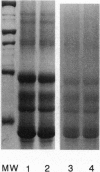
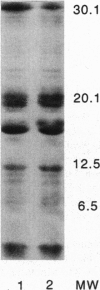
Abstract
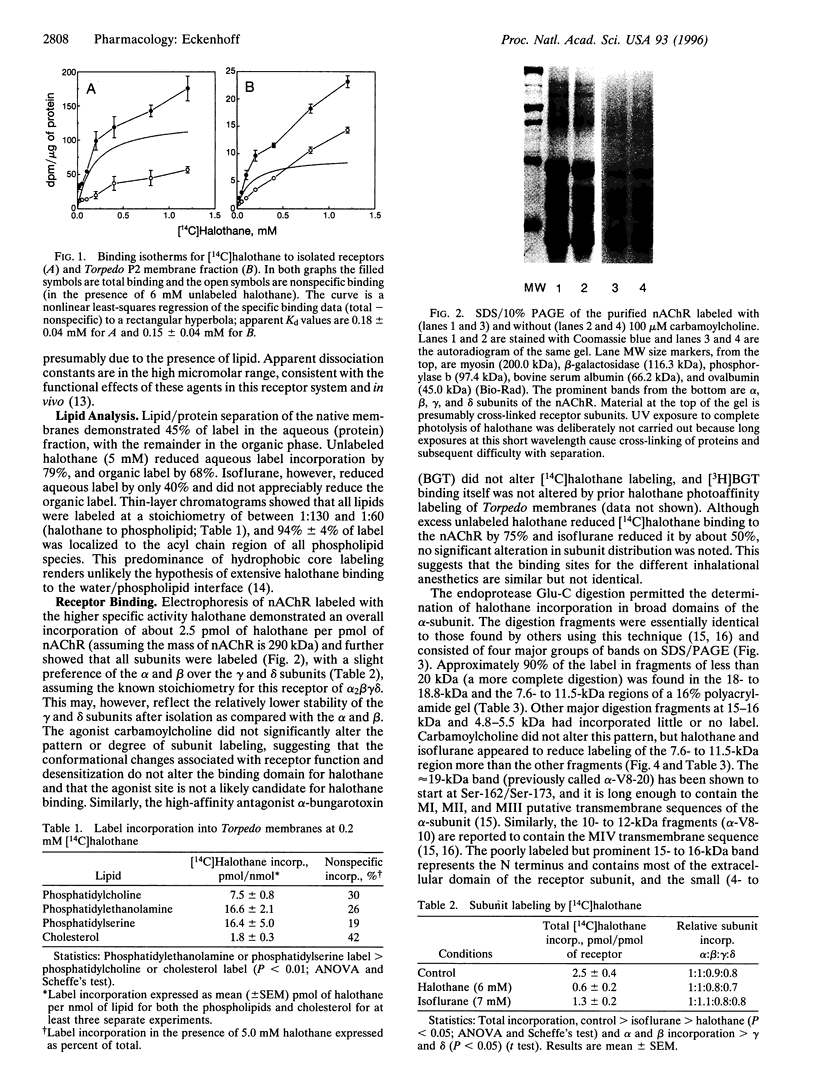
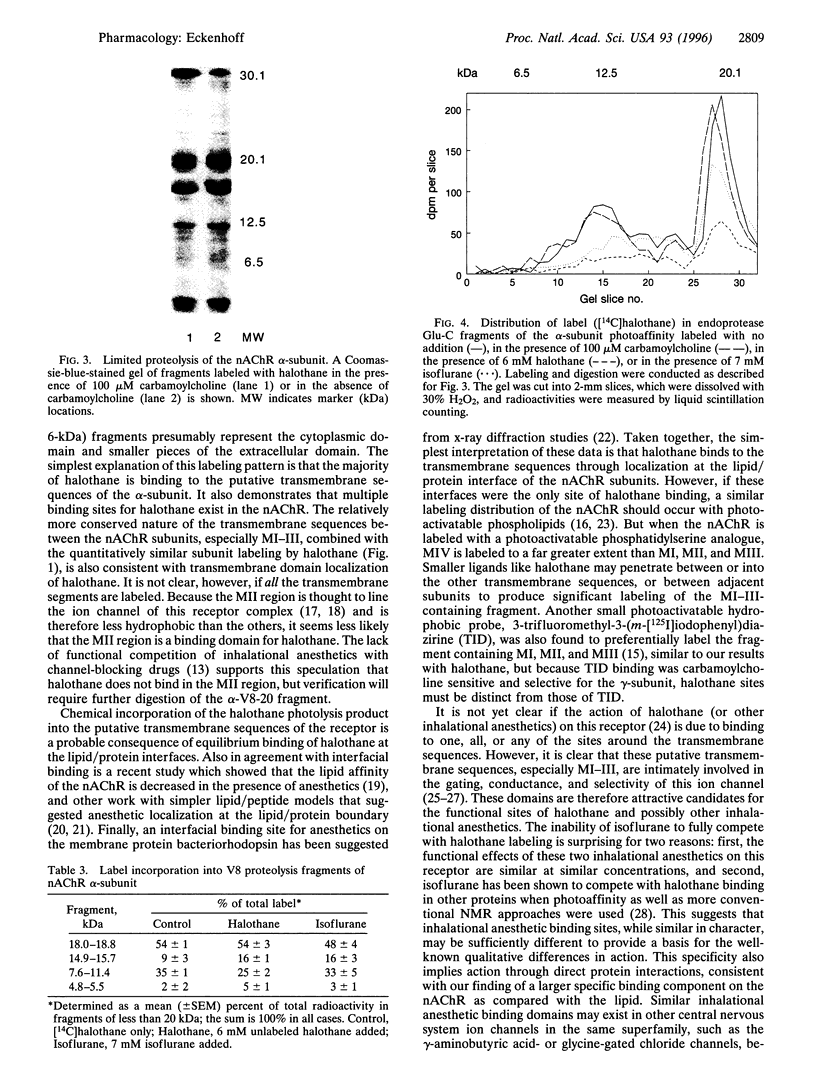
To determine inhalational anesthetic binding domains on a ligand-gated ion channel, I used halothane direct photoaffinity labeling of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) in native Torpedo membranes. [14C]Halothane photoaffinity labeling of both the native Torpedo membranes and the isolated nAChR was saturable, with Kd values within the clinically relevant range. All phospholipids were labeled, with greater than 95% of the label in the acyl chain region. Electrophoresis of labeled nAChR demonstrated no significant subunit selectivity for halothane incorporation. Within the alpha-subunit, greater than 90% of label was found in the endoprotease Glu-C digestion fragments which contain the four transmembrane regions, and the pattern was different from that reported for photoactivatable phospholipid binding to the nAChR. Unlabeled halothane reduced labeling more than did isoflurane, suggesting differences in the binding domains for inhalational anesthetics in the nAChR. These data suggest multiple similar binding domains for halothane in the transmembrane region of the nAChR.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton M. P., Wang H. H. Photoaffinity labeling of the Torpedo californica nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with an aryl azide derivative of phosphatidylserine. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 6;29(5):1186–1194. doi: 10.1021/bi00457a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chak A., Karlin A. Purification and reconstitution of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:546–555. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07038-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Vidal A. M. Cooperative interactions between general anesthetics and QX-222 within the pore of the acetylcholine receptor ion channel. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;46(1):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilger J. P., Vidal A. M., Mody H. I., Liu Y. Evidence for direct actions of general anesthetics on an ion channel protein. A new look at a unified mechanism of action. Anesthesiology. 1994 Aug;81(2):431–442. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199408000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois B. W., Cherian S. F., Evers A. S. Volatile anesthetics compete for common binding sites on bovine serum albumin: a 19F-NMR study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6478–6482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenhoff R. G., Shuman H. Halothane binding to soluble proteins determined by photoaffinity labeling. Anesthesiology. 1993 Jul;79(1):96–106. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199307000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Purification and molecular properties of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):362–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):607–614. doi: 10.1038/367607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Stereospecific effects of inhalational general anesthetic optical isomers on nerve ion channels. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):427–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1925602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. M., Louro S. R., Horváath L. I., Miller K. W., Watts A. A study of the effect of general anesthetics on lipid-protein interactions in acetylcholine receptor enriched membranes from Torpedo nobiliana using nitroxide spin-labels. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2664–2669. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudat J., Montecucco C., Bisson R., Changeux J. P. Transmembrane topology of acetylcholine receptor subunits probed with photoreactive phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3121–3127. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Hilgenfeld R. The selectivity filter of a ligand-gated ion channel. The helix-M2 model of the ion channel of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81775-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. V., Brooks P. A., Harrison N. L. Enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid-activated Cl- currents in cultured rat hippocampal neurones by three volatile anaesthetics. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:279–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen K., Ipsen J. H., Mouritsen O. G., Zuckermann M. J. The effect of anaesthetics on the dynamic heterogeneity of lipid membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1993 Oct;65(3):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(93)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. J., Labarca C. G., Charnet P., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Evidence that the M2 membrane-spanning region lines the ion channel pore of the nicotinic receptor. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2462281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Schuchard M., Palma A., Pradier L., McNamee M. G. Functional role of the cysteine 451 thiol group in the M4 helix of the gamma subunit of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5428–5436. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo D. C., Pinkham J. L., Stevens C. F. Role of a key cysteine residue in the gating of the acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90119-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa T., Hamanaka T., Nishimura S., Uruga T., Kito Y. The specific binding site of the volatile anesthetic diiodomethane to purple membrane by X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 6;238(3):297–301. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Martin K., Gregory S., Keightley C. A., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Warren G. B., Metcalfe J. C. Degenerate perturbations of protein structure as the mechanism of anaesthetic action. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):775–779. doi: 10.1038/276775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanelian D. L., Kosek P., Mody I., MacIver M. B. The role of the GABAA receptor/chloride channel complex in anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1993 Apr;78(4):757–776. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199304000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobimatsu T., Fujita Y., Fukuda K., Tanaka K., Mori Y., Konno T., Mishina M., Numa S. Effects of substitution of putative transmembrane segments on nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 28;222(1):56–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veiro J. A., Hunt G. R. The modulation of ion channels by the inhalation general anaesthetics. A1H-NMR investigation using unilamellar phospholipid membranes. Chem Biol Interact. 1985 Aug-Sep;54(3):337–348. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(85)80174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. H., Cohen J. B. Photolabeling of membrane-bound Torpedo nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with the hydrophobic probe 3-trifluoromethyl-3-(m-[125I]iodophenyl)diazirine. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8741–8751. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Maghrabi E. A., Eckenhoff R. G., Shuman H. Saturable binding of halothane to rat brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4329–4332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]