Abstract
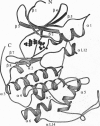
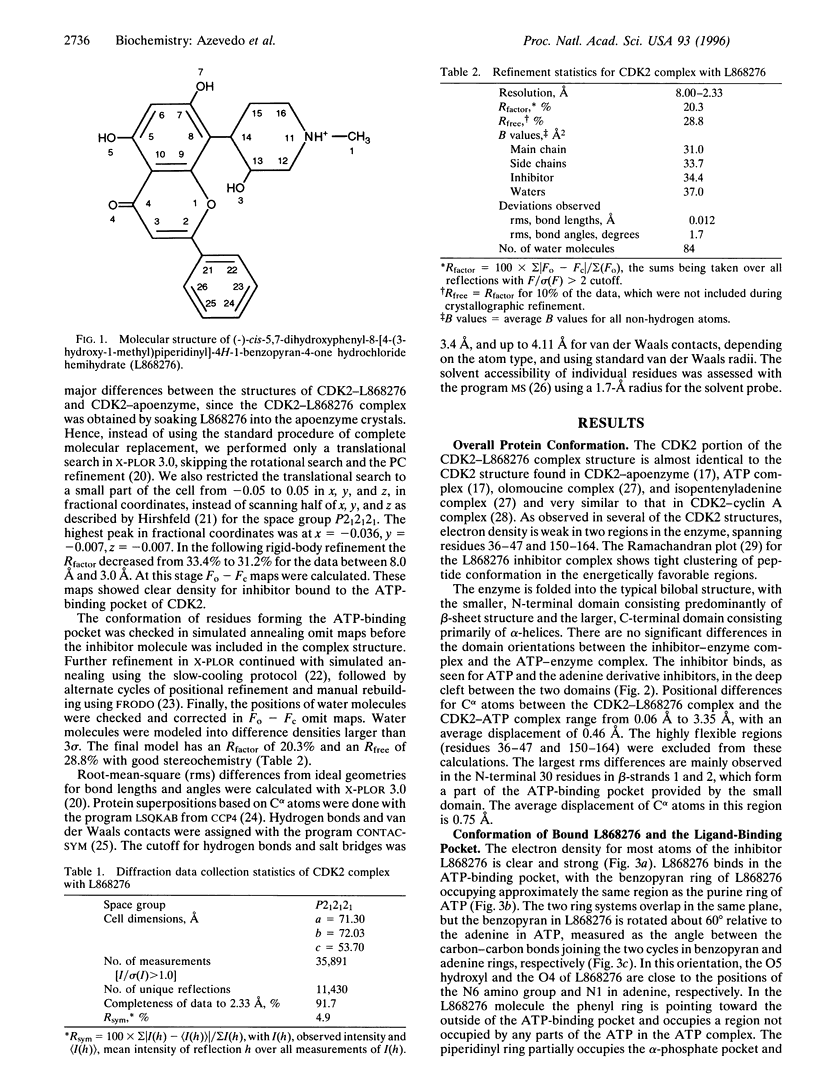
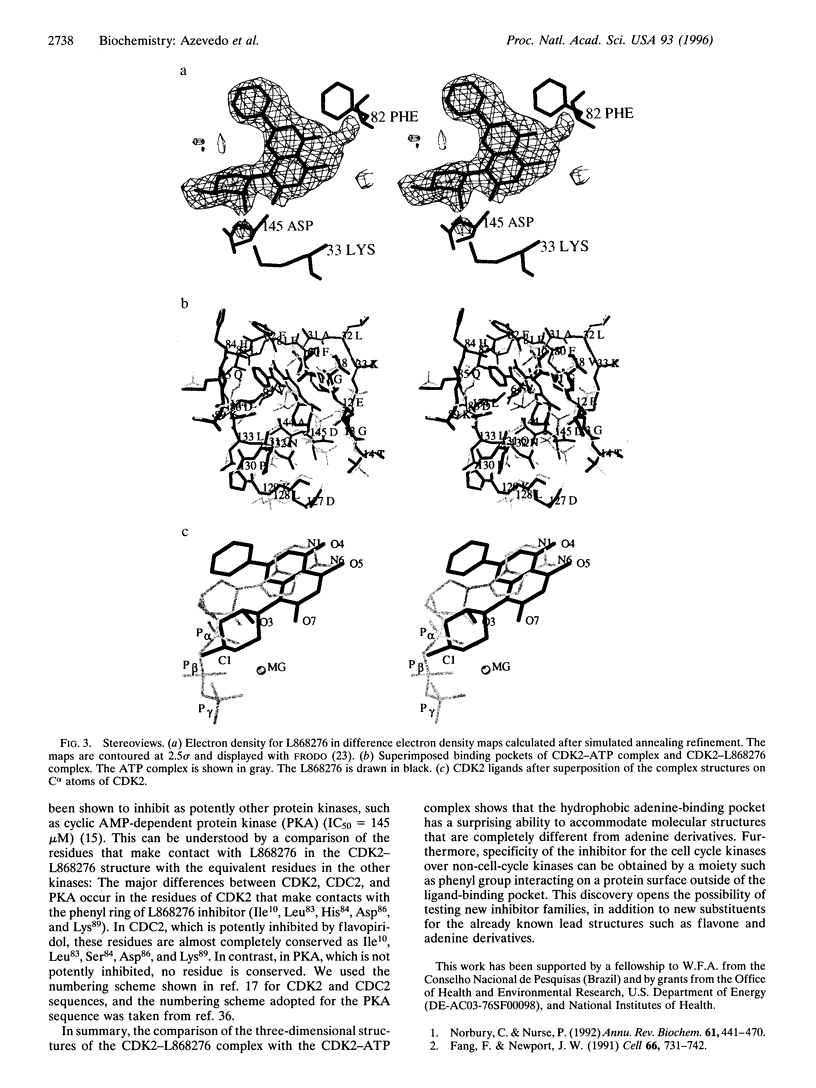
The central role of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) in cell cycle regulation makes them a promising target for studying inhibitory molecules that can modify the degree of cell proliferation. The discovery of specific inhibitors of CDKs such as polyhydroxylated flavones has opened the way to investigation and design of antimitotic compounds. A novel flavone, (-)-cis-5,7-dihydroxyphenyl-8-[4-(3-hydroxy-1-methyl)piperidinyl] -4H-1-benzopyran-4-one hydrochloride hemihydrate (L868276), is a potent inhibitor of CDKs. A chlorinated form, flavopiridol, is currently in phase I clinical trials as a drug against breast tumors. We determined the crystal structure of a complex between CDK2 and L868276 at 2.33 angstroms resolution and refined to an Rfactor 20.3%. The aromatic portion of the inhibitor binds to the adenine-binding pocket of CDK2, and the position of the phenyl group of the inhibitor enables the inhibitor to make contacts with the enzyme not observed in the ATP complex structure. The analysis of the position of this phenyl ring not only explains the great differences of kinase inhibition among the flavonoid inhibitors but also explains the specificity of L868276 to inhibit CDK2 and CDC2.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bossemeyer D., Engh R. A., Kinzel V., Ponstingl H., Huber R. Phosphotransferase and substrate binding mechanism of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit from porcine heart as deduced from the 2.0 A structure of the complex with Mn2+ adenylyl imidodiphosphate and inhibitor peptide PKI(5-24). EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):849–859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Krukowski A., Erickson J. W. Slow-cooling protocols for crystallographic refinement by simulated annealing. Acta Crystallogr A. 1990 Jul 1;46(Pt 7):585–593. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390002355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Activation of human cyclin-dependent kinases in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):571–582. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Kaufmann W. K., Wilson S. J., Tlsty T. D., Lees E., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Reed S. I. p53-dependent inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase activities in human fibroblasts during radiation-induced G1 arrest. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang F., Newport J. W. Evidence that the G1-S and G2-M transitions are controlled by different cdc2 proteins in higher eukaryotes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90117-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Rosenblatt J., Morgan D. O. Cell cycle regulation of CDK2 activity by phosphorylation of Thr160 and Tyr15. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3995–4005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengst L., Dulic V., Slingerland J. M., Lees E., Reed S. I. A cell cycle-regulated inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5291–5295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Freist W., Marutzky R., Shaltiel S. Mapping the ATP-binding site in the catalytic subunit of adenosine-3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Spatial relationship with the ATP site of the undissociated enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):427–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Maturation promoting factor, cyclin and the control of M-phase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;1(2):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Chothia C. The structure of protein-protein recognition sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16027–16030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. D., Russo A. A., Polyak K., Gibbs E., Hurwitz J., Massagué J., Pavletich N. P. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):313–320. doi: 10.1038/376313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur G., Stetler-Stevenson M., Sebers S., Worland P., Sedlacek H., Myers C., Czech J., Naik R., Sausville E. Growth inhibition with reversible cell cycle arrest of carcinoma cells by flavone L86-8275. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Nov 18;84(22):1736–1740. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.22.1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losiewicz M. D., Carlson B. A., Kaur G., Sausville E. A., Worland P. J. Potent inhibition of CDC2 kinase activity by the flavonoid L86-8275. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jun 15;201(2):589–595. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobori T., Miura K., Wu D. J., Lois A., Takabayashi K., Carson D. A. Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):753–756. doi: 10.1038/368753a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M., Herskowitz I. Joining the complex: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory proteins and the cell cycle. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran G. N., Venkatachalam C. M., Krimm S. Stereochemical criteria for polypeptide and protein chain conformations. 3. Helical and hydrogen-bonded polypeptide chains. Biophys J. 1966 Nov;6(6):849–872. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(66)86699-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Stueland C. S., Thomas J., Russell P., Reed S. I. Human cDNAs encoding homologs of the small p34Cdc28/Cdc2-associated protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1332–1344. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., De Bondt H., Jancarik J., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Purification and crystallization of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 20;230(4):1317–1319. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Gahmen U., Brandsen J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Meijer L., Vesely J., Kim S. H. Multiple modes of ligand recognition: crystal structures of cyclin-dependent protein kinase 2 in complex with ATP and two inhibitors, olomoucine and isopentenyladenine. Proteins. 1995 Aug;22(4):378–391. doi: 10.1002/prot.340220408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Hannon G. J., Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):704–707. doi: 10.1038/366704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff S., Hendrickson W. A., Smith J. L. Structure of myohemerythrin in the azidomet state at 1.7/1.3 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):273–296. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Radzio-Andzelm E. Three protein kinase structures define a common motif. Structure. 1994 May 15;2(5):345–355. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J., Knighton D. R., ten Eyck L. F., Karlsson R., Xuong N., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MgATP and peptide inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2154–2161. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]