Abstract
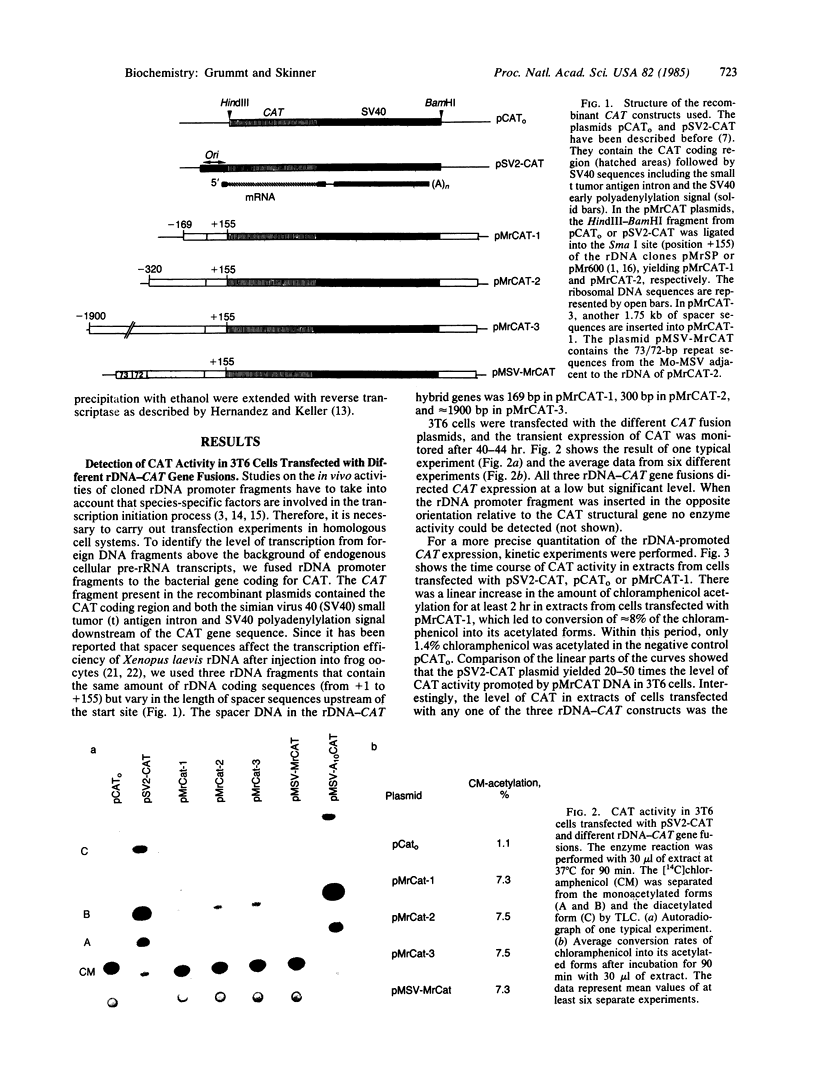
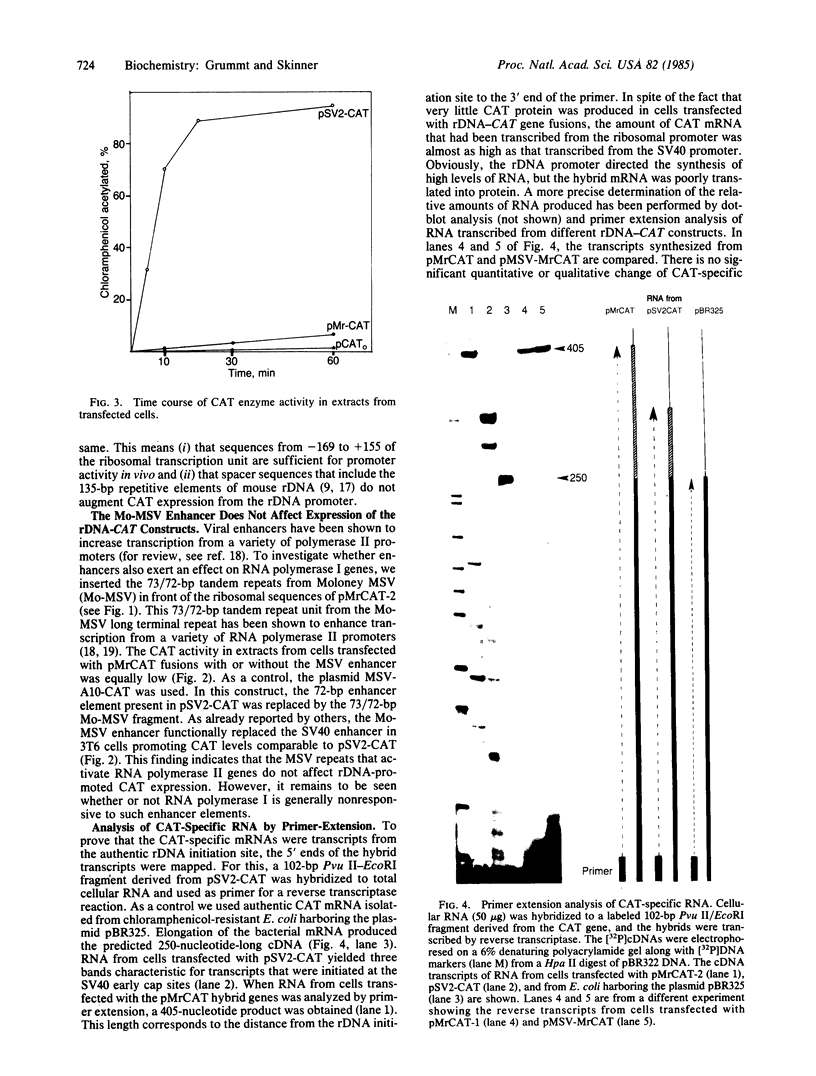
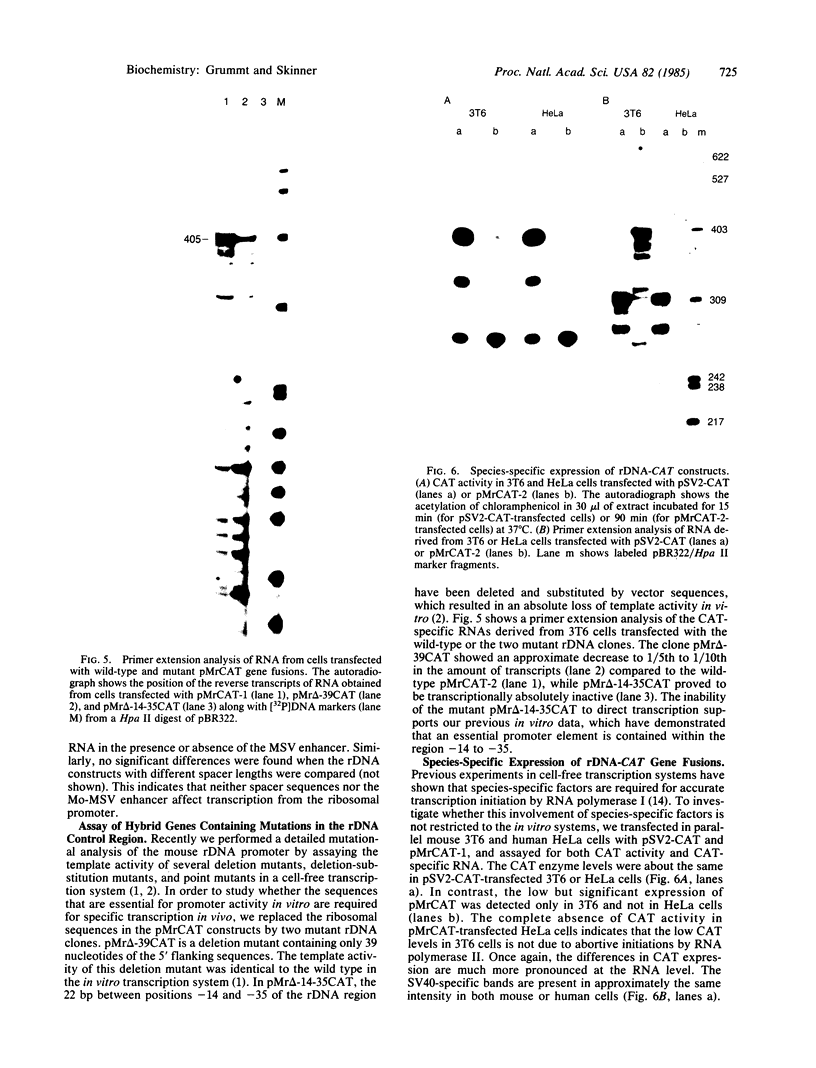
The activity of the mouse ribosomal promoter was examined after fusion to the gene coding for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) and transfection into mouse cells. Very little CAT enzyme but high levels of CAT-specific RNA correctly initiated at the ribosomal DNA start site were synthesized. The amount of specific transcripts was neither influenced by long stretches of upstream spacer sequences nor by the insertion of the Moloney murine sarcoma virus enhancer. The deletion mutant pMr delta-39, which has been shown to be fully active in vitro, exhibited a 90% decrease in template activity in vivo. A mutant in which 22 base pairs of ribosomal DNA (between positions -35 and -14) were substituted by foreign DNA sequences proved transcriptionally inactive. The fusion genes were only transcribed in mouse cells, indicating that species-specific transcription factors are involved in ribosomal promoter recognition.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair D. G., McClements W. L., Oskarsson M. K., Fischinger P. J., Vande Woude G. F. Biological activity of cloned Moloney sarcoma virus DNA: Terminally redundant sequences may enhance transformation efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S. J., Reeder R. H. Spacer sequences regulate transcription of ribosomal gene plasmids injected into Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y. "Pretranscriptional capping" in the biosynthesis of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1086–1090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Gross H. J. Structural organization of mouse rDNA: comparison of transcribed and non-transcribed regions. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Jan;177(2):223–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00267433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Manley J. L. Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II is inhibited by S-adenosylhomocysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Rae P. M. A component of Drosophila RNA polymerase I promoter lies within the rRNA transcription unit. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):179–181. doi: 10.1038/304179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M., Arnheim N. Nucleotide sequence of the genetically labile repeated elements 5' to the origin of mouse rRNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):211–224. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Smale S. T., Haltiner M. M., Tjian R. Regulation of human ribosomal RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3558–3562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Khoury G., Vande Woude G., Gruss P. Activation of SV40 genome by 72-base pair tandem repeats of Moloney sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):568–572. doi: 10.1038/295568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):223–228. doi: 10.1038/302223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner J. A., Ohrlein A., Grummt I. In vitro mutagenesis and transcriptional analysis of a mouse ribosomal promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Wilkinson J. A., Roan J., Reeder R. H. Nested control regions promote Xenopus ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt C., Grummt I. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes is a prerequisite for ribosomal DNA transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3795–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







