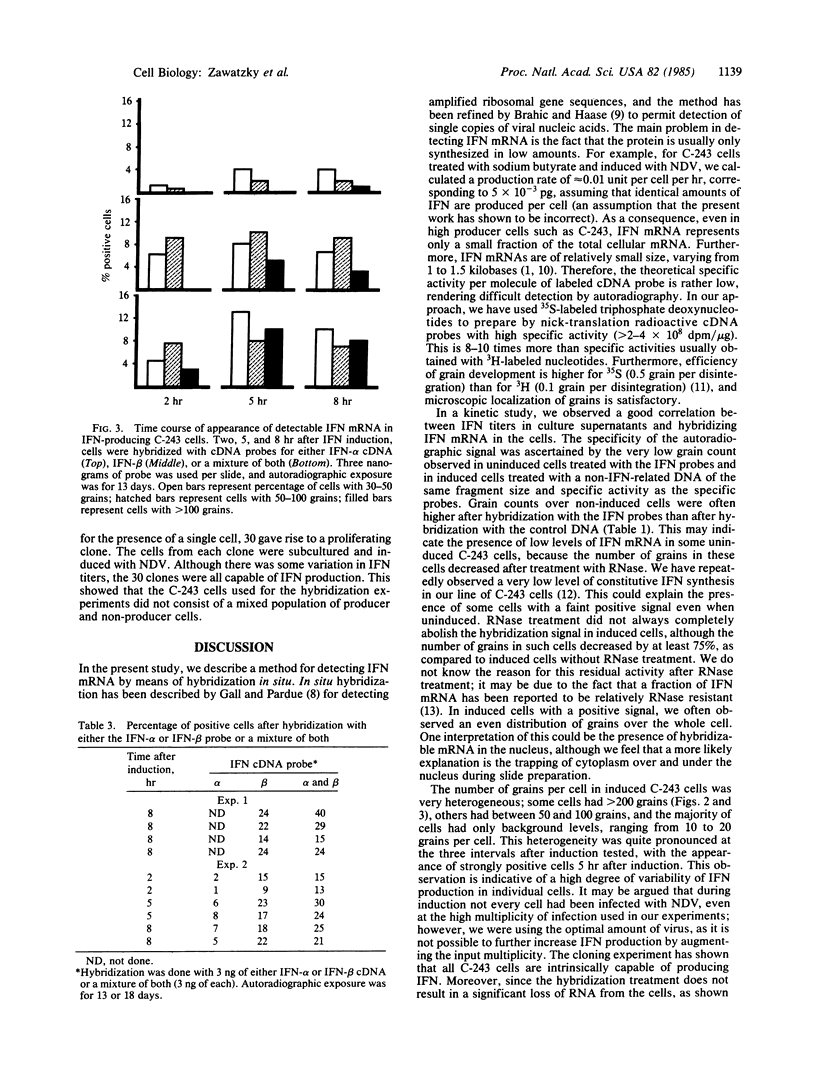
Abstract
Individual interferon (IFN)-producing cells were identified by hybridization in situ followed by autoradiography. cDNAs corresponding to murine IFN-alpha and murine IFN-beta labeled by nick-translation to high specific activity (2-4 X 10(8) dpm/micrograms) with alpha-35S-labeled dATP were used as probes for hybridization with IFN mRNA in mouse C-243 cells induced with Newcastle disease virus. Control experiments with non-induced cells or with non-IFN-related labeled DNA monitored the specificity of the autoradiographic signal. Under optimal conditions of IFN induction, between 15% and 40% of the cells gave a hybridization signal with a mixture of IFN-alpha and -beta probes. Differential hybridization with either the IFN-alpha or -beta probe or a mixture of both, at three different time intervals after induction, revealed that only a small fraction of cells had detectable amounts of IFN-alpha mRNA, whereas in the majority of the positive cells IFN-beta mRNA was present.
Full text
PDF
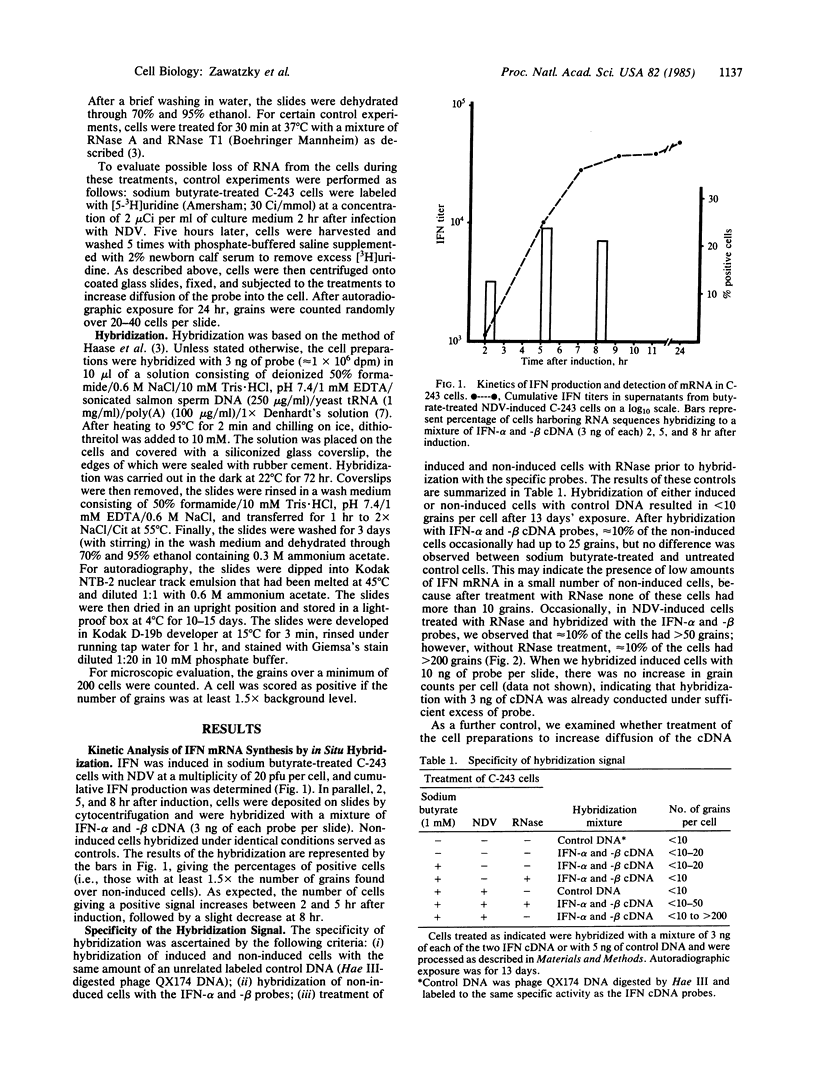
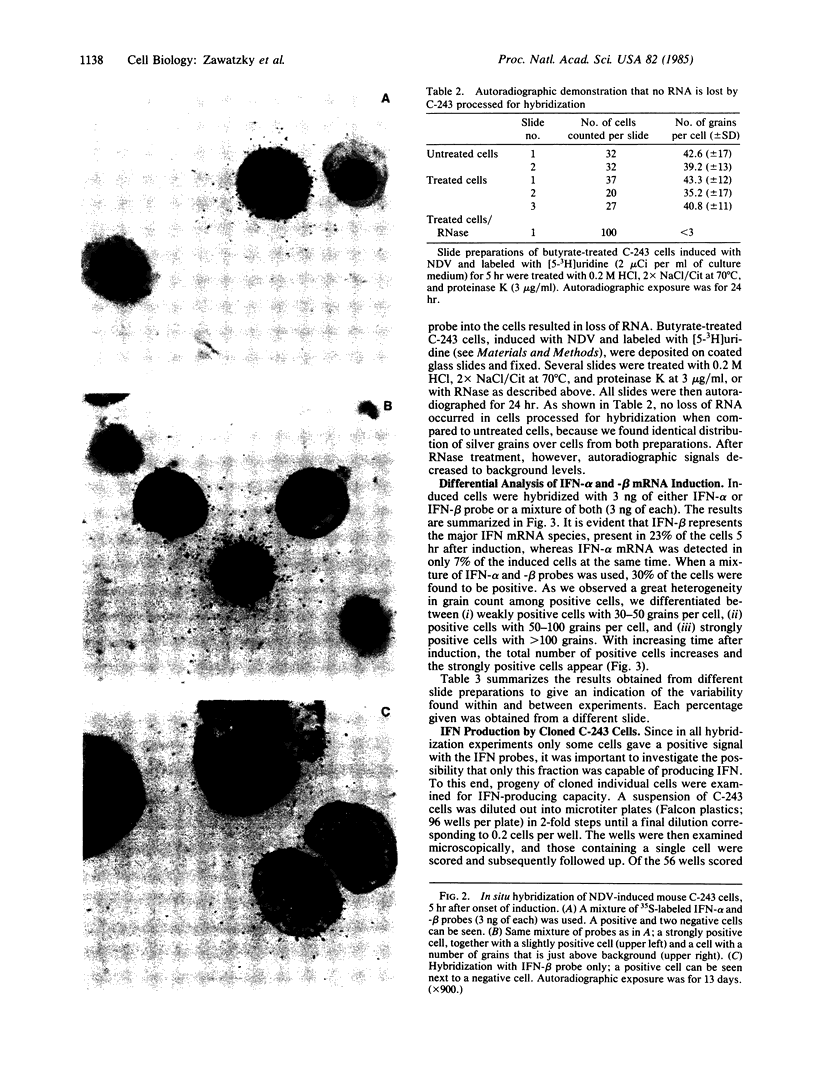

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., Gresser I., De Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by sequential affinity chromatography on poly(U)--and antibody--agarose columns. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):622–625. doi: 10.1038/271622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Pardue M. L. Formation and detection of RNA-DNA hybrid molecules in cytological preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):378–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Sokawa Y., Watanabe Y., Kawade Y., Ohno S., Takaoka C., Taniguchi T. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for mouse interferon-beta. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9522–9529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Kozak C. A., Dandoy F., Sor F., Skup D., Windass J. D., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., Pitha P. M., DeMaeyer E. Mapping of murine interferon-alpha genes to chromosome 4. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagnier L., Collandre H., De Maeyer-Guignard J., De Maeyer E. Two forms of mouse interferon messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1031–1038. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80083-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Buckler C. E., Baron S. High interferon producing line of transformed murine cells. J Gen Virol. 1972 Oct;17(1):107–109. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B. The interferon genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 30;695(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(82)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth J., Morser J., Burke D. C. Expression of interferon-alpha and interferon-beta genes in human lymphoblastoid (Namalwa) cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):399–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C., Nagata S., Boll W., Fountoulakis M., Fujisawa A., Fujisawa J. I., Haynes J., Henco K., Mantei N., Ragg H. Structure and expression of human IFN-alpha genes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Sep 24;299(1094):7–28. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y. Antigenicity of mouse interferons: two distinct molecular species common to interferons of various sources. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90335-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawatzky R., Kirchner H., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., DeMaeyer E. An X-linked locus influences the amount of circulating interferon induced in the mouse by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):325–332. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]