Abstract
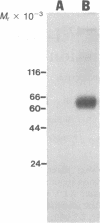
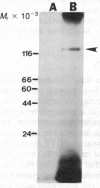
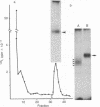
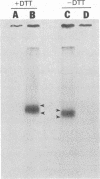
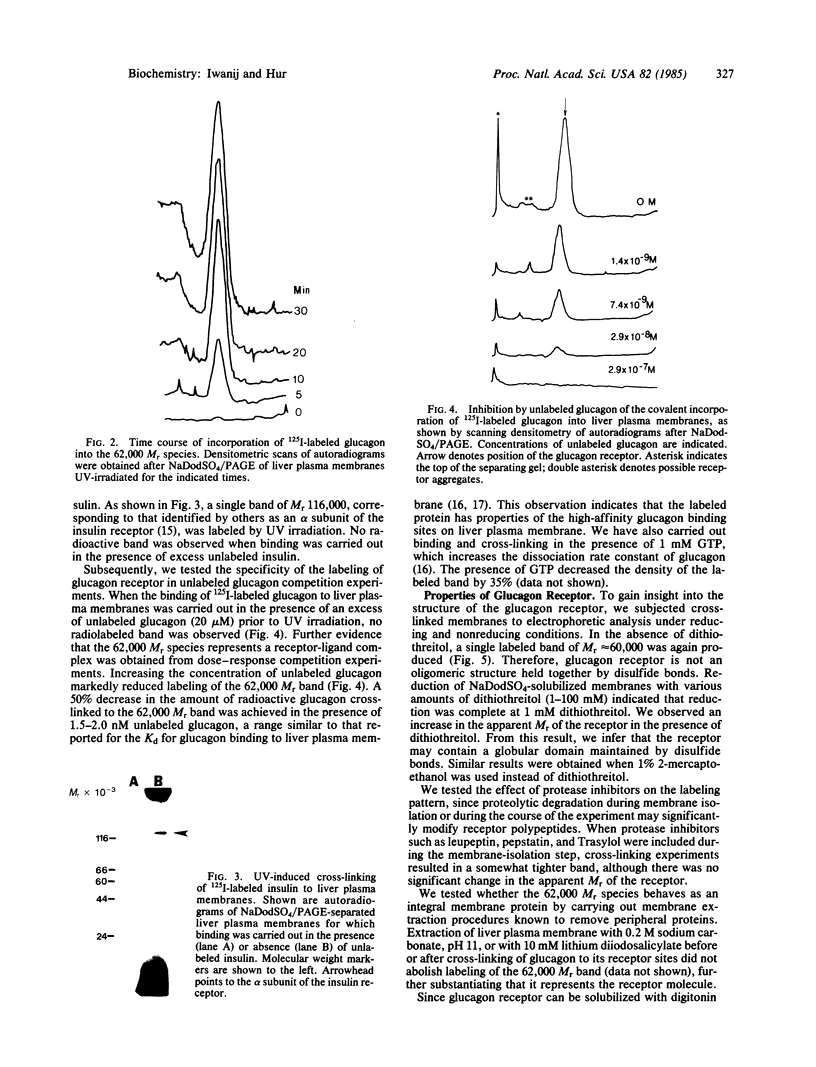
125I-labeled glucagon was directly crosslinked to its receptor in isolated liver plasma membranes and on the surface of intact hepatocytes, by using a UV irradiation procedure. This investigation resulted in the identification of a glucagon-receptor complex of apparent Mr 62,000. The specificity of labeling was shown by the interference of unlabeled hormone at physiological concentration with incorporation of radioactive glucagon into the 62,000 Mr species. The receptor behaved as a typical integral membrane protein: it was not released by extraction with lithium diiodosalicylate or at basic pH but was solubilized by digitonin treatment. Reduction of the receptor polypeptide with dithiothreitol resulted in a decrease in its electrophoretic mobility, suggesting the presence of intramolecular disulfide bonds. Soluble glucagon-receptor complexes adsorbed to Con A-Sepharose and could be eluted with methyl alpha-D-mannoside, indicating that the receptor molecule is a glycoprotein. Treatment of glucagon-labeled liver plasma membrane with endoglycosidase F resulted in the appearance of four intermediate species, indicating that glucagon receptor contains at least four N-linked oligosaccharide chains.
Full text
PDF

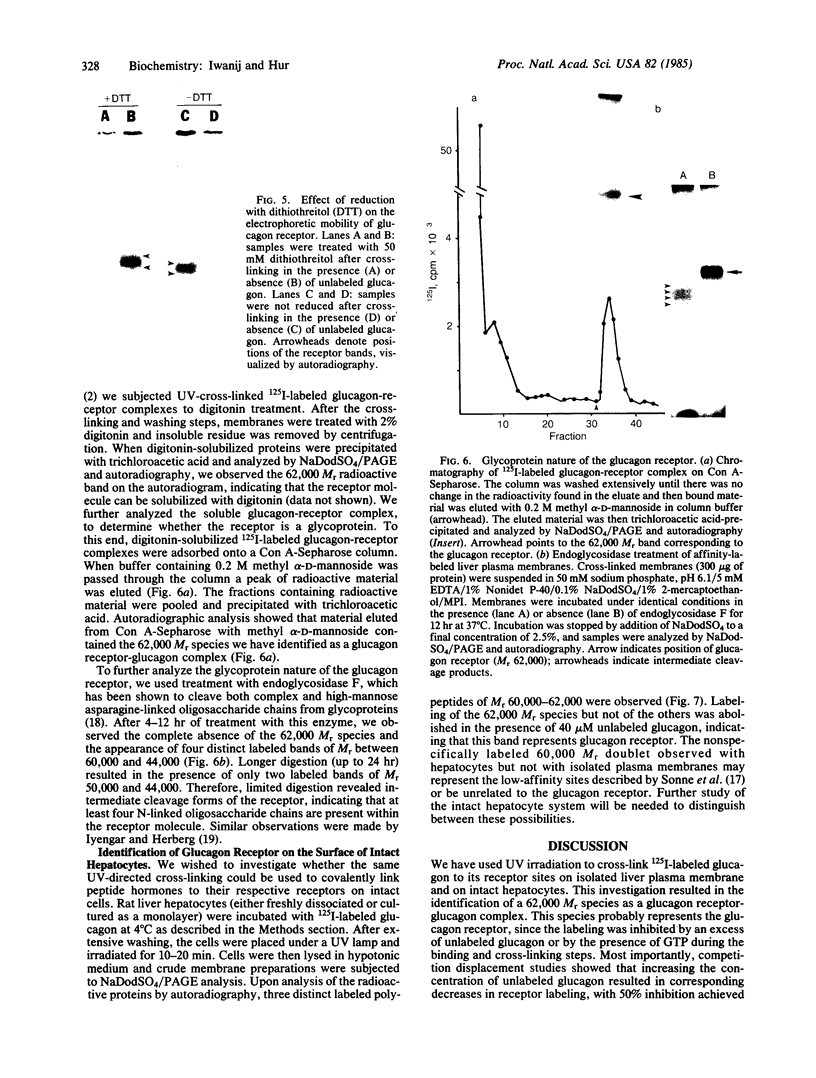

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akera T., Brody T. M. The interaction between chlorpromazine free radical and microsomal sodium- and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Nov;5(6):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Dufau M. L. Structure of the ovarian lactogen receptors. Analysis with bifunctional cross-linking reagents. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4542–4549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregman M. D., Levy D. Labeling of glucagon binding components in hepatocyte plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 23;78(2):584–590. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:217–249. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demoliou-Mason C., Epand R. M. Identification of the glucagon receptor by covalent labeling with a radiolabeled photoreactive glucagon analogue. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 27;21(9):1996–2004. doi: 10.1021/bi00538a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
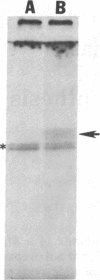
- Hubbard A. L., Ma A. Isolation of rat hepatocyte plasma membranes. II. Identification of membrane-associated cytoskeletal proteins. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):230–239. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Herberg J. T. Structural analysis of the hepatic glucagon receptor. Identification of a guanine nucleotide-sensitive hormone-binding region. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5222–5229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., MacAndrew V. I., Jr, Pilch P. F. Identification of the glucagon receptor in rat liver membranes by photoaffinity crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):875–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Wright D. E., Hruby V. J., Rodbell M. Structure-function relationships in glucagon: properties of highly purified des-His-1-, monoiodo-, and (des-Asn-28, Thr-29)(homoserine lactone-27)-glucagon. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1559–1563. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Changeux J. P. Crosslinking of alpha-bungarotoxin to the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo marmorata by ultraviolet light irradiation. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80857-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglin S., Jamieson J. D. Covalent crosslinking of angiotensin II to its binding sites in rat adrenal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3739–3743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessin J. E., Tillotson L. G., Yamada K., Gitomer W., Carter-Su C., Mora R., Isselbacher K. J., Czech M. P. Identification of the stereospecific hexose transporter from starved and fed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2286–2290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter S., Froehner S. C. Characterization and localization of the Mr = 43,000 proteins associated with acetylcholine receptor-rich membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10034–10040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig S. A., Madison L. D., Jamieson J. D. Analysis of cholecystokinin-binding proteins using endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1110–1116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of rat liver cells. 3. Enzymatic requirements for tissue dispersion. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Dec;82(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonne O., Berg T., Christoffersen T. Binding of 125I-labeled glucagon and glucagon-stimulated accumulation of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in isolated intact rat hepatocytes. Evidence for receptor heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3203–3210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M., Lambert M., Furnelle J., Christophe J. Specific photoaffinity crosslinking of [125I]cholecystokinin to pancreatic plasma membranes. Evidence for a disulfide-linked Mr 76 000 peptide in cholecystokinin receptors. Regul Pept. 1982 Aug;4(3):163–172. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(82)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Dobbs R. E., Orci L. Insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin secretion in the regulation of metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:307–343. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welton A. F., Lad P. M., Newby A. C., Yamamura H., Nicosia S., Rodbell M. Solubilization and separation of the glucagon receptor and adenylate cyclase in guanine nucleotide-sensitive states. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5947–5950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]