Abstract
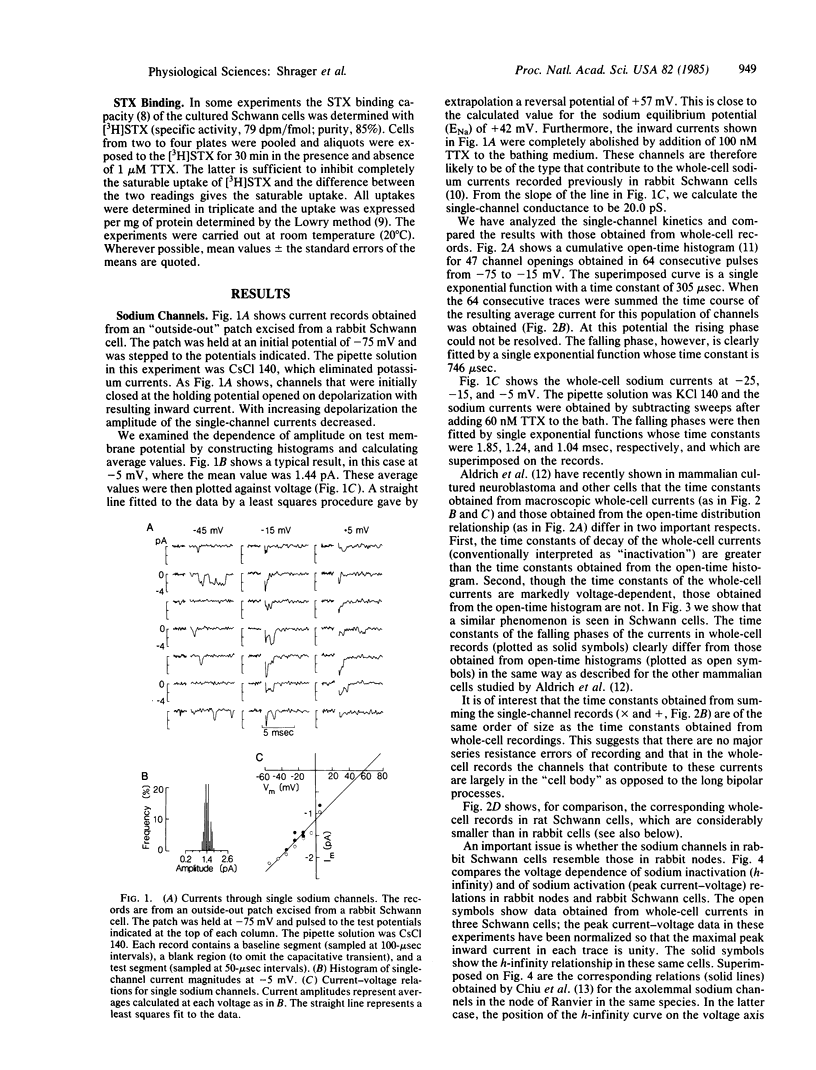
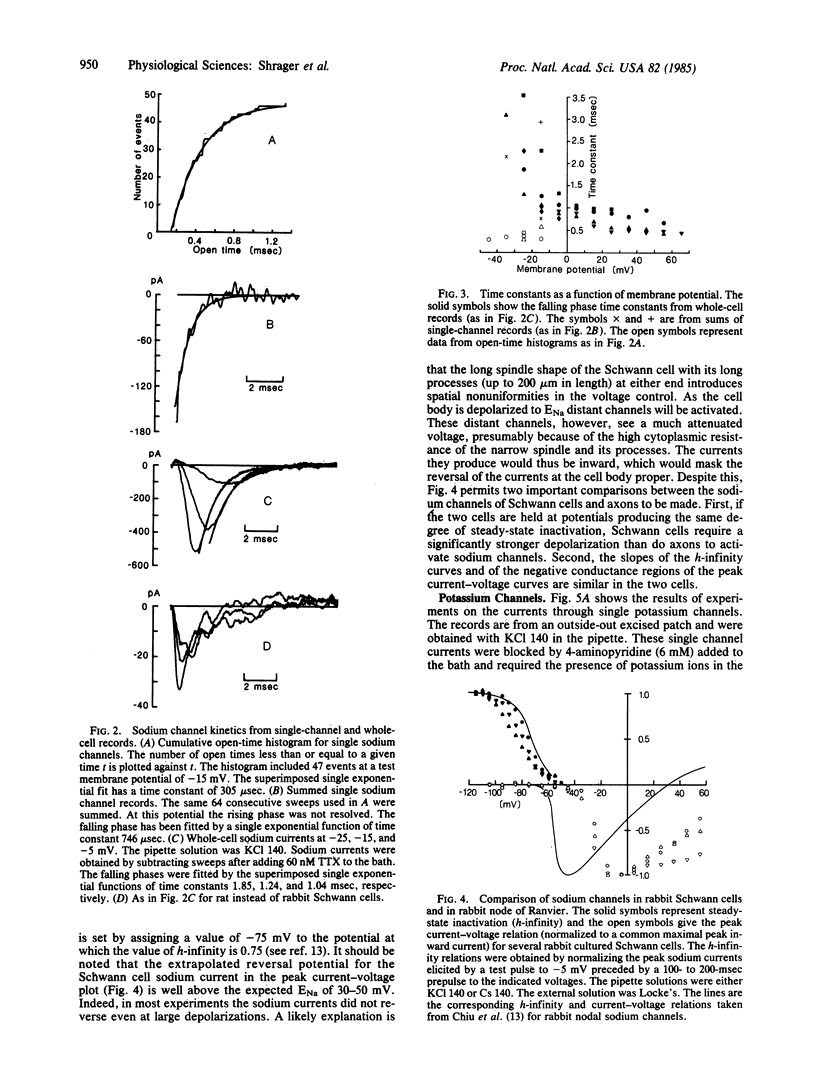
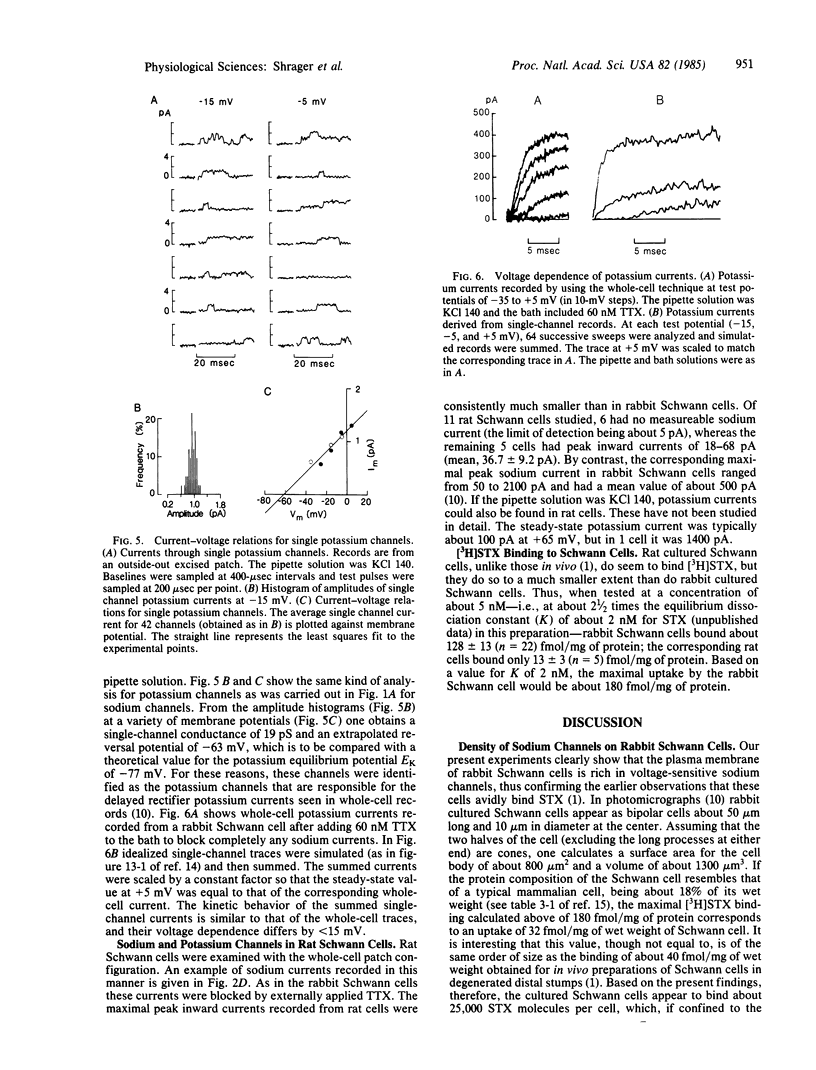
Cultured Schwann cells from sciatic nerves of newborn rabbits and rats have been examined with patch-clamp techniques. In rabbit cells, single sodium and potassium channels have been detected with single channel conductances of 20 pS and 19 pS, respectively. Single sodium channels have a reversal potential within 15 mV of ENa, are blocked by tetrodotoxin, and have rapid and voltage-independent inactivation kinetics. Single potassium channels show current reversal close to EK and are blocked by 4-aminopyridine. From these results, and from comparisons of single-channel and whole-cell data, we show that these Schwann cells contain voltage-dependent sodium and potassium channels that are similar in most respects to the corresponding channels in mammalian axonal membranes. Cultured rat Schwann cells also have sodium channels, but at a density about 1/10th that of rabbit cells, a result in agreement with saxitoxin binding experiments on axon-free sectioned nerves. Saxitoxin binding to cultured cells suggests that there are up to 25,000 sodium channels in a single rabbit Schwann cell. We speculate that in vivo Schwann cells in myelinated axons might act as a local source for sodium channels at the nodal axolemma.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldrich R. W., Corey D. P., Stevens C. F. A reinterpretation of mammalian sodium channel gating based on single channel recording. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):436–441. doi: 10.1038/306436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Fryxell K. J., Lemke G. E. Studies on cultured Schwann cells: the induction of myelin synthesis, and the control of their proliferation by a new growth factor. J Exp Biol. 1981 Dec;95:215–230. doi: 10.1242/jeb.95.1.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Stagg D. A quantitative description of membrane currents in rabbit myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:149–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Schrager P., Ritchie J. M. Neuronal-type Na+ and K+ channels in rabbit cultured Schwann cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):156–157. doi: 10.1038/311156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E., Chandy K. G., Gupta S., Cahalan M. D. Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis? Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):465–468. doi: 10.1038/307465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. T., Bevan S., Ritchie J. M. High conductance anion-selective channels in rat cultured Schwann cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Jun 22;221(1225):395–409. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler J. S., Krishnan N., Singer M. Trophic interactions of neurons and glia. Adv Neurol. 1981;31:479–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson R., Jr, Westermark B., Glaser L. Tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in normal human fibroblasts and normal human glia-like cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6425–6429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino R. G., Ritchie J. M. Sodium channels in the axolemma of normal and degenerating rabbit optic nerve. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Aug 22;222(1227):155–160. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Jacques Y., Lazdunski M. Identification of a tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na+ channel in a variety in fibroblast lines. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):162–164. doi: 10.1038/286162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rang H. P. Extraneuronal saxitoxin binding sites in rabbit myelinated nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B. The binding of saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin to excitable tissue. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;79:1–50. doi: 10.1007/BFb0037088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Strichartz G. R., Orkand R. K. Sodium channels in axons and glial cells of the optic nerve of Necturus maculosa. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Nov;74(5):629–642. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas J., Sevcik C., Barnola F. V., Villegas R. Grayanotoxin, veratrine, and tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium pathways in the Schwann cell membrane of squid nerve fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):369–380. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



