Abstract
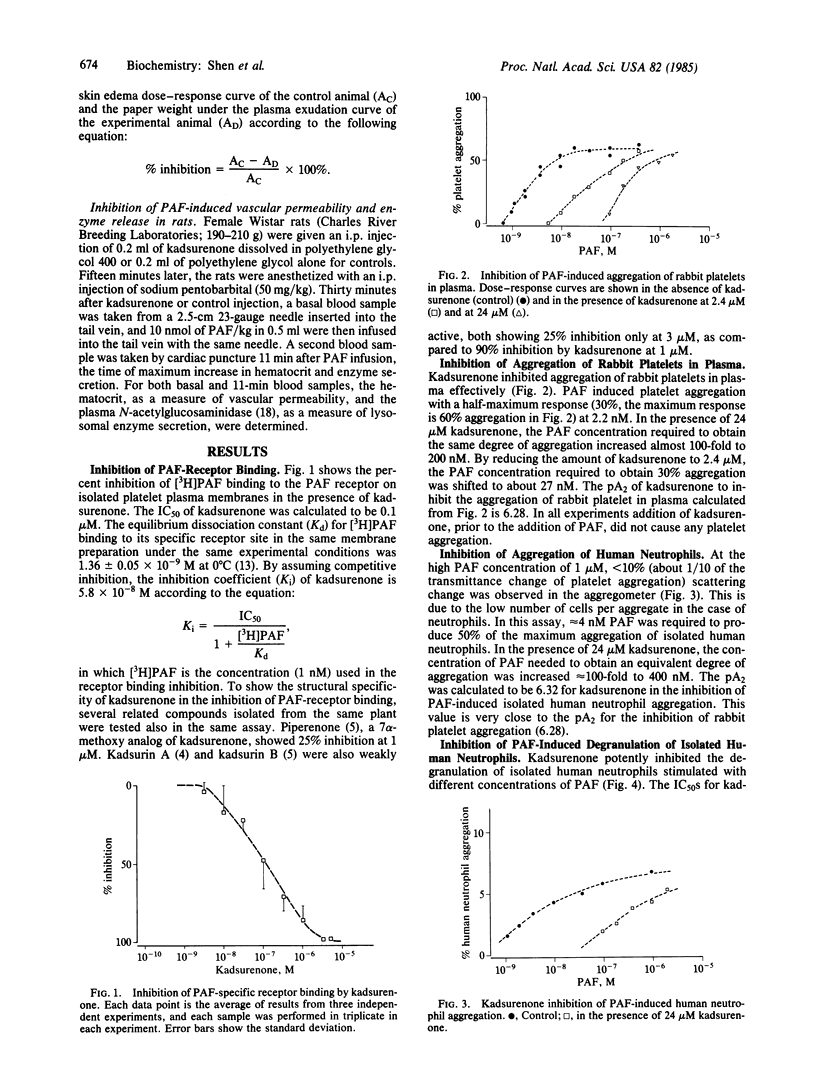
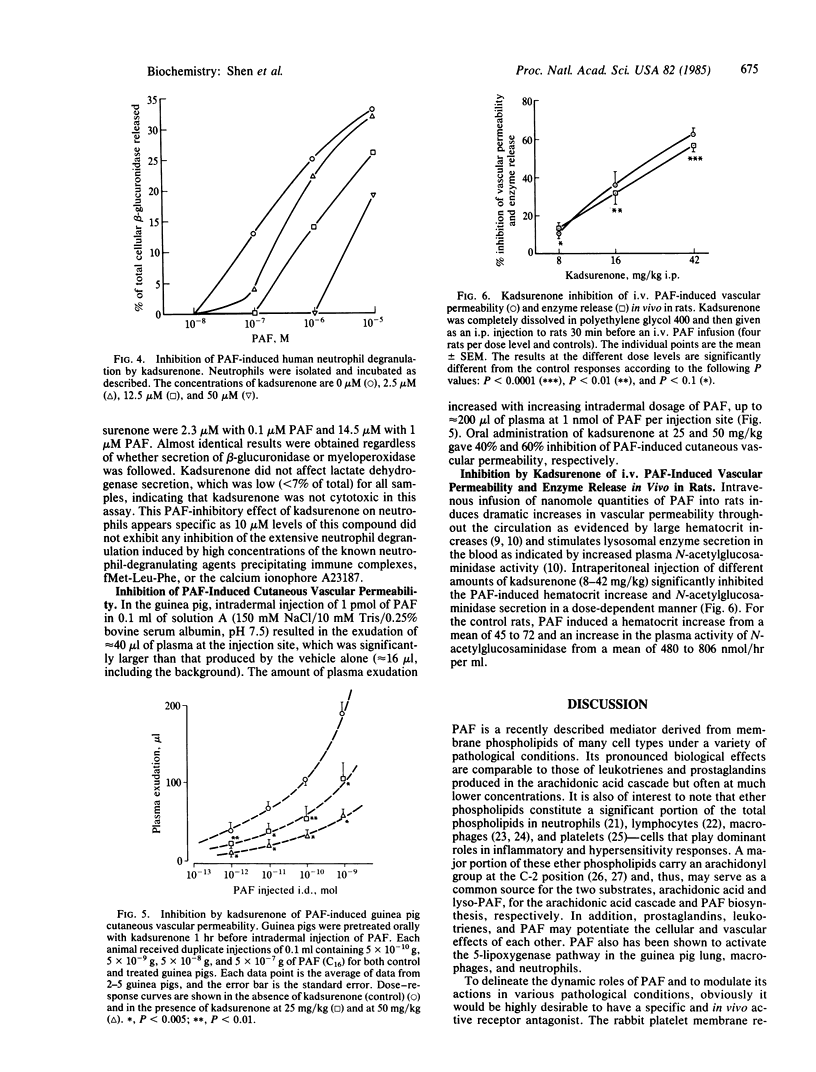
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is a potent lipid mediator of inflammation and asthma. Using a receptor preparation of rabbit platelet membranes, we identified a novel antagonist of PAF in the methylene chloride extract of a Chinese herbal plant, haifenteng (Piper futokadsura). The active antagonist, kadsurenone, was isolated and characterized in several in vitro and in vivo assays. It is a specific and competitive inhibitor of PAF binding to its receptor with a Ki of 5.8 X 10(-8) M vs. a Ki of 6.3 X 10(-9) M for PAF itself. It inhibits PAF-induced aggregation of rabbit platelets and human neutrophils at 2.4-24 microM, without showing any PAF agonistic activity. It potently inhibits PAF-induced degranulation of human neutrophils at 2.5-50 microM, also without any agonist activity. Kadsurenone is active orally at 25-50 mg/kg of body weight in blocking PAF-induced cutaneous permeability in the guinea pig. It also inhibits PAF-induced increases of hematocrit and circulating N-acetylglucosaminidase in the rat at greater than 10 mg/kg i.p. in a dose-dependent manner. Kadsurenone does not interfere with the function of several pharmacological mediators and receptors tested. Its structural specificity is evidenced by the poor PAF-antagonistic activities of three related structures isolated from the same haifenteng extract.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer C. B., Page C. P., Paul W., Morley J., MacDonald D. M. Inflammatory characteristics of platelet activating factor (PAF-acether) in human skin. Br J Dermatol. 1984 Jan;110(1):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1984.tb07310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Boullet C., Brink C., Labat C. The actions of Paf-acether (platelet-activating factor) on guinea-pig isolated heart preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;80(1):81–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Le Couedic J. P., Polonsky J., Tence M. Structural analysis of purified platelet-activating factor by lipases. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):170–171. doi: 10.1038/269170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Tencé M., Varenne P., Bidault J., Boullet C., Polonsky J. Semi-synthèse et structure proposée du facteur activant les plaquettes (P.A.F.): PAF-acether, un alkyl ether analogue de la lysophosphatidylcholine. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1979 Nov 26;289(14):1037–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., O'Flaherty J. T., Ellis J. M., Swendsen C. L., Wykle R. L. Selective acylation of lyso platelet activating factor by arachidonate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7268–7271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demopoulos C. A., Pinckard R. N., Hanahan D. J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators). J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9355–9358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada M., Takeuchi M., Fukao T., Katagiri K. A simple method for the quantitative extraction of dye extravasated into the skin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;23(3):218–219. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P. Acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (platelet-activating factor) mediates heightened metabolic activity in macrophages. Studies on PGE, TXB2 and O2- production, spreading, and the influence of calmodulin-inhibitor W-7. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80968-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey D. M., McManus L. M., Satouchi K., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Vasoactive properties of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine and analogues. Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;46(4):422–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lee C. S., Cheah M. J., Shen T. Y. Specific receptor sites for 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor) on rabbit platelet and guinea pig smooth muscle membranes. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4756–4763. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi R., Burke J. A., Guo Z. G., Hattori Y., Hoppens C. M., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (AGEPC). A putative mediator of cardiac anaphylaxis in the guinea pig. Circ Res. 1984 Feb;54(2):117–124. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencia-Huerta J. M., Lewis R. A., Razin E., Austen K. F. Antigen-initiated release of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) from mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells sensitized with monoclonal IgE. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2958–2964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller H. W., O'Flaherty J. T., Greene D. G., Samuel M. P., Wykle R. L. 1-O-alkyl-linked glycerophospholipids of human neutrophils: distribution of arachidonate and other acyl residues in the ether-linked and diacyl species. J Lipid Res. 1984 Apr;25(4):383–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller H. W., O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L. Ether lipid content and fatty acid distribution in rabbit polymorphonuclear neutrophil phospholipids. Lipids. 1982 Feb;17(2):72–77. doi: 10.1007/BF02535178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P., Rodman J. S., Schlesinger P. Clearance of lysosomal hydrolases following intravenous infusion. Kinetic and competition experiments with beta-glucuronidase and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Dec;177(2):594–605. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura T., Masuzawa Y., Waku K. Alkenyl and alkyl ether phospholipids in pig mesenteric lymph node lymphocytes. Lipids. 1980 Jun;15(6):475–478. doi: 10.1007/BF02534076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura T., Onuma Y., Sekiguchi N., Waku K. Ether phospholipids in guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages. Occurrence of high levels of 1-O-alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 14;712(3):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura T., Soga N., Nitta H., Waku K. Occurrence of alkyl ether phospholipids in rabbit platelets: compositions and fatty chain profiles. J Biochem. 1983 Nov;94(5):1719–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Crespo M., Alonso F., Iñarrea P., Alvarez V., Egido J. Vascular actions of synthetic PAF-acether (a synthetic platelet-activating factor) in the rat: evidence for a platelet independent mechanism. Immunopharmacology. 1982 Apr;4(2):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(82)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


