Abstract
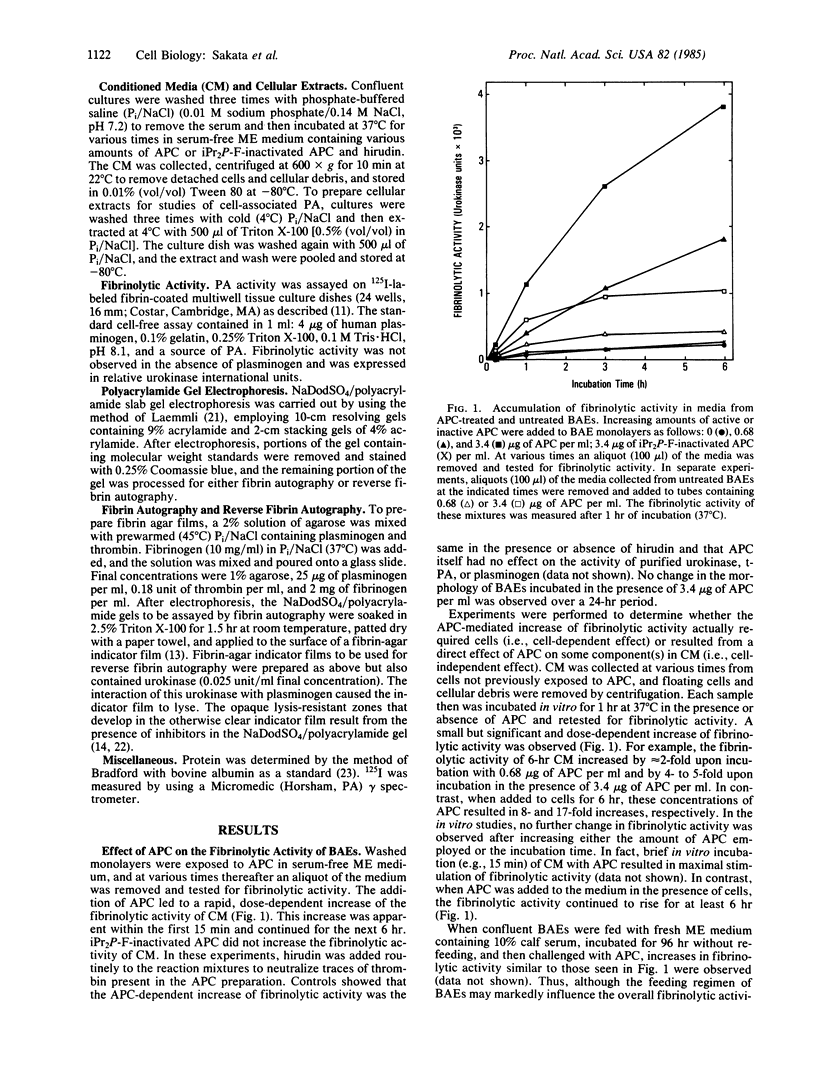
The effects of bovine activated protein C (APC) on the fibrinolytic activity of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells were investigated. Confluent monolayers were incubated with purified APC under various conditions and changes in total fibrinolytic activity and in the level of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor (antiactivator) were monitored. The addition of APC to the cells in the absence of other blood or plasma components led to a rapid, dose-dependent increase of fibrinolytic activity both in the media and in cellular extracts. For example, 3.4 micrograms of APC per ml resulted in a 15-fold increase of fibrinolytic activity in the medium within 1 hour. The enhanced fibrinolytic activity reflected increases in both the urokinase-related and tissue-type plasminogen activators produced by these cells. Interestingly, treatment of cells with APC also caused a rapid, dose-dependent decrease in antiactivator activity. Diisopropyl fluorophosphate-inactivated APC did not decrease antiactivator or increase plasminogen activator. Although a small but significant direct (i.e., cell-independent) effect of APC on both fibrinolytic activity and antiactivator activity could be demonstrated, the major portion of these changes appeared to be cell-mediated. These observations indicate that the fibrinolytic potential of cultured endothelial cells is increased by APC and that the enzyme active site is essential for this change. Moreover, the results suggest that one of the primary mechanisms for this stimulation of endothelial cell fibrinolytic activity involves an APC-mediated decrease in antiactivator.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Sakata Y., Yoshida N., Matsuda M. Abnormal plasminogen. A hereditary molecular abnormality found in a patient with recurrent thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1186–1195. doi: 10.1172/JCI109034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockway W. J., Castellino F. J. Measurement of the binding of antifibrinolytic amino acids to various plasminogens. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekmans A. W., Veltkamp J. J., Bertina R. M. Congenital protein C deficiency and venous thromboembolism. A study of three Dutch families. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 11;309(6):340–344. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308113090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Stassen J. M., Collen D. Influence of protein C activation on blood coagulation and fibrinolysis in squirrel monkeys. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):200–204. doi: 10.1172/JCI111402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comp P. C., Esmon C. T. Generation of fibrinolytic activity by infusion of activated protein C into dogs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1221–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI110368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., van Hinsbergh V. W., Verheijen J. H., Wijngaards G. Inhibition of tissue-type plasminogen activator by conditioned medium from cultured human and porcine vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
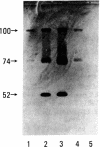
- Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Reverse fibrin autography: a method to detect and partially characterize protease inhibitors after sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Esmon N. L., Harris K. W. Complex formation between thrombin and thrombomodulin inhibits both thrombin-catalyzed fibrin formation and factor V activation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7944–7947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Evatt B., Zimmerman T. S., Kleiss A. J., Wideman C. Deficiency of protein C in congenital thrombotic disease. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1370–1373. doi: 10.1172/JCI110385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson L., Hedner U., Nilsson I. M. A family with thromboembolic disease associated with deficient fibrinolytic activity in vessel wall. Acta Med Scand. 1978;203(6):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1978.tb14911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Canfield W. M., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Anticoagulant properties of bovine plasma protein C following activation by thrombin. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 27;16(26):5824–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00645a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laug W. E. Secretion of plasminogen activators by cultured bovine endothelial cells: partial purification, characterization and evidence for multiple forms. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Jun 30;45(3):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G. Latent tissue plasminogen activator produced by human endothelial cells in culture: evidence for an enzyme-inhibitor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6804–6808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Cultured bovine endothelial cells produce both urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):631–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Loskutoff D. J. Serum-mediated suppression of cell-associated plasminogen activator activity in cultured endothelial cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):701–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J. Effect of thrombin on the fibrinolytic activity of cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):329–332. doi: 10.1172/JCI109457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., van Mourik J. A., Erickson L. A., Lawrence D. Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAMMEN E. F., THOMAS W. R., SEEGERS W. H. Activation of purified prothrombin to autoprothrombin I or autoprothrombin II (platelet cofactor II or autoprothrombin II-A). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960 Dec 15;5:218–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Kleiss A. J., Griffin J. H. Mechanism of action of human activated protein C, a thrombin-dependent anticoagulant enzyme. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1067–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., van Hinsbergh V. W., Sens E. H. Quantitation of tissue-type plasminogen activator in human endothelial cell cultures by use of an enzyme immunoassay. Thromb Res. 1984 Jan 15;33(2):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Berger A., Abend M., Rubin L., Attias D., Zivelin A., Rapaport S. I. Homozygous protein C deficiency manifested by massive venous thrombosis in the newborn. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 1;310(9):559–562. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403013100904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. A new vitamin K-dependent protein. Purification from bovine plasma and preliminary characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):355–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]