Abstract
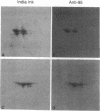
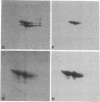
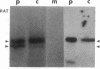
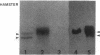
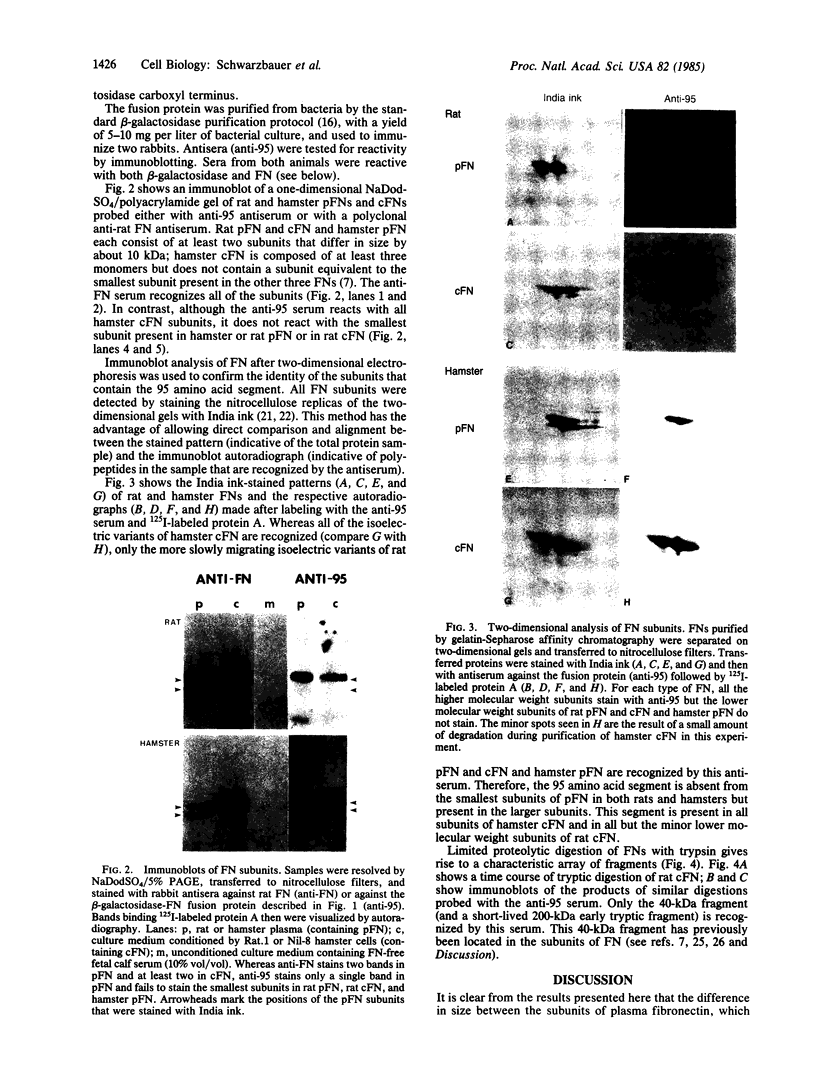
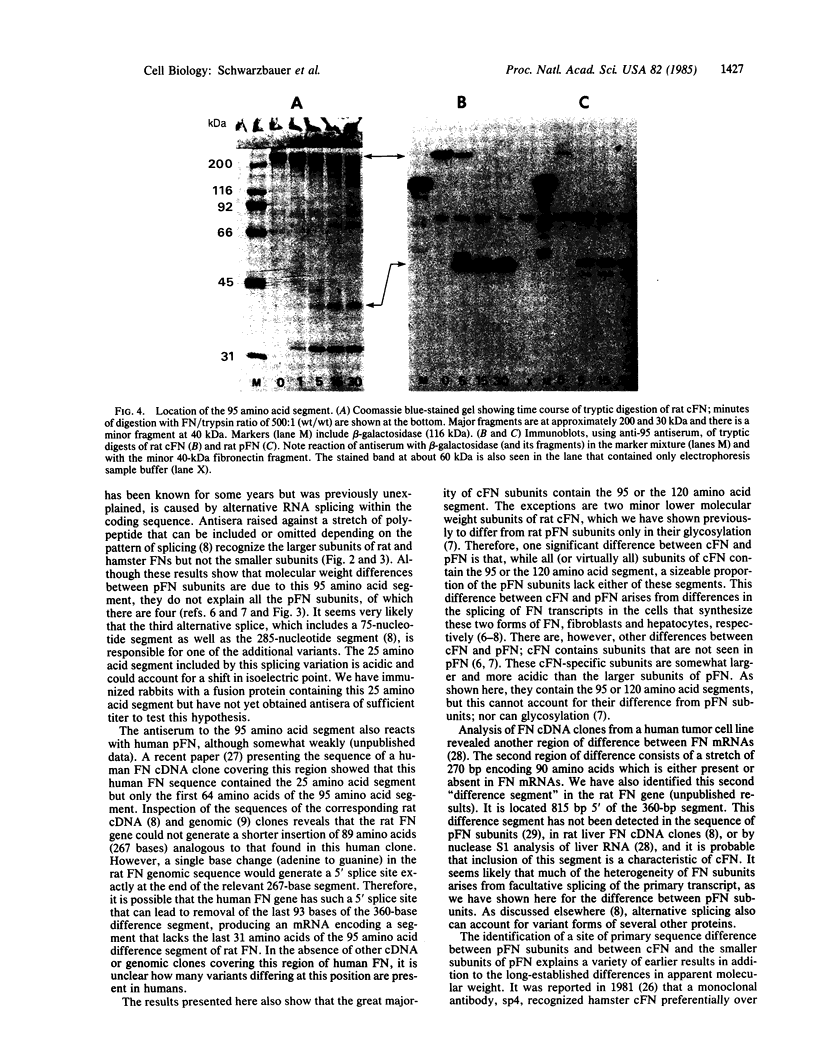
Multiple different subunits of fibronectin are known to occur and their origin has been unclear. Recent results showing that a single fibronectin gene can give rise to several different mRNAs by alternative splicing suggested an explanation for some of this diversity of fibronectin subunits. Because the alternative splicing events occur within the coding region, the mRNAs differ in coding potential. We have prepared recombinant phage containing a rat fibronectin cDNA segment that is present in some fibronectin mRNAs and not in others. This segment was inserted in the beta-galatosidase gene of lambda gt11, and fusion protein produced by lysogens of the recombinant phage was purified and used as immunogen. The resulting antisera recognized some subunits of rat and hamster fibronectins but not others, indicating that inclusion or removal of this segment gives rise to mRNAs that encode different fibronectin subunits. In particular, presence or absence of a 95 amino acid segment appears to account for differences in size among the subunits of plasma fibronectin, whose origin is therefore explained by alternative patterns of RNA splicing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atherton B. T., Hynes R. O. A difference between plasma and cellular fibronectins located with monoclonal antibodies. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdwell C. R., Brasier A. R., Taylor L. A. Two-dimensional peptide mapping of fibronectins from bovine aortic endothelial cells and bovine plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):574–581. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrismann R., Roth D. E., Eppenberger H. M., Turner D. C. Arrangement of attachment-promoting, self-association, and heparin-binding sites in horse serum fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7381–7387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. E., Gilden R. V., Vernon M. L., Wolford R. G., Hugunin P. E., Huebner R. J. 5-Bromo-2'-deoxyuridine potentiation of transformation of rat-embryo cells induced in vitro by 3-methylcholanthrene: induction of rat leukemia virus gs antigen in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2415–2419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Yamada K. M. Differences in domain structures between plasma and cellular fibronectins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11292–11300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Yamada K. M. Domain structure of the carboxyl-terminal half of human plasma fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3332–3340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: cell specific alternative mRNA splicing generates polypeptide chains differing in the number of internal repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5853–5868. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblihtt A. R., Vibe-Pedersen K., Baralle F. E. Human fibronectin: molecular cloning evidence for two mRNA species differing by an internal segment coding for a structural domain. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):221–226. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mautner V., Hynes R. O. Surface distribution of LETS protein in relation to the cytoskeleton of normal and transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):743–768. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. I., Hynes R. O. Multiple fibronectin subunits and their post-translational modifications. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13477–13487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen T. E., Thøgersen H. C., Skorstengaard K., Vibe-Pedersen K., Sahl P., Sottrup-Jensen L., Magnusson S. Partial primary structure of bovine plasma fibronectin: three types of internal homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter H., Seidl M., Hörmann H. Location of heparin-binding sites of fibronectin. Detection of a hitherto unrecognized transamidase sensitive site. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Apr;362(4):399–408. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.1.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzbauer J. E., Tamkun J. W., Lemischka I. R., Hynes R. O. Three different fibronectin mRNAs arise by alternative splicing within the coding region. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi K., Fukuda M., Hakomori S. Domain structure of hamster plasma fibronectin. Isolation and characterization of four functionally distinct domains and their unequal distribution between two subunit polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6452–6462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi K., Hakomori S. Domain structure of human plasma fibronectin. Differences and similarities between human and hamster fibronectins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3967–3973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Plasma fibronectin is synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4641–4647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Schwarzbauer J. E., Hynes R. O. A single rat fibronectin gene generates three different mRNAs by alternative splicing of a complex exon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Hynes R. O. Topological arrangement of the major structural features of fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4304–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Fibroblast cellular and plasma fibronectins are similar but not identical. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):492–498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]