Abstract
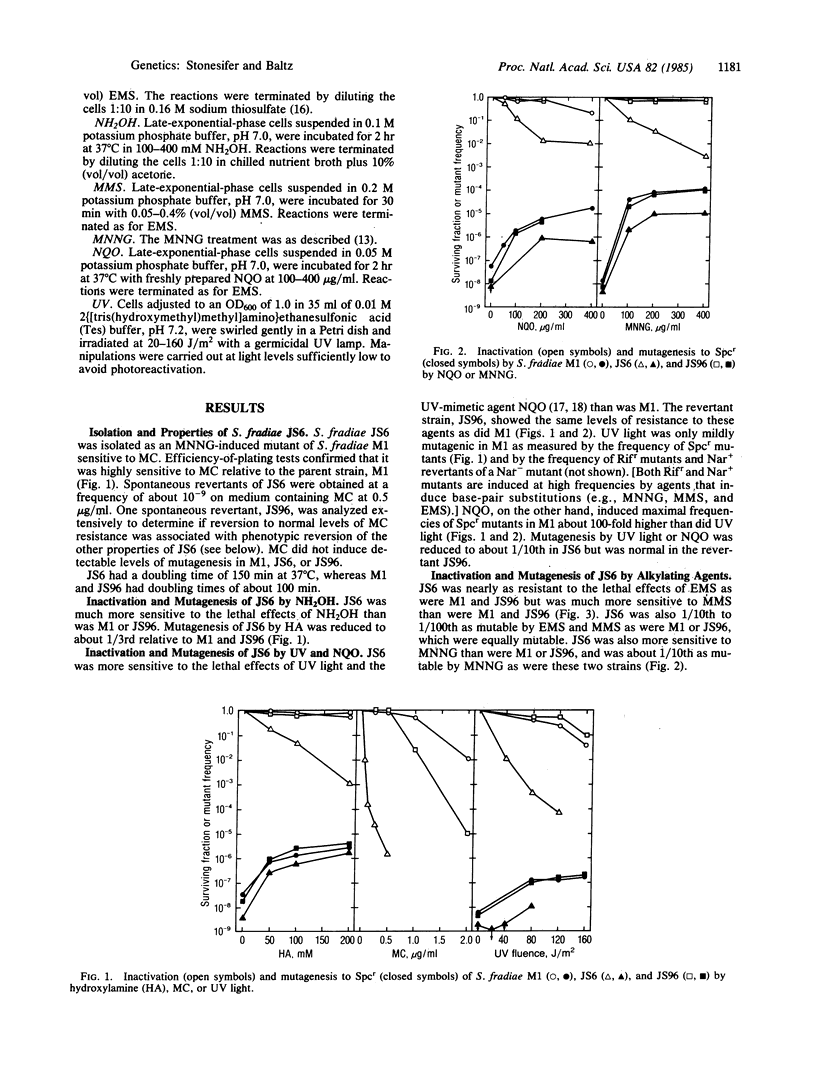
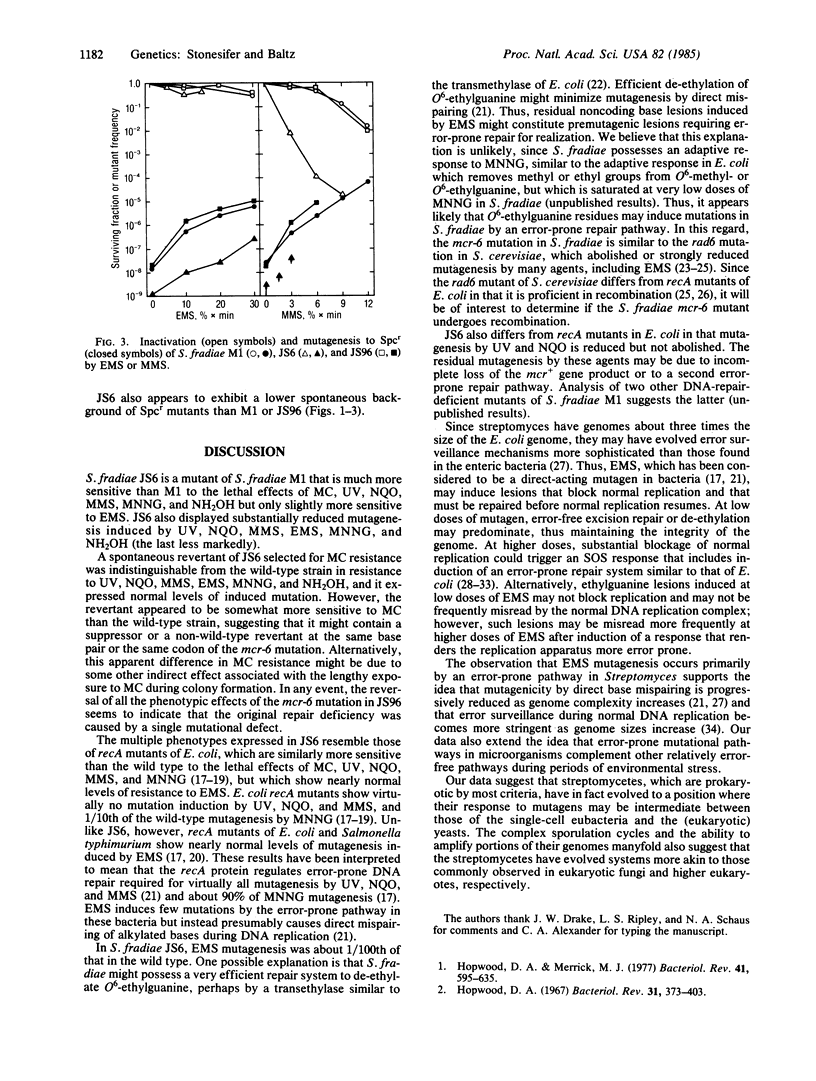
Streptomyces fradiae JS6 (mcr-6) is defective in the repair of potentially lethal damage to DNA induced by mitomycin C (MC), hydroxylamine (NH2OH), methyl methanesulfonate (MMS), 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide (NQO), N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG), and ultraviolet light (UV), but it exhibits nearly normal sensitivity to ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS)-induced lethality. JS6 is substantially less mutable by MNNG, MMS, NQO, UV, NH2OH, and also EMS than is the parental strain. A spontaneous revertant of JS6 showed wild-type levels of resistance to all of these agents and wild-type levels of induced mutagenesis, indicating that a single mutation caused the multiple traits displayed by JS6. The mcr-6 gene product thus appears to control an error-prone (mutagenic) DNA repair system. Mediation of EMS mutagenesis by an error-prone repair pathway in S. fradiae, rather than by direct mispairing as in Escherichia coli, suggests that the streptomycetes have evolved more efficient error-avoidance mechanisms than those commonly observed in the single-celled eubacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltz R. H. Genetic recombination in Streptomyces fradiae by protoplast fusion and cell regeneration. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Jul;107(1):93–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-107-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz R. H., Seno E. T. Properties of Streptomyces fradiae mutants blocked in biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic tylosin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):214–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz R. H., Seno E. T., Stonesifer J., Wild G. M. Biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic tylosin. A preferred pathway from tylactone to tylosin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Feb;36(2):131–141. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benigni R., Petrov P. A., Carere A. Estimate of the genome size by renaturation studies in Streptomyces. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):324–326. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.324-326.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. W., Baltz R. H. The biochemistry of mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:11–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. W. Comparative rates of spontaneous mutation. Nature. 1969 Mar 22;221(5186):1132–1132. doi: 10.1038/2211132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman S. E., Hershberger C. L. Amplified DNA in Streptomyces fradiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):459–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.459-466.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S. Genetic control of the SOS system in E. coli. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A. Genetic analysis and genome structure in Streptomyces coelicolor. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):373–403. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.373-403.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Merrick M. J. Genetics of antibiotic production. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):595–635. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.595-635.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga M., Ichikawa-Ryo H., Kondo S. The major cause of inactivation and mutation by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oixde in Escherichia coli: excisable 4NQO-purine adducts. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 25;92(2):341–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii Y., Kondo S. Comparative analysis of deletion and base-change mutabilities of Escherichia coli B strains differing in DNA repair capacity (wild-type, uvrA-, polA-, recA-) by various mutagens. Mutat Res. 1975 Jan;27(1):27–44. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Ichikawa H., Iwo K., Kato T. Base-change mutagenesis and prophage induction in strains of Escherichia coli with different DNA repair capacities. Genetics. 1970 Oct;66(2):187–217. doi: 10.1093/genetics/66.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPartland A., Green L., Echols H. Control of recA gene RNA in E. coli: regulatory and signal genes. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):731–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono H., Hintermann G., Crameri R., Wallis G., Hütter R. Reiterated DNA sequences in a mutant strain of Streptomyces glaucescens and cloning of the sequence in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(1):106–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00422920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizicky E. M., Roberts J. W. Induction of SOS functions: regulation of proteolytic activity of E. coli RecA protein by interaction with DNA and nucleoside triphosphate. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L. Characterization of postreplication repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and effects of rad6, rad18, rev3 and rad52 mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):471–478. doi: 10.1007/BF00352525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L., Higgins D. Role of DNA repair in ethyl methanesulfonate-induced mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Carcinogenesis. 1982;3(4):439–444. doi: 10.1093/carcin/3.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash L. Lack of chemically induced mutation in repair-deficient mutants of yeast. Genetics. 1974 Dec;78(4):1101–1118. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.4.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray U., Bartenstein L., Drake J. W. Inactivation of bacteriophage T4 by ethyl methanesulfonate: influence of host and viral genotypes. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):440–447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.440-447.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Lewis E., Napier E. Occurrence of reiterated DNA sequences in strains of Streptomyces produced by an interspecific protoplast fusion. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):336–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00269680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrempf H. Deletion and amplification of DNA sequences in melanin-negative variants of Streptomyces reticuli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(3):501–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00325917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrempf H. Plasmid loss and changes within the chromosomal DNA of Streptomyces reticuli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):701–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.701-707.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G., Yarranton G. T. How cells in distress use SOS. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):606–607. doi: 10.1038/296606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno E. T., Baltz R. H. Properties of S-adenosyl-L-methionine:macrocin O-methyltransferase in extracts of Streptomyces fradiae strains which produce normal or elevated levels of tylosin and in mutants blocked in specific O-methylations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Sep;20(3):370–377. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.3.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno E. T., Baltz R. H. S-Adenosyl-L-methionine: macrocin O-methyltransferase activities in a series of Streptomyces fradiae mutants that produce different levels of the macrolide antibiotic tylosin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):758–763. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanabruch W. G., Rein R. P., Behlau I., Walker G. C. Mutagenesis, by methylating and ethylating agents, in mutH, mutL, mutS, and uvrD mutants of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):33–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.33-44.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



