Abstract
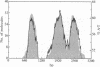
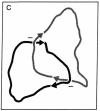
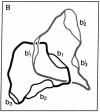
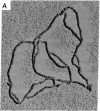
A method has been developed for determination of the absolute structure of DNA catenanes. The catenated DNA is partially denatured before being thickened with a coating of RecA protein and spread for electron microscopy. This treatment allows visualization of the orientation of each ring as well as identification of the overlying and underlying DNAs at crossing points. These determinations define the topology of a catenane, providing a powerful means for testing mechanisms of catenane-producing enzymes in DNA recombination and replication. The technique was used to show that the single interlock of the catenated products of site-specific recombination mediated by Tn3 resolvase is exclusively of negative sign. The unique topology of the products indicates that resolvase fixes the sum of the number of supercoils between recombination sites at synapsis and the number of such supercoils lost or gained during strand exchange. The data strongly suggest that there are in fact three negative supercoils between synapsed sites; one supercoil is dissolved in the cross-over mechanism, whereas the other two are metamorphosed into the unique catenane interlock.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Delius H., Mantell N. J., Alberts B. Characterization by electron microscopy of the complex formed between T4 bacteriophage gene 32-protein and DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Capua E., Engel A., Stasiak A., Koller T. Characterization of complexes between recA protein and duplex DNA by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):87–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T., Hajduk S. L., Marini J. C. The molecular biology of trypanosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funnell B. E., Inman R. B. Comparison of partial denaturation maps with the known sequence of simian virus 40 and phi X174 replicative form DNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield L., Simpson L., Kaplan D. Conversion of closed circular DNA molecules to single-nicked molecules by digestion with DNAase I in the presence of ethidium bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 15;407(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. B. A denaturation map of the lambda phage DNA molecule determined by electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):464–476. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A new method of DNA denaturation mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Nov;2(11):2049–2054. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.11.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Vinograd J. Replication of circular DNA in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):695–719. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific relaxation and recombination by the Tn3 resolvase: recognition of the DNA path between oriented res sites. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1313–1324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Stasiak A., Spengler S. J., Dean F., Koller T., Cozzarelli N. R. Determination of the absolute handedness of knots and catenanes of DNA. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):559–560. doi: 10.1038/304559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Gellert M., Weisberg R. A., Nash H. A. Catenation and supercoiling in the products of bacteriophage lambda integrative recombination in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 25;141(4):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: the mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock T. J., Nash H. A. Knotting of DNA caused by a genetic rearrangement. Evidence for a nucleosome-like structure in site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Shibuya G. I., Steitz J. A. Nucleotide sequence of gamma delta resolvase gene and demonstration that its gene product acts as a repressor of transcription. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):381–383. doi: 10.1038/300381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Klug A. Studies of nucleosome structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):493–501. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Nathans D. Local mutagenesis: a method for generating viral mutants with base substitutions in preselected regions of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Terminal stages of SV40 DNA replication proceed via multiply intertwined catenated dimers. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C. Use of polylysine for adsorption of nuclei acids and enzymes to electron microscope specimen films. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]