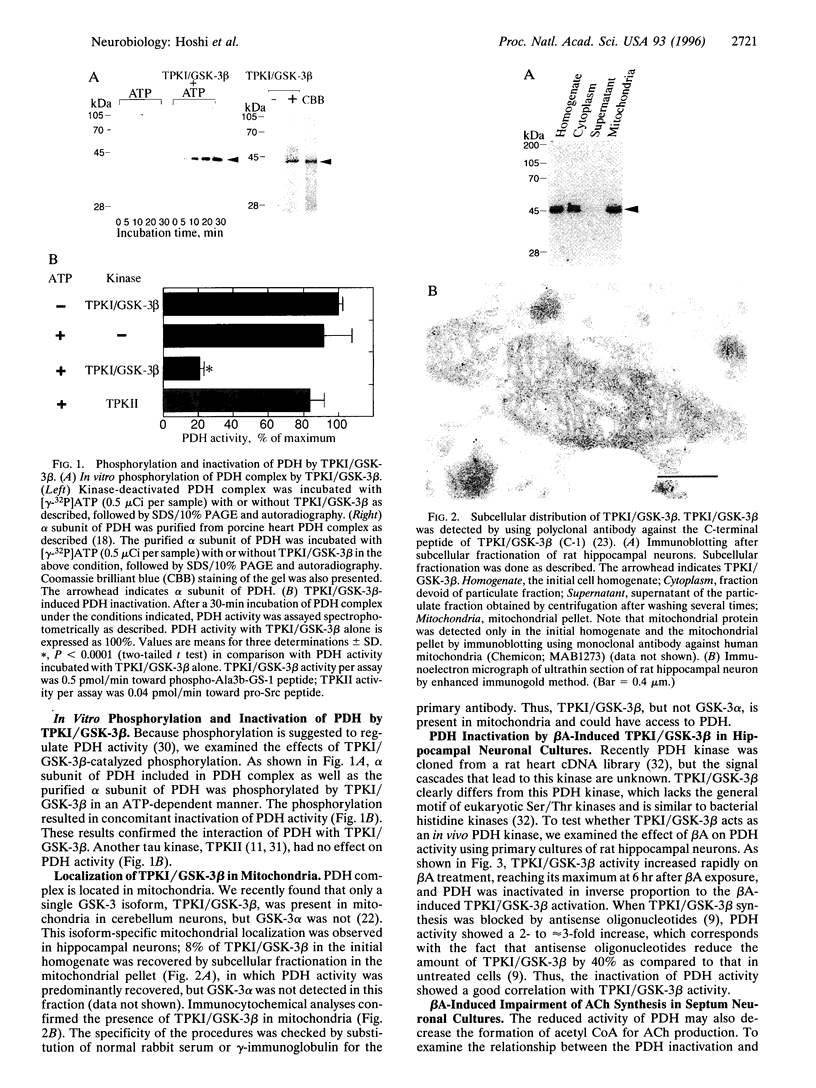
- Hoshi M., Sato M., Kondo S., Takashima A., Noguchi K., Takahashi M., Ishiguro K., Imahori K. Different localization of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta from glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha in cerebellum mitochondria. J Biochem. 1995 Oct;118(4):683–685. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer S., Oesterreich K., Wagner O. Glucose metabolism as the site of the primary abnormality in early-onset dementia of Alzheimer type? J Neurol. 1988 Jan;235(3):143–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00314304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
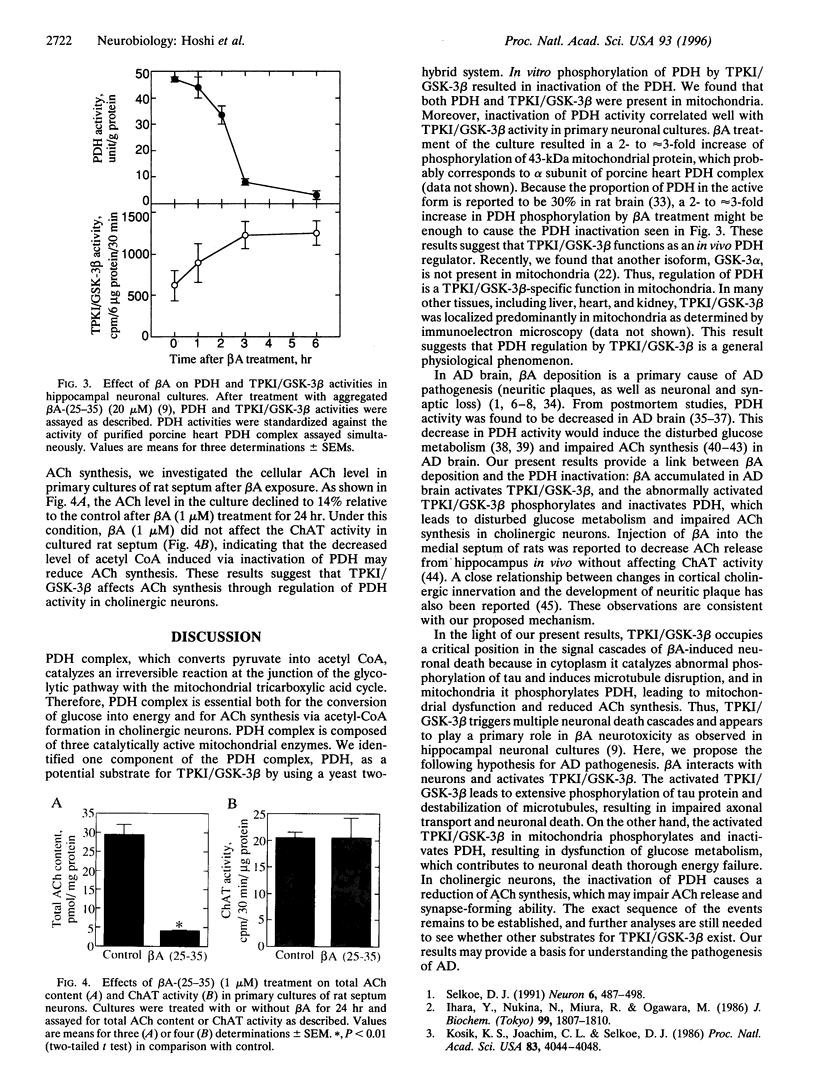
- Ihara Y., Nukina N., Miura R., Ogawara M. Phosphorylated tau protein is integrated into paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J Biochem. 1986 Jun;99(6):1807–1810. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Kobayashi S., Omori A., Takamatsu M., Yonekura S., Anzai K., Imahori K., Uchida T. Identification of the 23 kDa subunit of tau protein kinase II as a putative activator of cdk5 in bovine brain. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 4;342(2):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80501-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Shiratsuchi A., Sato S., Omori A., Arioka M., Kobayashi S., Uchida T., Imahori K. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta is identical to tau protein kinase I generating several epitopes of paired helical filaments. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 5;325(3):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Takamatsu M., Tomizawa K., Omori A., Takahashi M., Arioka M., Uchida T., Imahori K. Tau protein kinase I converts normal tau protein into A68-like component of paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10897–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Joachim C. L., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4044–4048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Blass J. P., Gibson G. E. Studies on the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in brain with the arylamine acetyltransferase-coupled assay. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1627–1636. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latimer D. A., Gallo J. M., Lovestone S., Miller C. C., Reynolds C. H., Marquardt B., Stabel S., Woodgett J. R., Anderton B. H. Stimulation of MAP kinase by v-raf transformation of fibroblasts fails to induce hyperphosphorylation of transfected tau. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 22;365(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00434-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew J., Beaudette K., Litwin C. M., Wang J. H. Purification and characterization of a novel proline-directed protein kinase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13383–13390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. X. Regulation of the activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from beef kidney mitochondria by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):234–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuda S., Shirahama T., Saheki T., Miura S., Mori M. Purification and immunochemical studies of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from rat heart, and cell-free synthesis of lipoamide dehydrogenase, a component of the complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 13;741(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnetti L., Gaiti A., Brunetti M., Avellini L., Polidori C., Cecchetti R., Palumbo B., Senin U. Increased CSF pyruvate levels as a marker of impaired energy metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1995 Mar;43(3):316–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1995.tb07351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry E. K., Gibson P. H., Blessed G., Perry R. H., Tomlinson B. E. Neurotransmitter enzyme abnormalities in senile dementia. Choline acetyltransferase and glutamic acid decarboxylase activities in necropsy brain tissue. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Nov;34(2):247–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry E. K., Perry R. H., Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Gibson P. H. Coenzyme A-acetylating enzymes in Alzheimer's disease: possible cholinergic 'compartment' of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Neurosci Lett. 1980 May 15;18(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov K. M., Kedishvili N. Y., Zhao Y., Shimomura Y., Crabb D. W., Harris R. A. Primary structure of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase establishes a new family of eukaryotic protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26602–26606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter P. E., Meek J. L., Neff N. H. Acetylcholine and choline in neuronal tissue measured by HPLC with electrochemical detection. J Neurochem. 1983 Jul;41(1):188–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorbi S., Bird E. D., Blass J. P. Decreased pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity in Huntington and Alzheimer brain. Ann Neurol. 1983 Jan;13(1):72–78. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struble R. G., Cork L. C., Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L. Cholinergic innervation in neuritic plaques. Science. 1982 Apr 23;216(4544):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6803359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Cheung T. T., Cai X. D., Odaka A., Otvos L., Jr, Eckman C., Golde T. E., Younkin S. G. An increased percentage of long amyloid beta protein secreted by familial amyloid beta protein precursor (beta APP717) mutants. Science. 1994 May 27;264(5163):1336–1340. doi: 10.1126/science.8191290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tomizawa K., Kato R., Sato K., Uchida T., Fujita S. C., Imahori K. Localization and developmental changes of tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1994 Jul;63(1):245–255. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63010245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima A., Noguchi K., Sato K., Hoshino T., Imahori K. Tau protein kinase I is essential for amyloid beta-protein-induced neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7789–7793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima A., Yamaguchi H., Noguchi K., Michel G., Ishiguro K., Sato K., Hoshino T., Hoshi M., Imahori K. Amyloid beta peptide induces cytoplasmic accumulation of amyloid protein precursor via tau protein kinase I/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta in rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Sep 29;198(2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11964-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lint J., Khandelwal R. L., Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R. A specific immunoprecipitation assay for the protein kinase FA/glycogen synthase kinase 3. Anal Biochem. 1993 Jan;208(1):132–137. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P., Hiley C. R., Goodhardt M. J., Carrasco L. H., Keet J. P., Williams I. E., Bowen D. M. Neocortical cholinergic neurons in elderly people. Lancet. 1977 Mar 26;1(8013):668–671. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Cooper R. H., Randle P. J. Mechanism of activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by dichloroacetate and other halogenated carboxylic acids. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):761–774. doi: 10.1042/bj1410761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R. Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2431–2438. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07419.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates C. M., Butterworth J., Tennant M. C., Gordon A. Enzyme activities in relation to pH and lactate in postmortem brain in Alzheimer-type and other dementias. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1624–1630. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]