Abstract
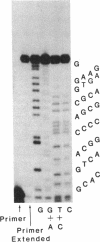
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), an evolutionarily conserved glycolytic enzyme, is constitutively expressed in most cell types yet is induced to high levels during the development of fast twitch muscle fibers. To analyze the organization and regulation of the chicken GAPDH gene, we first constructed a nearly full-length GAPDH cDNA clone (pGAD-28). pGAD-28 was used in the current study to screen a genomic library, and several overlapping clones were selected. The GAPDH coding region was detected within a 4.65-kilobase Xho I/EcoRI genomic fragment that was completely sequenced by using the M13 cloning vector system. A small portion of pGAD-28 was used as a primer to extend a 33-nucleotide sequence from the 5' end of GAPDH mRNA. The canonical promoter "TATA" region was found 22 base pairs from the 5' end of the mRNA. The 5' end of the GAPDH gene is extraordinarily G+C-rich (80%) and contains two inverted sequences with a 9-base-pair homology found at -58 (G-G-G-G-C-G-G-G-C) and -93 (G-C-C-C-G-C-C-C-C) nucleotides from the transcription start site. Sequencing also revealed the location of 11 introns within the transcribed portion of the GAPDH gene. The placement of at least 3 of the introns corresponds to the boundaries of protein domains within prokaryotic and eukaryotic GAPDHs that were previously detected by x-ray crystallography. This concordance suggests that introns may have participated in the construction of the earliest GAPDH gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alevy M. C., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. DNase I sensitive domain of the gene coding for the glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2309–2314. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Harris J. I., Thierry J. C., Walker J. E., Wonacott A. J. Sequence and structure of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):328–333. doi: 10.1038/266328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Implications of RNA-RNA splicing in evolution of eukaryotic cells. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1257–1260. doi: 10.1126/science.364651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. E., Sajgò M., Noller H. F., Harris J. I. Amino-acid sequence of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from lobster muscle. Nature. 1967 Dec 23;216(5121):1181–1185. doi: 10.1038/2161181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Strommer J., Engel J. D. Isolation of the chicken beta-globin gene and a linked embryonic beta-like globin gene from a chicken DNA recombinant library. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90328-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Wang R. Y. 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1981 Jun 19;212(4501):1350–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.6262918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Santer M., Steitz J. A., Mans R. J. Conservation of the primary structure at the 3' end of 18S rRNA from eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking J. D., Harris J. I. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from an extreme thermophile, Thermus aquaticus. Experientia Suppl. 1976;26:121–133. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7675-9_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. Structural comparison of two nontandemly repeated yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2596–2605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P., Thill G. P., Jackson K. A. The primary structures of two yeast enolase genes. Homology between the 5' noncoding flanking regions of yeast enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1385–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. M.T., Harris J. I. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase: Amino acid sequence of enzyme from baker's yeast. FEBS Lett. 1972 May 1;22(2):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. T., Iyer B., Schwarz R. J. Condensation of chromatin into chromosomes preserves an open configuration but alters the DNase I hypersensitive cleavage sites of the transcribed gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4565–4579. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebherz H. G. Ontogeny and regulation of fructose diphosphate aldolase isoenzymes in "red" and "white" skeletal muscles of the chick. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5976–5981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg N., Gilbert W. Primary structure of chicken muscle pyruvate kinase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3661–3665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moras D., Olsen K. W., Sabesan M. N., Buehner M., Ford G. C., Rossmann M. G. Studies of asymmetry in the three-dimensional structure of lobster D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9137–9162. doi: 10.2210/pdb1gpd/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak K., Wolny M., Banaś T. The complete amino acid sequence of human muscle glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 16;134(2):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80587-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]