Abstract
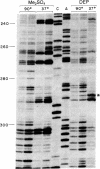
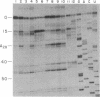
The structure of the intervening sequence (IVS) of the Tetrahymena rRNA precursor mediates cleavage-ligation reactions that result in pre-rRNA splicing and IVS cyclization. We have developed a method for RNA structure analysis and applied it to the circular form of the IVS RNA. The native RNA was treated with dimethyl sulfate or diethyl pyrocarbonate to modify bases not involved in secondary or tertiary interactions. The RNA was then used as a template for reverse transcription. Elongation of synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide primers was found to stop (or pause) one nucleotide prior to 1-methyladenosine, 3-methylcytidine, and 7-ethoxycarbonyladenosine residues. The detection of 1-methyladenosine is particularly useful for locating single-stranded regions. After chemical cleavage of the RNA, 7-methylguanosine also could be detected. In general, the sites of modification were consistent with a previous model of the secondary structure of the linear form of the IVS RNA, a model based on enzymatic cleavage data, free energy calculations, and phylogenetic comparison. Thus, IVS RNA autocyclization does not involve major rearrangements of the secondary structure, although there is evidence for a conformational change in one region of the molecule. The methods described here should be of general use for obtaining information about structure far from the ends of RNA molecules.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke J. M., RajBhandary U. L. Intron within the large rRNA gene of N. crassa mitochondria: a long open reading frame and a consensus sequence possibly important in splicing. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. RNA splicing: three themes with variations. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Tanner N. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Weir B. R., Zuker M., Perlman P. S. Secondary structure of the Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA intervening sequence: structural homology with fungal mitochondrial intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWLEY P. D., BROOKES P. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE ALKYLATION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS AND THEIR CONSTITUENT NUCLEOTIDES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:127–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0890127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu H. L., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Improved methods for structure probing in large RNAs: a rapid 'heterologous' sequencing approach is coupled to the direct mapping of nuclease accessible sites. Application to the 5' terminal domain of eukaryotic 28S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5903–5920. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow H., Guthrie C. Structure of intron-containing tRNA precursors. Analysis of solution conformation using chemical and enzymatic probes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5197–5207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Hearst J. E. Structure of E. coli 16S RNA elucidated by psoralen crosslinking. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1355–1365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Scazzocchio C., Brown T. A., Davies R. W. Close relationship between certain nuclear and mitochondrial introns. Implications for the mechanism of RNA splicing. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):595–605. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Brummer B., Holl J., Schweyen R. J., Rödel G., Kaudewitz F. Processing of yeast mitochondrial RNA: involvement of intramolecular hybrids in splicing of cob intron 4 RNA by mutation and reversion. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Woo N. H., Rich A. Initiator tRNAs have a unique anticodon loop conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3289–3293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurst R. M., Vournakis J. N., Maxam A. M. Structure mapping of 5'-32P-labeled RNA with S1 nuclease. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4493–4499. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youvan D. C., Hearst J. E. A sequence from Drosophila melanogaster 18S rRNA bearing the conserved hypermodified nucleoside am psi: analysis by reverse transcription and high-performance liquid chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1723–1741. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youvan D. C., Hearst J. E. Reverse transcriptase pauses at N2-methylguanine during in vitro transcription of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3751–3754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Grabowski P. J., Cech T. R. Autocatalytic cyclization of an excised intervening sequence RNA is a cleavage-ligation reaction. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):578–583. doi: 10.1038/301578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. A labile phosphodiester bond at the ligation junction in a circular intervening sequence RNA. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):574–578. doi: 10.1126/science.6200938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]