Abstract
Like human gliomas, the rat 9L gliosarcoma secretes the immunosuppressive transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta). Using the 9L model, we tested our hypothesis that genetic modification of glioma cells to block TGF-beta expression may enhance their immunogenicity and make them more suitable for active tumor immunotherapy. Subcutaneous immunizations of tumor-bearing animals with 9L cells genetically modified to inhibit TGF-beta expression with an antisense plasmid vector resulted in a significantly higher number of animals surviving for 12 weeks (11/11, 100%) compared to immunizations with control vector-modified 9L cells (2/15, 13%) or 9L cells transduced with an interleukin 2 retroviral vector (3/10, 30%) (P < 0.001 for both comparisons). Histologic evaluation of implantation sites 12 weeks after treatment revealed no evidence of residual tumor. In vitro tumor cytotoxicity assays with lymph node effector cells revealed a 3- to 4-fold increase in lytic activity for the animals immunized with TGF-beta antisense-modified tumor cells compared to immunizations with control vector or interleukin 2 gene-modified tumor cells. These results indicate that inhibition of TGF-beta expression significantly enhances tumor-cell immunogenicity and supports future clinical evaluation of TGF-beta antisense gene therapy for TGF-beta-expressing tumors.
Full text
PDF

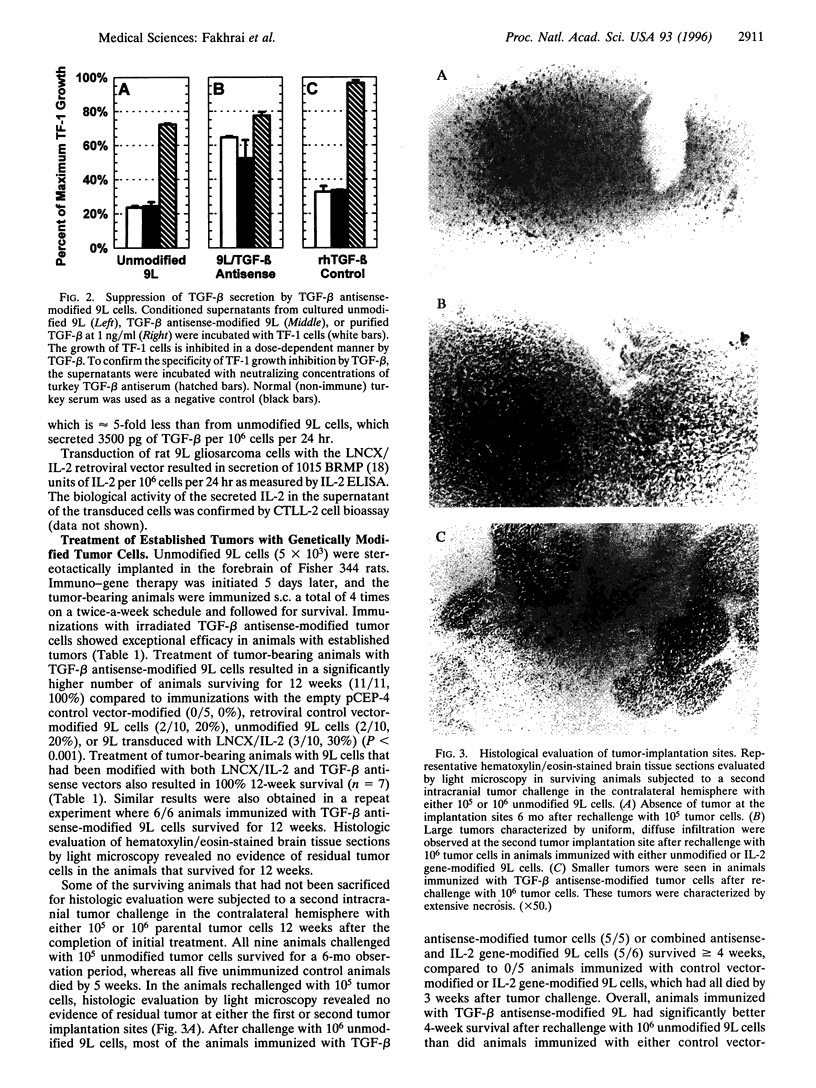
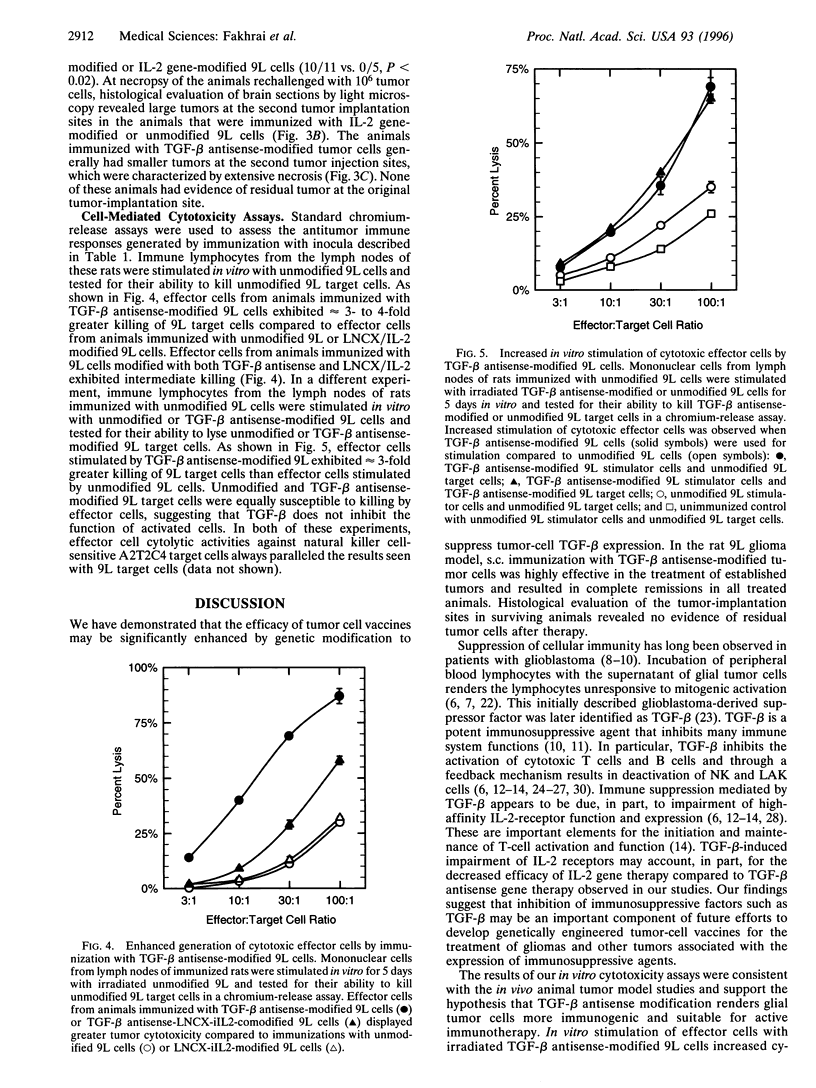


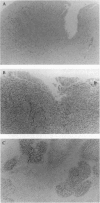
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alleva D. G., Burger C. J., Elgert K. D. Tumor-induced regulation of suppressor macrophage nitric oxide and TNF-alpha production. Role of tumor-derived IL-10, TGF-beta, and prostaglandin E2. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 15;153(4):1674–1686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreason G. L., Evans G. A. Introduction and expression of DNA molecules in eukaryotic cells by electroporation. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):650–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzano M. A., Rieman D., Prichett W., Bowen-Pope D. F., Greig R. Growth factor production by human colon carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2898–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer S., Strommer K., Frei K., Siepl C., de Tribolet N., Heid I., Fontana A. Immunosuppression and transforming growth factor-beta in glioblastoma. Preferential production of transforming growth factor-beta 2. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3222–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver K. W., Ram Z., Wallbridge S., Ishii H., Oldfield E. H., Blaese R. M. In vivo gene transfer with retroviral vector-producer cells for treatment of experimental brain tumors. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1550–1552. doi: 10.1126/science.1317968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillman R. O., Johnson D. E., Shawler D. L. Immune interferon modulation of in vitro murine anti-human T cell monoclonal antibody-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):728–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott L. H., Brooks W. H., Roszman T. L. Suppression of high affinity IL-2 receptors on mitogen activated lymphocytes by glioma-derived suppressor factor. J Neurooncol. 1992 Sep;14(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00170940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakhrai H., Shawler D. L., Gjerset R., Naviaux R. K., Koziol J., Royston I., Sobol R. E. Cytokine gene therapy with interleukin-2-transduced fibroblasts: effects of IL-2 dose on anti-tumor immunity. Hum Gene Ther. 1995 May;6(5):591–601. doi: 10.1089/hum.1995.6.5-591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Frei K., Bodmer S., Hofer E., Schreier M. H., Palladino M. A., Jr, Zinkernagel R. M. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits the generation of cytotoxic T cells in virus-infected mice. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3230–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Armour R., Baldwin J. H., Maldonado F., Spiess J., Holley R. W. Amino acid sequence of the BSC-1 cell growth inhibitor (polyergin) deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):79–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirte H. W., Clark D. A., O'Connell G., Rusthoven J., Mazurka J. Reversal of suppression of lymphokine-activated killer cells by transforming growth factor-beta in ovarian carcinoma ascitic fluid requires interleukin-2 combined with anti-CD3 antibody. Cell Immunol. 1992 Jun;142(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90281-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirte H., Clark D. A. Generation of lymphokine-activated killer cells in human ovarian carcinoma ascitic fluid: identification of transforming growth factor-beta as a suppressive factor. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1991;32(5):296–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01789047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber D., Philipp J., Fontana A. Protease inhibitors interfere with the transforming growth factor-beta-dependent but not the transforming growth factor-beta-independent pathway of tumor cell-mediated immunosuppression. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse C. A., Lillehei K. O., Mitchell D. H., Kleinschmidt-DeMasters B., Bellgrau D. Analysis of interleukin 2 and various effector cell populations in adoptive immunotherapy of 9L rat gliosarcoma: allogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes prevent tumor take. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9577–9581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse C. A., Schiltz P. M., Bellgrau D., Kong Q., Kleinschmidt-DeMasters B. K. Intracranial administrations of single or multiple source allogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes: chronic therapy for primary brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 1994;19(2):161–168. doi: 10.1007/BF01306458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppner M. C., Hamou M. F., Sawamura Y., Bodmer S., de Tribolet N. Inhibition of lymphocyte function by glioblastoma-derived transforming growth factor beta 2. J Neurosurg. 1989 Aug;71(2):211–217. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.2.0211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCallum J., Bartlett J. M., Thompson A. M., Keen J. C., Dixon J. M., Miller W. R. Expression of transforming growth factor beta mRNA isoforms in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1994 Jun;69(6):1006–1009. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaley M. S., Jr, Mettlin C., Natarajan N., Laws E. R., Jr, Peace B. B. National survey of patterns of care for brain-tumor patients. J Neurosurg. 1989 Dec;71(6):826–836. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.6.0826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. The TGF-beta family of growth and differentiation factors. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):437–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90443-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisa P., Halapi E., Pisa E. K., Gerdin E., Hising C., Bucht A., Gerdin B., Kiessling R. Selective expression of interleukin 10, interferon gamma, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in ovarian cancer biopsies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. A., Wadhwa M., Thorpe R., Mire-Sluis A. R. A novel, sensitive bioassay for transforming growth factor beta. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Aug 26;164(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90276-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Figari I. S., Espevik T., Palladino M. A., Jr Inhibition of cytotoxic T cell development by transforming growth factor beta and reversal by recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):991–998. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnicoff M., Sell C., Rubini M., Coppola D., Ambrose D., Baserga R., Rubin R. Rat glioblastoma cells expressing an antisense RNA to the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor are nontumorigenic and induce regression of wild-type tumors. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 15;54(8):2218–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi D., Romero P., Carrel S. The human melanoma antigen-encoding gene, MAGE-1, is expressed by other tumour cells of neuroectodermal origin such as glioblastomas and neuroblastomas. Int J Cancer. 1993 May 28;54(3):527–528. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook A. H., Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Burlington D. B., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Effects of transforming growth factor beta on the functions of natural killer cells: depressed cytolytic activity and blunting of interferon responsiveness. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3916–3920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszman T., Elliott L., Brooks W. Modulation of T-cell function by gliomas. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):370–374. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffini P. A., Rivoltini L., Silvani A., Boiardi A., Parmiani G. Factors, including transforming growth factor beta, released in the glioblastoma residual cavity, impair activity of adherent lymphokine-activated killer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1993 Jun;36(6):409–416. doi: 10.1007/BF01742258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura Y., De Tribolet N. Immunotherapy of brain tumors. J Neurosurg Sci. 1990 Jul-Dec;34(3-4):265–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura Y., Diserens A. C., de Tribolet N. In vitro prostaglandin E2 production by glioblastoma cells and its effect on interleukin-2 activation of oncolytic lymphocytes. J Neurooncol. 1990 Oct;9(2):125–130. doi: 10.1007/BF02427832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1169–1176. doi: 10.1126/science.3131876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Lowest dose interleukin-2 immunotherapy. Blood. 1993 Mar 15;81(6):1414–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., Assoian R. K. Transforming growth factor-beta: biological function and chemical structure. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):532–534. doi: 10.1126/science.3487831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tigges M. A., Casey L. S., Koshland M. E. Mechanism of interleukin-2 signaling: mediation of different outcomes by a single receptor and transduction pathway. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):781–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2492678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojan J., Blossey B. K., Johnson T. R., Rudin S. D., Tykocinski M., Ilan J., Ilan J. Loss of tumorigenicity of rat glioblastoma directed by episome-based antisense cDNA transcription of insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4874–4878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojan J., Johnson T. R., Rudin S. D., Ilan J., Tykocinski M. L., Ilan J. Treatment and prevention of rat glioblastoma by immunogenic C6 cells expressing antisense insulin-like growth factor I RNA. Science. 1993 Jan 1;259(5091):94–97. doi: 10.1126/science.8418502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truong L. D., Kadmon D., McCune B. K., Flanders K. C., Scardino P. T., Thompson T. C. Association of transforming growth factor-beta 1 with prostate cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Hum Pathol. 1993 Jan;24(1):4–9. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90055-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunawaki S., Sporn M., Ding A., Nathan C. Deactivation of macrophages by transforming growth factor-beta. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):260–262. doi: 10.1038/334260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrann M., Bodmer S., de Martin R., Siepl C., Hofer-Warbinek R., Frei K., Hofer E., Fontana A. T cell suppressor factor from human glioblastoma cells is a 12.5-kd protein closely related to transforming growth factor-beta. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1633–1636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]