Abstract
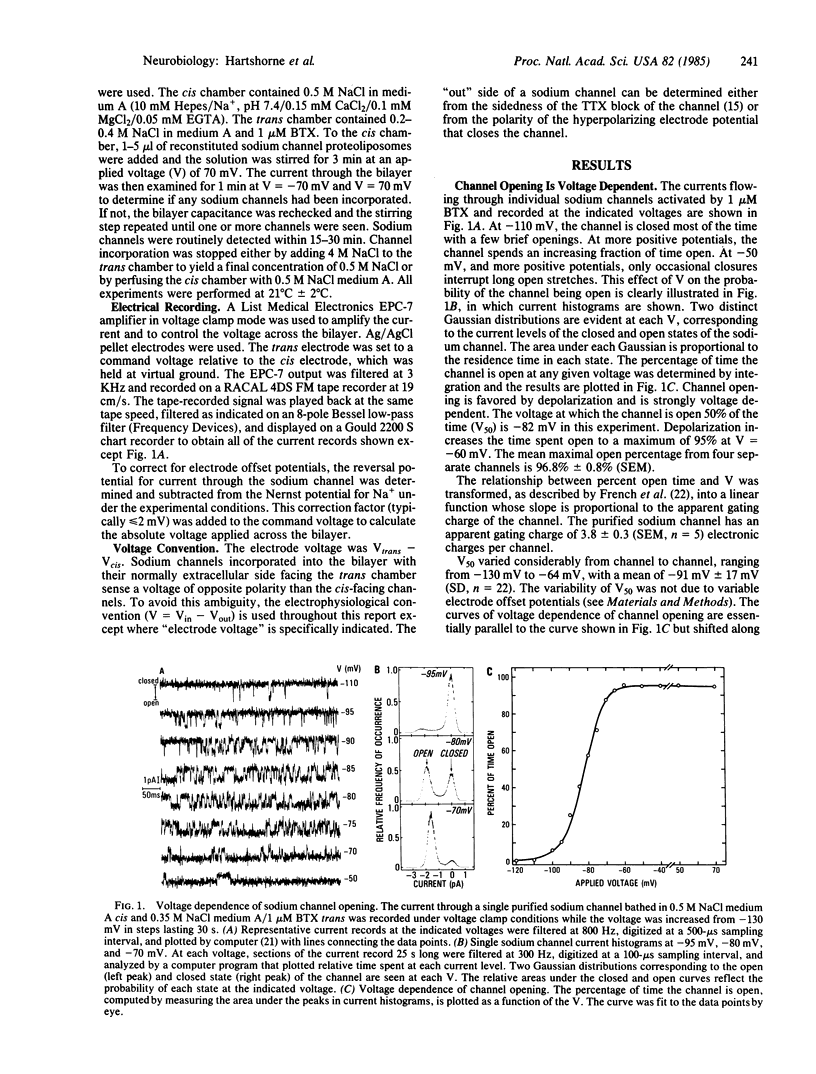
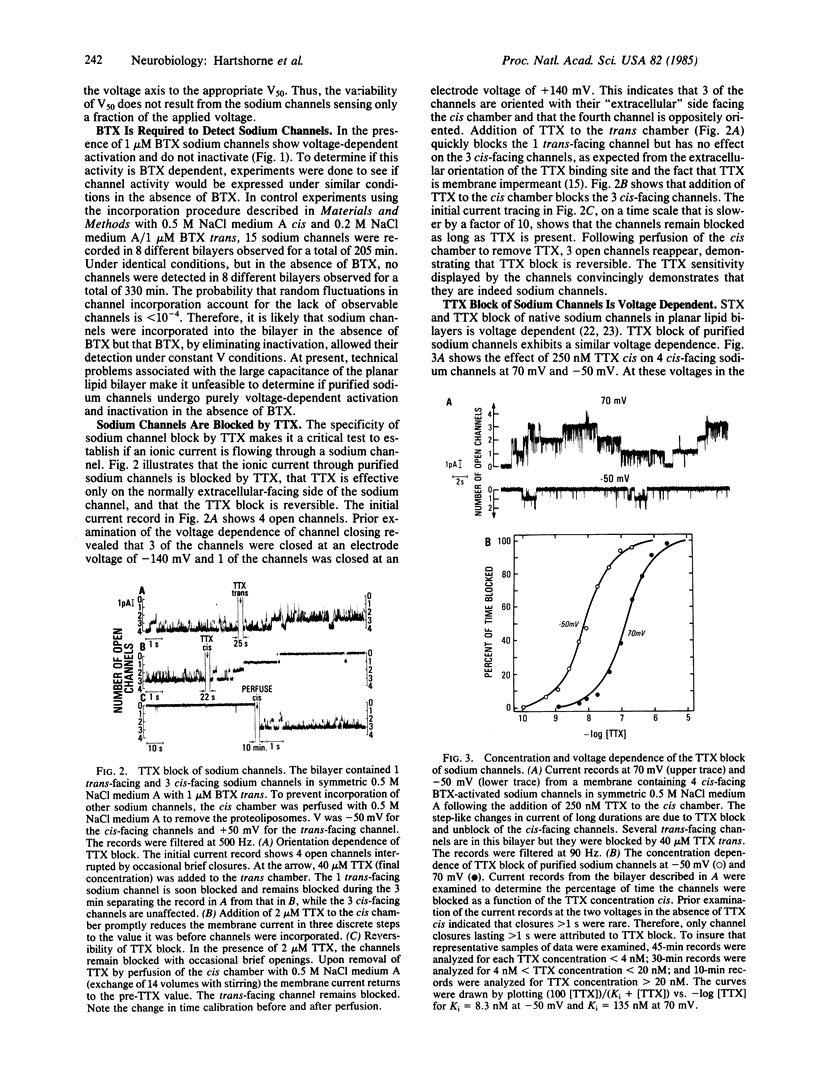
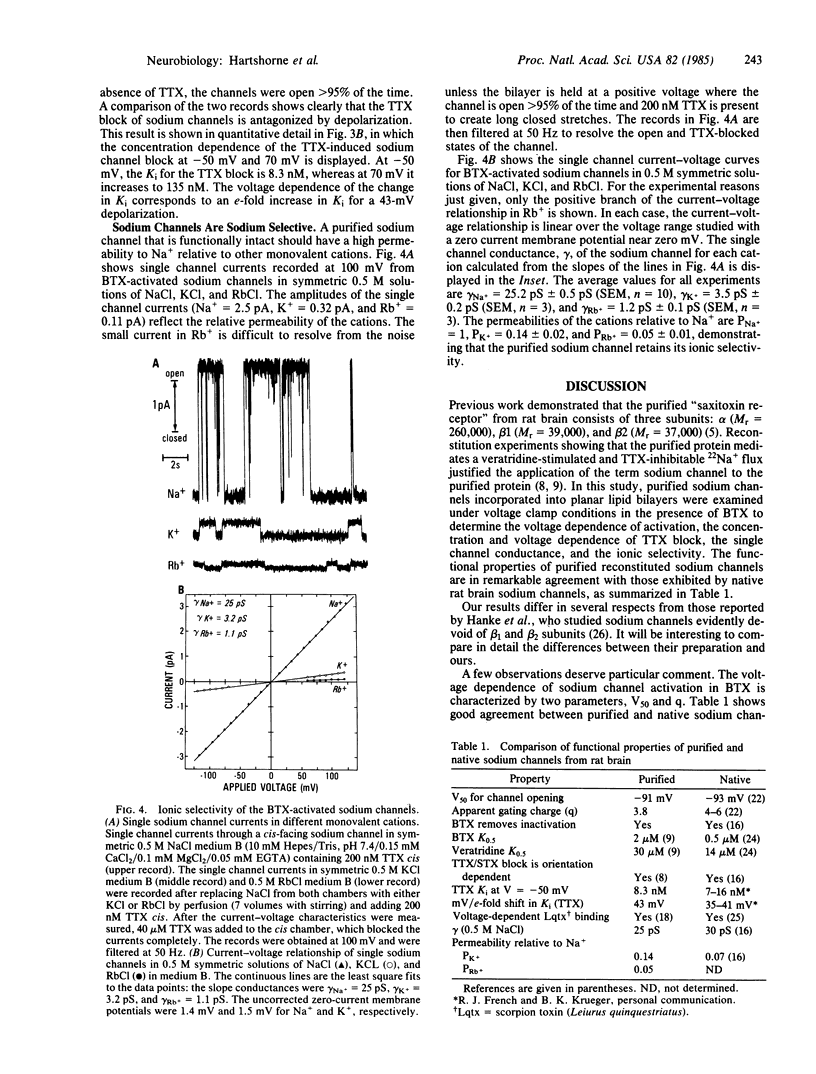
The ion conduction and voltage dependence of sodium channels purified from rat brain were investigated in planar lipid bilayers in the presence of batrachotoxin. Single channel currents are clearly resolved. Channel opening is voltage dependent and favored by depolarization. The voltage at which the channel is open 50% of the time is -91 +/- 17 mV (SD, n = 22) and the apparent gating charge is approximately 4. Tetrodotoxin reversibly blocks the ionic current through the sodium channels. The Ki for the tetrodotoxin block is 8.3 nM at -50 mV and is voltage dependent with the Ki increasing e-fold for depolarizations of 43 mV. The single channel conductance, gamma, is ohmic. At 0.5 M salt concentrations gamma = 25 pS for Na+, 3.5 pS for K+, and 1.2 pS for Rb+. This study demonstrates that the purified brain sodium channel--which consists of three polypeptide subunits: alpha (Mr approximately 260,000), beta 1 (Mr approximately 39,000), and beta 2 (Mr approximately 37,000)--exhibits the same voltage dependence, neurotoxin sensitivity, and ionic selectivity associated with native sodium channels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R., Brabson J. S., Raftery M. A. Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2606–2610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L., Cohen S. A., Murphy L. E. Purification from rat sarcolemma of the saxitoxin-binding component of the excitable membrane sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1306–1310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Protein components of the purified sodium channel from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Neurochem. 1983 May;40(5):1377–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. E., Miller C. Effects of phospholipid surface charge on ion conduction in the K+ channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):279–287. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84154-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M., Begenisich T. Sodium channel selectivity. Dependence on internal permeant ion concentration. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Aug;68(2):111–125. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.2.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:15–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Worley J. F., 3rd, Krueger B. K. Voltage-dependent block by saxitoxin of sodium channels incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):301–310. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84156-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Boheim G., Barhanin J., Pauron D., Lazdunski M. Reconstitution of highly purified saxitoxin-sensitive Na+-channels into planar lipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):509–515. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. Purification of the saxitoxin receptor of the sodium channel from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic channels in excitable membranes. Current problems and biophysical approaches. Biophys J. 1978 May;22(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85489-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Catterall W. A., Ehrenstein G. Comparison of ionic selectivity of batrachotoxin-activated channels with different tetrodotoxin dissociation constants. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Jun;73(6):839–854. doi: 10.1085/jgp.73.6.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Moran N., Ehrenstein G. Batrachotoxin modifies the gating kinetics of sodium channels in internally perfused neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2082–2085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Moran N., Ehrenstein G. Gating kinetics of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in neuroblastoma cells determined from single-channel measurements. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):313–322. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84157-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I., Revenko S. V. Further analysis of the mechanisms of action of batrachotoxin on the membrane of myelinated nerve. Neuroscience. 1979;4(9):1315–1330. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J. Single sodium channels from rat brain incorporated into planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):172–175. doi: 10.1038/303172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca P., Lindstrom J., Montal M. Acetylcholine receptor in planar lipid bilayers. Characterization of the channel properties of the purified nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica reconstituted in planar lipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Apr;83(4):473–496. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.4.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Racker E. Ca++-induced fusion of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with artificial planar bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1976;30(3):283–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01869673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R. Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):462–470. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Hall S., Garber S. S., Strichartz G. S., Miller C. Voltage-dependent blockade of muscle Na+ channels by guanidinium toxins. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):687–704. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Anderson N. C., Moore J. W. Tetrodotoxin does not block excitation from inside the nerve membrane. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):765–767. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray R., Morrow C. S., Catterall W. A. Binding of scorpion toxin to receptor sites associated with voltage-sensitive sodium channels in synaptic nerve ending particles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7307–7313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Reconstitution of neurotoxin-modulated ion transport by the voltage-regulated sodium channel isolated from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Single-channel properties of the reconstituted voltage-regulated Na channel isolated from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5594–5598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talvenheimo J. A., Tamkun M. M., Catterall W. A. Reconstitution of neurotoxin-stimulated sodium transport by the voltage-sensitive sodium channel purified from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11868–11871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Catterall W. A. Ion flux studies of voltage-sensitive sodium channels in synaptic nerve-ending particles. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;19(1):78–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Talvenheimo J. A., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Reconstitution of neurotoxin-activated ion flux and scorpion toxin binding from purified components. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1676–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J. C., Eccleston J. F., Barchi R. L. Cation selectivity characteristics of the reconstituted voltage-dependent sodium channel purified from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7519–7526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigele J. B., Barchi R. L. Functional reconstitution of the purified sodium channel protein from rat sarcolemma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



