Abstract
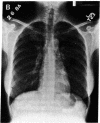
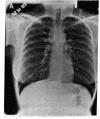
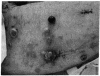
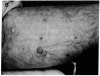
R24 is an IgG3 mouse monoclonal antibody that identifies GD3, a prominent ganglioside on the surface of melanoma cells and other cells of neuroectodermal origin. Twelve patients with metastatic melanoma were treated with R24 at three dose levels, 8, 80, or 240 mg/m2, over a period of 2 weeks. Peak antibody levels in the serum were dose related and ranged from less than 0.1 to 62 micrograms/ml. Inflammatory reactions (urticaria, pruritus, erythema, subcutaneous ecchymoses) were observed around tumor sites in patients treated at doses greater than or equal to 80 mg/m2. Tumor biopsies during and after treatment showed lymphocyte and mast cell infiltration, mast cell degranulation, and complement deposition. Side effects were mild and were readily controlled by antihistamines. Major tumor regression has been observed in three patients.
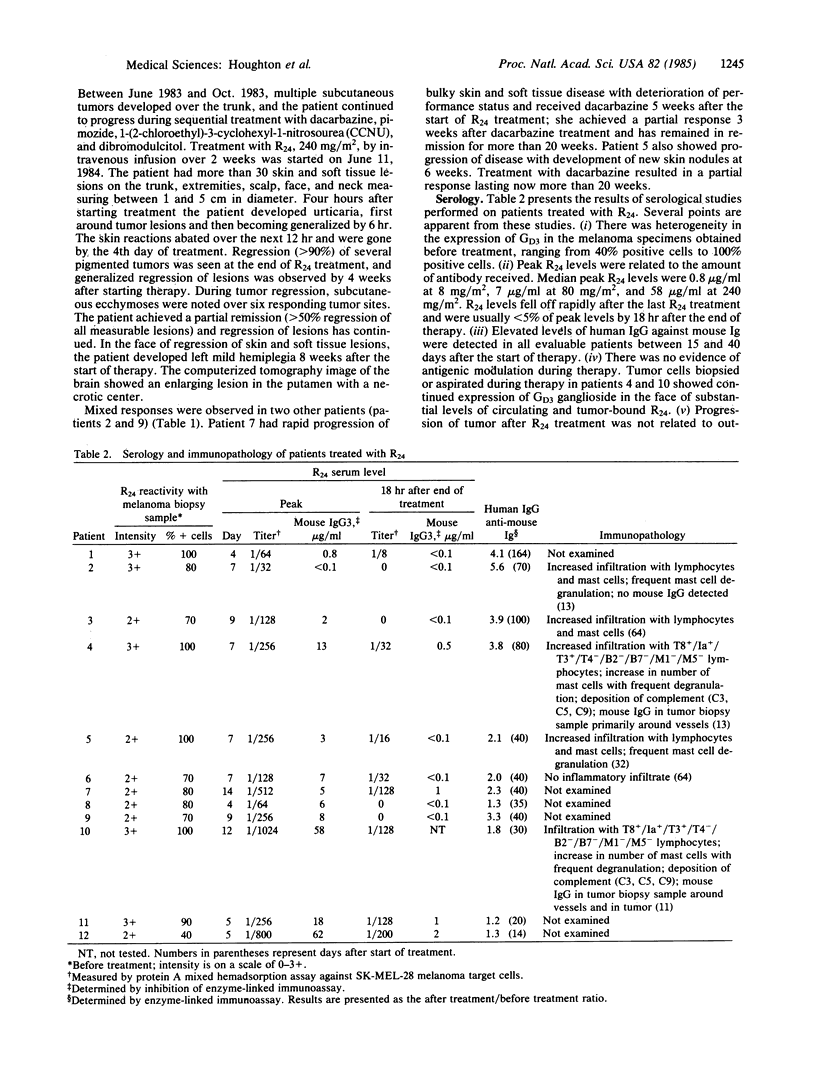
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dippold W. G., Knuth A., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Inhibition of human melanoma cell growth in vitro by monoclonal anti-GD3-ganglioside antibody. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):806–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Lloyd K. O., Li L. T., Ikeda H., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: definition of six antigenic systems with mouse monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6114–6118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson R. A., Cardon-Cardo C., Higgins P. J. Histogenesis of benign pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor) of the major salivary glands. An ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984 Nov;8(11):803–820. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198411000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton A. N., Brooks H., Cote R. J., Taormina M. C., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Detection of cell surface and intracellular antigens by human monoclonal antibodies. Hybrid cell lines derived from lymphocytes of patients with malignant melanoma. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):53–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton A. N., Eisinger M., Albino A. P., Cairncross J. G., Old L. J. Surface antigens of melanocytes and melanomas. Markers of melanocyte differentiation and melanoma subsets. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1755–1766. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. L., Weigle W. O., Hugli T. E. Anaphylatoxin-mediated regulation of human and murine immune responses. Fed Proc. 1984 Jul;43(10):2543–2547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfreundschuh M., Shiku H., Takahashi T., Ueda R., Ransohoff J., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Serological analysis of cell surface antigens of malignant human brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5122–5126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukel C. S., Lloyd K. O., Travassos L. R., Dippold W. G., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. GD3, a prominent ganglioside of human melanoma. Detection and characterisation by mouse monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1133–1147. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]