Abstract
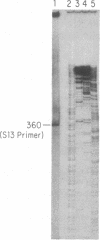
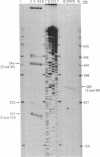
The portion of the Leishmania tarentolae kinetoplast maxicircle DNA encoding the 9S RNA gene was sequenced, and the 5' and 3' ends of the transcript were determined. A secondary structure for the 9S RNA was determined based on the Escherichia coli 16S model. The 610-nucleotide 9S RNA exhibits a minimal secondary structure in which all four domains of the E. coli 16S structure are preserved. Within domains, however, some stems and loops have been greatly reduced or eliminated entirely. It is presumed that these reduced domains represent the minimal essential small ribosomal RNA secondary structures necessary for a functional ribosome. Alignment of the L. tarentolae 9S rRNA sequence with the published Trypanosoma brucei 9S rRNA sequence shows a nucleotide similarity of 84% and a transversion/transition ratio of 1.66.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. Shotgun DNA sequencing using cloned DNase I-generated fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3015–3027. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Machatt M. A., Pouyet J., Ebel J. P., Edwards K., Kössel H. Primary and secondary structures of Escherichia coli MRE 600 23S ribosomal RNA. Comparison with models of secondary structure for maize chloroplast 23S rRNA and for large portions of mouse and human 16S mitochondrial rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4303–4324. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Maly P., Zwieb C. The structure of ribosomal RNA and its organization relative to ribosomal protein. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:1–48. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Brown W. M., Wilson A. C. Polymorphic sites and the mechanism of evolution in human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics. 1984 Mar;106(3):479–499. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connaughton J. F., Rairkar A., Lockard R. E., Kumar A. Primary structure of rabbit 18S ribosomal RNA determined by direct RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4731–4745. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., Mendu N., Ginsburg H., Kridl J. C. Sequence analysis of the maize mitochondrial 26 S rRNA gene and flanking regions. Plasmid. 1984 Mar;11(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E., Doolittle W. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 23S rRNA gene of the Cyanobacterium, Anacystis nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3373–3386. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C., Anderson S., Nierlich D. P. Distinctive sequence of human mitochondrial ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):460–467. doi: 10.1038/286460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C., Janssen J. W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Borst P. The major transcripts of the kinetoplast DNA of Trypanosoma brucei are very small ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):105–125. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Ansorge W. Improvements of DNA sequencing gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotz C., Zwieb C., Brimacombe R., Edwards K., Kössel H. Secondary structure of the large subunit ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, Zea mays chloroplast, and human and mouse mitochondrial ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3287–3306. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Sankoff D., Cedergren R. J. On the evolutionary descent of organisms and organelles: a global phylogeny based on a highly conserved structural core in small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5837–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Georgiev O. I., Nosikov V. V., Yavachev L. P. Primary and secondary structure of rat 28 S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3677–3693. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J., Linden G., Stuart K. Mitochondrial and cytoplasmic ribosomes and their activity in blood and culture form Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):103–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna N., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3563–3583. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., Snijders A., Janssen J. W., Borst P. Transcription of kinetoplast DNA in Trypanosoma brucei bloodstream and culture forms. Plasmid. 1981 May;5(3):329–350. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F. A systemic DNA sequencing strategy. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keus R. J., Dekker A. F., van Roon M. A., Groot G. S. The nucleotide sequences of the regions flanking the genes coding for 23S, 16S and 4.5S ribosomal RNA on chloroplast DNA from Spirodela oligorhiza. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6465–6474. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleisen C. M., Borst P. Are 50% of all cellular proteins synthesized on mitochondrial ribosomes in Crithidia luciliae? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 16;390(1):78–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Seki T., Yaginuma K., Koike K. Nucleotide sequences of small ribosomal RNA and adjacent transfer RNA genes in rat mitochondrial DNA. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumano M., Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S rRNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. The ribosome. Sci Am. 1981 Aug;245(2):84–97. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0881-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub-Kupersztejn R., Thirion J. Existence of two distinct protein synthesis systems in the trypanosomatid Crithidia luciliae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 27;340(3):314–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly P., Brimacombe R. Refined secondary structure models for the 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7263–7286. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Simpson L., Rosenblatt H., Simpson A. M. Restriction map, partial cloning and localization of 9S and 12S kinetoplast RNA genes on the maxicircle component of the kinetoplast DNA of Leishmania tarentolae. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):51–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Kop J., Wheaton V., Brosius J., Gutell R. R., Kopylov A. M., Dohme F., Herr W., Stahl D. A., Gupta R. Secondary structure model for 23S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6167–6189. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura N., Ray D. S. Expression of a DNA strand initiation sequence of ColE1 plasmid in a single-stranded DNA phage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6566–6570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince J. B., Taylor B. H., Thurlow D. L., Ofengand J., Zimmermann R. A. Covalent crosslinking of tRNA1Val to 16S RNA at the ribosomal P site: identification of crosslinked residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5450–5454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Shander M. H., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Maniatis T. Structure and in vitro transcription of human globin genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1329–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.6158093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A high speed, high capacity homology matrix: zooming through SV40 and polyoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4765–4782. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccone C., Cantatore P., Gadaleta G., Gallerani R., Lanave C., Pepe G., Kroon A. M. The nucleotide sequence of the large ribosomal RNA gene and the adjacent tRNA genes from rat mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4139–4148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Gutell R. R., Cummings D. J. Paramecium mitochondrial genes. II. Large subunit rRNA gene sequence and microevolution. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5173–5181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Olsen G. J., Cummings D. J. Paramecium mitochondrial genes. I. Small subunit rRNA gene sequence and microevolution. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5167–5172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. M., Simpson L., Livingston L. Transcription of the maxicircle kinetoplast DNA of Leishmania tarentolae. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Oct;6(4):237–252. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L., Simpson A. G. Kinetoplast RNA of Leishmania tarentolae. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Fukuhara H. Complete DNA sequence coding for the large ribosomal RNA of yeast mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):339–348. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spithill T. W., Shimer S. P., Hill G. C. Inhibitory effects of chloramphenicol isomers and other antibiotics on protein synthesis and respiration in procyclic Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Feb;2(3-4):235–255. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Fields S. Cloning of influenza cDNA ino M13: the sequence of the RNA segment encoding the A/PR/8/34 matrix protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1965–1974. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Glotz C., Brimacombe R. Secondary structure comparisons between small subunit ribosomal RNA molecules from six different species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3621–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Cruz V. F., Neckelmann N., Simpson L. Sequences of six genes and several open reading frames in the kinetoplast maxicircle DNA of Leishmania tarentolae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15136–15147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]