Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinase enzymes have been implicated in degenerative processes like tumor cell invasion, metastasis, and arthritis. Specific metalloproteinase inhibitors have been used to block tumor cell proliferation. We have examined the interaction of batimastat (BB-94) with a metalloproteinase [atrolysin C (Ht-d), EC 3.4.24.42] active site at 2.0-angstroms resolution (R = 16.8%). The title structure exhibits an unexpected binding geometry, with the thiophene ring deeply inserted into the primary specificity site. This unprecedented binding geometry dramatizes the significance of the cavernous primary specificity site, pointing the way for the design of a new generation of potential antitumor drugs.
Full text
PDF

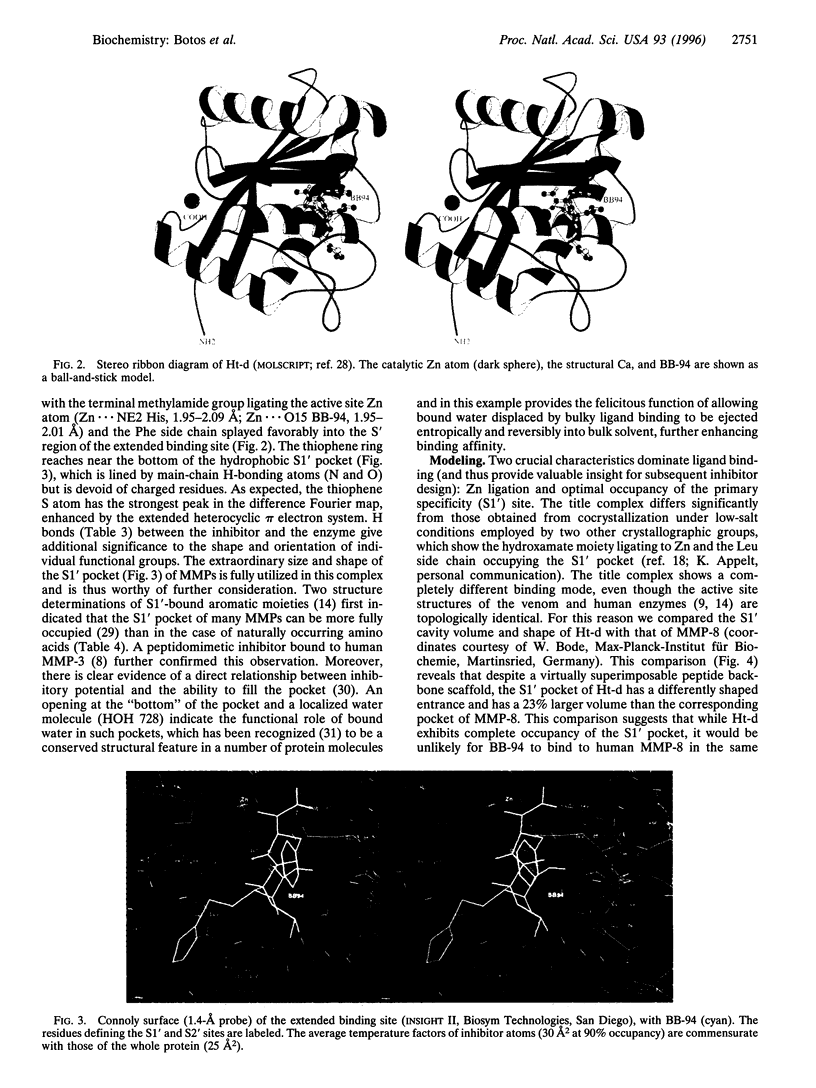
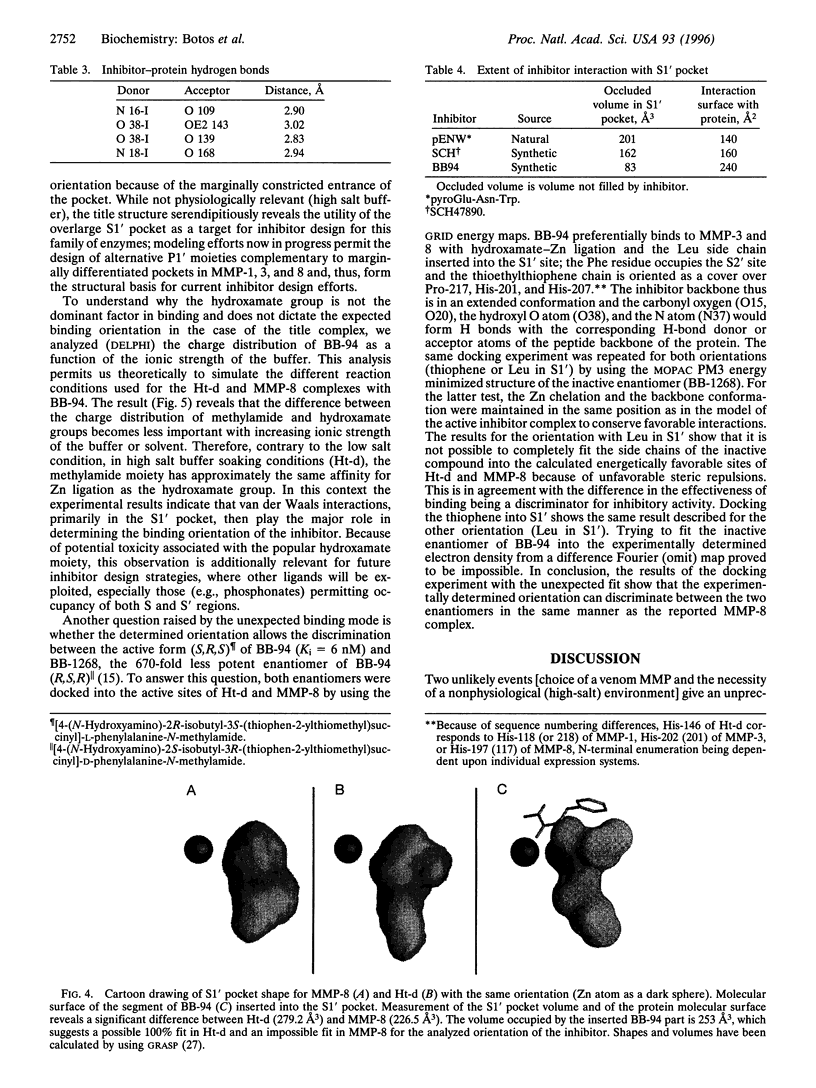


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albini A., Melchiori A., Santi L., Liotta L. A., Brown P. D., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Tumor cell invasion inhibited by TIMP-2. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1991 Jun 5;83(11):775–779. doi: 10.1093/jnci/83.11.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. W., Marcy A. I., Rokosz L. L., Axel M. G., Burbaum J. J., Fitzgerald P. M., Cameron P. M., Esser C. K., Hagmann W. K., Hermes J. D. Stromelysin-1: three-dimensional structure of the inhibited catalytic domain and of the C-truncated proenzyme. Protein Sci. 1995 Oct;4(10):1966–1976. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560041002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Gomis-Rüth F. X., Stöckler W. Astacins, serralysins, snake venom and matrix metalloproteinases exhibit identical zinc-binding environments (HEXXHXXGXXH and Met-turn) and topologies and should be grouped into a common family, the 'metzincins'. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 27;331(1-2):134–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80312-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Meyer E., Jr, Powers J. C. Human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase: X-ray crystal structures, mechanism, substrate specificity, and mechanism-based inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):1951–1963. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Reinemer P., Huber R., Kleine T., Schnierer S., Tschesche H. The X-ray crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human neutrophil collagenase inhibited by a substrate analogue reveals the essentials for catalysis and specificity. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1263–1269. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkakoti N., Winkler F. K., Williams D. H., D'Arcy A., Broadhurst M. J., Brown P. A., Johnson W. H., Murray E. J. Structure of the catalytic domain of human fibroblast collagenase complexed with an inhibitor. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Feb;1(2):106–110. doi: 10.1038/nsb0294-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botos I., Scapozza L., Shannon J. D., Fox J. W., Meyer E. F. Structure-based analysis of inhibitor binding to Ht-d. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1995 Jul 1;51(Pt 4):597–604. doi: 10.1107/S0907444995001910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. D., Bloxidge R. E., Anderson E., Howell A. Expression of activated gelatinase in human invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1993 Mar;11(2):183–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00114976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. D., Bloxidge R. E., Stuart N. S., Gatter K. C., Carmichael J. Association between expression of activated 72-kilodalton gelatinase and tumor spread in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Apr 7;85(7):574–578. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.7.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirivi R. G., Garofalo A., Crimmin M. J., Bawden L. J., Stoppacciaro A., Brown P. D., Giavazzi R. Inhibition of the metastatic spread and growth of B16-BL6 murine melanoma by a synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. Int J Cancer. 1994 Aug 1;58(3):460–464. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B., Brown P. D., East N., Crimmin M. J., Balkwill F. R. A synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor decreases tumor burden and prolongs survival of mice bearing human ovarian carcinoma xenografts. Cancer Res. 1993 May 1;53(9):2087–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. W., Campbell R., Beggerly L., Bjarnason J. B. Substrate specificities and inhibition of two hemorrhagic zinc proteases Ht-c and Ht-d from Crotalus atrox venom. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomis-Rüth F. X., Kress L. F., Kellermann J., Mayr I., Lee X., Huber R., Bode W. Refined 2.0 A X-ray crystal structure of the snake venom zinc-endopeptidase adamalysin II. Primary and tertiary structure determination, refinement, molecular structure and comparison with astacin, collagenase and thermolysin. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jun 17;239(4):513–544. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J. A computational procedure for determining energetically favorable binding sites on biologically important macromolecules. J Med Chem. 1985 Jul;28(7):849–857. doi: 10.1021/jm00145a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grams F., Crimmin M., Hinnes L., Huxley P., Pieper M., Tschesche H., Bode W. Structure determination and analysis of human neutrophil collagenase complexed with a hydroxamate inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 31;34(43):14012–14020. doi: 10.1021/bi00043a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. Internal water molecules and H-bonding in biological macromolecules: a review of structural features with functional implications. Protein Sci. 1992 Dec;1(12):1543–1562. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaper H. W., Grant D. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Fridman R., D'Orazi G., Murphy A. N., Bird R. E., Hoythya M., Fuerst T. R., French D. L. Type IV collagenase(s) and TIMPs modulate endothelial cell morphogenesis in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Aug;156(2):235–246. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041560204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sledge G. W., Jr, Qulali M., Goulet R., Bone E. A., Fife R. Effect of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat on breast cancer regrowth and metastasis in athymic mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995 Oct 18;87(20):1546–1550. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.20.1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Aznavoorian S., Liotta L. A. Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:541–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. J. MOPAC: a semiempirical molecular orbital program. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1990 Mar;4(1):1–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00128336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Botos I., Gomis-Rüth F. X., Doll R., Blood C., Njoroge F. G., Fox J. W., Bode W., Meyer E. F. Structural interaction of natural and synthetic inhibitors with the venom metalloproteinase, atrolysin C (form d). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8447–8451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]