Abstract
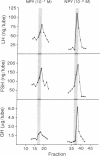
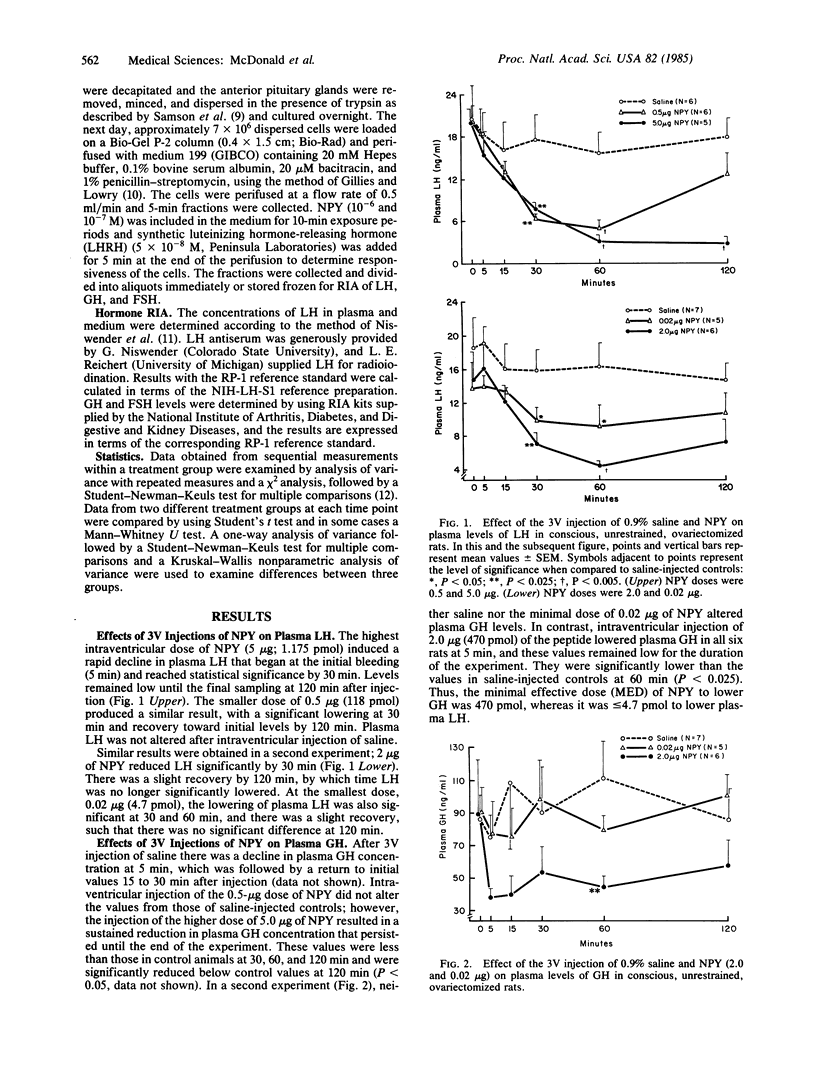
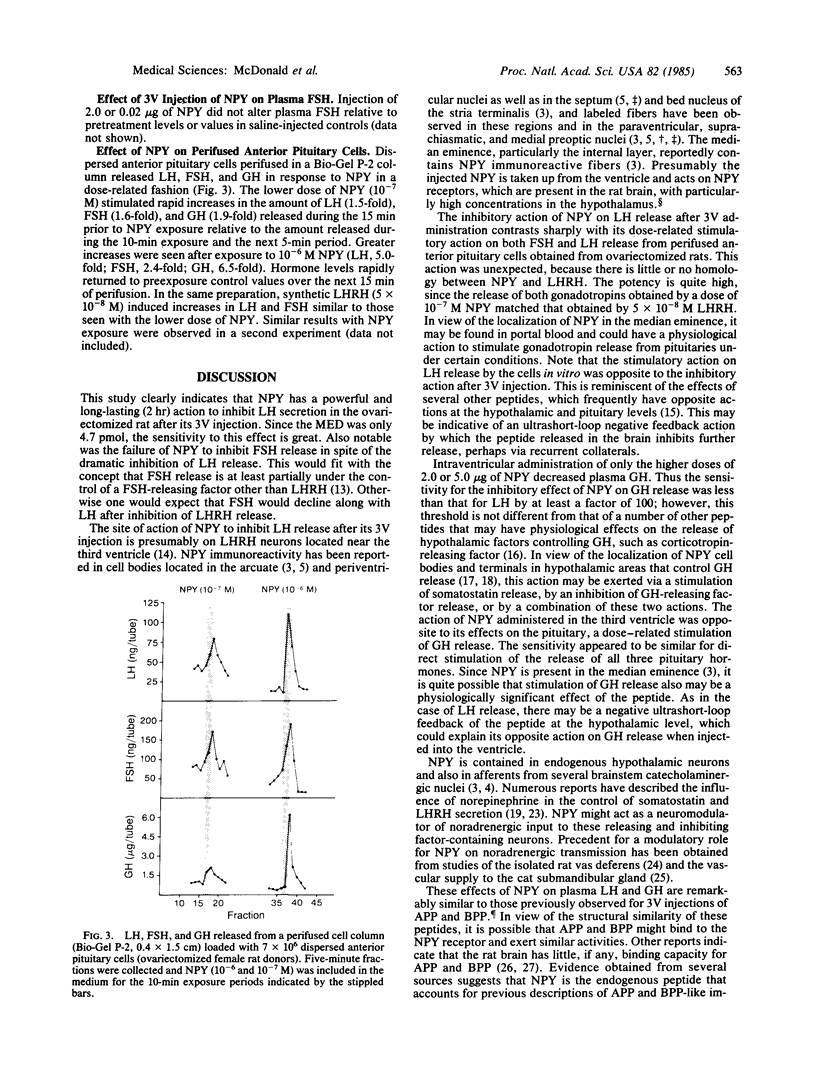
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) has recently been localized in the rat hypothalamus. We have evaluated the effects of NPY on hypothalamic and pituitary function by injecting NPY into the third ventricle in vivo and by examining its action on perifused pituitary cells in vitro. Injections of NPY into the third ventricle of conscious ovariectomized rats led to a dramatic and highly significant reduction in plasma luteinizing hormone (LH) relative to pretreatment levels in these animals or to those of controls injected with physiological saline. Significant inhibition was obtained with doses ranging from 0.02 to 5.0 micrograms (4.7-1175 pmol) of NPY. These inhibitory effects on LH release were dose dependent and lasted for at least 120 min after injection of 5.0 micrograms of NPY. Intraventricular injection of NPY also significantly decreased plasma growth hormone; however, the threshold dose was 2.0 micrograms (470 pmol), a dose 100-fold greater than the lowest dose that inhibited LH release. Plasma follicle-stimulating hormone was unaffected by injection of NPY. NPY (10(-6) and 10(-7) M) stimulated secretion of LH, growth hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone from perifused anterior pituitary cells loaded in a Bio-Gel P-2 column. These results indicate that NPY acts on structures adjacent to the third ventricle to inhibit the secretion of LH and growth hormone but not follicle-stimulating hormone, whereas it can directly stimulate the secretion of all three hormones from the cells of the anterior pituitary in vitro. Since NPY has been found in the hypothalamus and median eminence, it is quite likely that it plays a physiologically significant role at both hypothalamic and pituitary sites: influencing secretion of pituitary hormones.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M. L., Dyckes D. F., Hazelwood R. L. In vitro binding and degradation of avian pancreatic polypeptide by chicken and rat tissues. Endocrinology. 1983 Aug;113(2):508–516. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-2-508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamo M. L., Hazelwood R. L. Cerebellar binding of avian pancreatic polypeptide. Endocrinology. 1984 Mar;114(3):794–800. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-3-794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Rossor M. N., Roberts G. W., Crow T. J., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in human brain. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):584–586. doi: 10.1038/306584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antunes-Rodrigues J., McCann S. M. Water, sodium chloride, and food intake induced by injections of cholinergic and adrenergic drugs into the third ventricle of the rat brain. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1464–1470. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett-Clarke C., Romagnano M. A., Joseph S. A. Distribution of somatostatin in the rat brain: telencephalon and diencephalon. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 28;188(2):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch B., Brazeau P., Ling N., Bohlen P., Esch F., Wehrenberg W. B., Benoit R., Bloom F., Guillemin R. Immunohistochemical detection of growth hormone-releasing factor in brain. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):607–608. doi: 10.1038/301607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Brecha N., Moore R. Y. Immunohistochemical localization of avian pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the rat hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Jun 20;217(2):123–136. doi: 10.1002/cne.902170202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt B. J., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Goldstein M. Differential co-existence of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines in the central nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1984 Feb;11(2):443–462. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. V., Drouva S. V. Effect of intraventricular infusion of catecholamines on luteinizing hormone release in ovariectomized and ovariectomized, steroid-primed rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1979;29(3):149–162. doi: 10.1159/000122917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies G., Lowry P. J. Perfused rat isolated anterior pituitary cell column as bioassay for factor(s) controlling release of adrenocorticotropin: validation of a technique. Endocrinology. 1978 Aug;103(2):521–527. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-2-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms P. G., Ojeda S. R. A rapid and simple procedure for chronic cannulation of the rat jugular vein. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Mar;36(3):391–392. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Terenius L., Polak J., Bloom S., Sasek C., Elde R., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)- and FMRFamide neuropeptide-like immunoreactivities in catecholamine neurons of the rat medulla oblongata. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Feb;117(2):315–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. C., Parsons J. A., Erlandsen S. L., Williams T. H. Luteinizing hormone--releasing hormone (LH-RH) pathway of the rat hypothalamus revealed by the unlabeled antibody peroxidase-antiperoxidase method. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;153(2):211–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00226609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorén I., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Immunoreactive pancreatic polypeptide (PP) occurs in the central and peripheral nervous system: preliminary immunocytochemical observations. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Aug;200(2):179–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00236410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann S. M., Mizunuma H., Samson W. K., Lumpkin M. D. Differential hypothalamic control of FSH secretion: a review. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1983;8(3):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(83)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann S. M. Physiology and pharmacology of LHRH and somatostatin. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:491–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Parnavelas J. G., Karamanlidis A. N., Brecha N. The morphology and distribution of peptide-containing neurons in the adult and developing visual cortex of the rat. IV. Avian pancreatic polypeptide. J Neurocytol. 1982 Dec;11(6):985–995. doi: 10.1007/BF01148312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Gustafson E. L., Card J. P. Identical immunoreactivity of afferents to the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus with antisera against avian pancreatic polypeptide, molluscan cardioexcitatory peptide and neuropeptide Y. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;236(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00216511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro-Vilar A., Ojeda S. R., Advis J. P., McCann S. M. Evidence for noradrenergic involvement in episodic prolactin and growth hormone release in ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):86–91. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro-Vilar A., Ojeda S. R., Arimura A., McCann S. M. Dopamine and norepinephrine stimulate somatostatin release by median eminence fragments in vitro. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 9;23(14):1493–1497. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro-Vilar A., Ojeda S. R., McCann S. M. Catecholaminergic modulation of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release by median eminence terminals in vitro. Endocrinology. 1979 Jun;104(6):1749–1757. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-6-1749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niswender G. D., Midgley A. R., Jr, Monroe S. E., Reichert L. E., Jr Radioimmunoassay for rat luteinizing hormone with antiovine LH serum and ovine LH-131-I. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jul;128(3):807–811. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohhashi T., Jacobowitz D. M. The effects of pancreatic polypeptides and neuropeptide Y on the rat vas deferens. Peptides. 1983 May-Jun;4(3):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschowka J. A., O'Donohue T. L., Jacobowitz D. M. The distribution of bovine pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactive neurons in rat brain. Peptides. 1981 Fall;2(3):309–331. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(81)80125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono N., Lumpkin M. D., Samson W. K., McDonald J. K., McCann S. M. Intrahypothalamic action of corticotrophin-releasing factor (CRF) to inhibit growth hormone and LH release in the rat. Life Sci. 1984 Sep 3;35(10):1117–1123. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson W. K., Said S. I., Snyder G., McCann S. M. In vitro stimulation of prolactin release by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Peptides. 1980 Winter;1(4):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(80)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]