Abstract
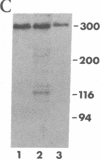
We describe an antigen of Plasmodium falciparum that is a dominant immunogen in man. The corresponding cDNA clone, Ag231, expressing this antigen in Escherichia coli reacted in an in situ colony assay with sera from up to approximately equal to 93% of 65 people living in an area in which P. falciparum is endemic. Human antibodies affinity purified on immobilized Ag231 lysates identified the corresponding parasite antigen as a polypeptide of Mr approximately equal to 300,000. It was present in schizonts and also in ring-stage trophozoites, where a speckled immunofluorescence pattern suggested an association with the erythrocyte. Its mRNA was enriched in merozoites relative to other blood stages, a distinctive property shared by a recently described antigen located on the surface of ring-infected erythrocytes, and it is encoded by a single gene having a number of allelic variants. The complete nucleotide sequence of Ag231 revealed a structural unit composed of 13 hexapeptide repeats flanked by a highly charged region containing both acidic and basic amino acids. This structural unit is itself repeated, so that blocks of repeats and charged units are interspersed along the molecule. The sequences within the repeats vary much more extensively than those in the charged units.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Gough N. M., Webb E. A., Tyler B. M., Jackson J., Cory S. Molecular cloning of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain messenger ribonucleic acids coding for mu, alpha, gamma 1, gamma 2a, and gamma 3 chains. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2711–2719. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders R. F., Brown G. V., Edwards A. Characterization of an S antigen synthesized by several isolates of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6652–6656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Bianco A. E., Saint R. B., Lingelbach K. R., Kemp D. J., Brown G. V. Immune sera recognize on erythrocytes Plasmodium falciparum antigen composed of repeated amino acid sequences. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):789–792. doi: 10.1038/310789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Lingelbach K. R., Brown G. V., Saint R. B., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Isolate-specific S-antigen of Plasmodium falciparum contains a repeated sequence of eleven amino acids. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):751–756. doi: 10.1038/306751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Brown G. V., Anders R. F. Expression of Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage antigens in Escherichia coli: detection with antibodies from immune humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3787–3791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Hansen J. L., Dame J. B., Mullins J. A. Mung bean nuclease cleaves Plasmodium genomic DNA at sites before and after genes. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.6330899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki L. S., Svec P., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V., Godson G. N. Structure of the plasmodium knowlesi gene coding for the circumsporozoite protein. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann H., Berzins K., Wahlgren M., Carlsson J., Björkman A., Patarroyo M. E., Perlmann P. Antibodies in malarial sera to parasite antigens in the membrane of erythrocytes infected with early asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1686–1704. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H. D., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Saint R., Lingelbach K., Cowman A. F., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Differential antibody screening of cloned Plasmodium falciparum sequences expressed in Escherichia coli: procedure for isolation of defined antigens and analysis of human antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2456–2460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Bartholomew R. K. The release of antigens by Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitology. 1975 Oct;71(2):183–192. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000046631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala F., Cochrane A. H., Nardin E. H., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Circumsporozoite proteins of malaria parasites contain a single immunodominant region with two or more identical epitopes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1947–1957. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]