Abstract
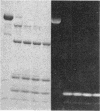
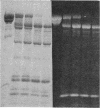
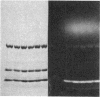
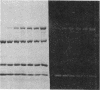
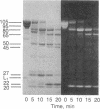
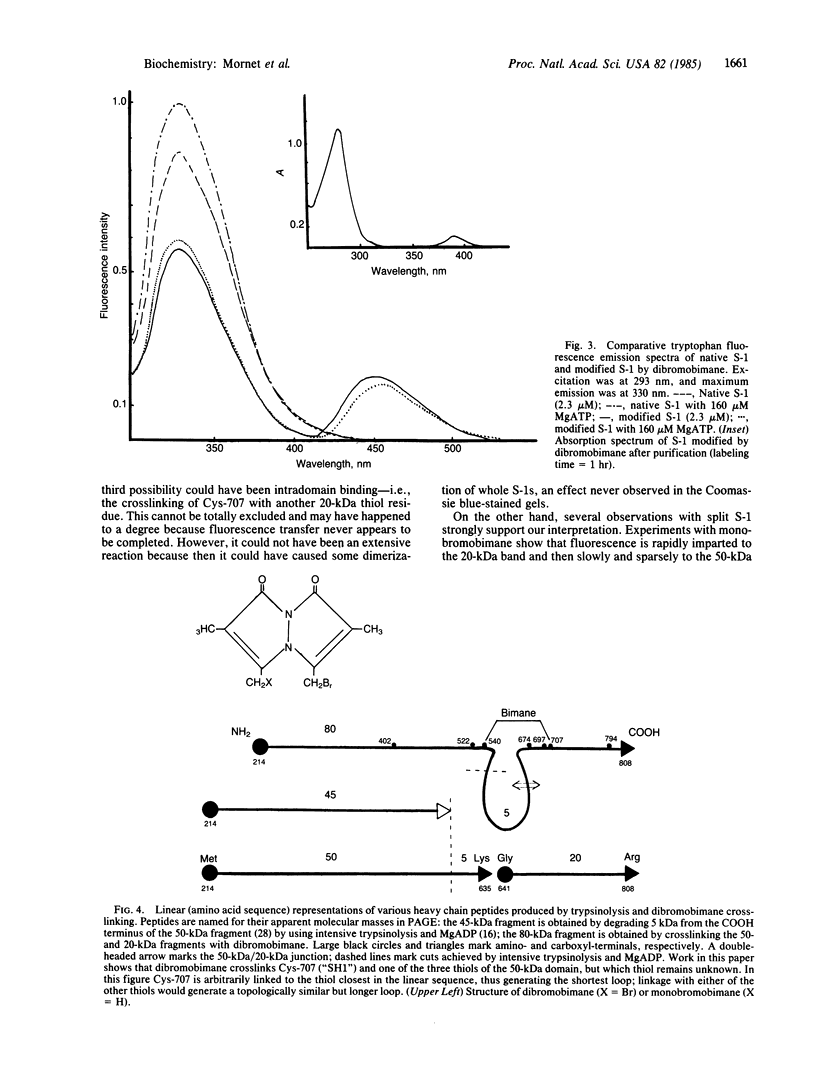
A bifunctional fluorescent alkylating agent, dibromobimane, has been used to stabilize a preexisting primary loop in myosin subfragment 1 (S-1). The crosslink achieved joins Cys-707 (called sulfhydryl group "SH1") of the 20-kDa domain (formerly called "20K" domain) with a thiol of the 50-kDa domain and seems to place the dibromobimane near the ATP-perturbable tryptophan.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applegate D., Reisler E. Protease-sensitive regions in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7109–7112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Balian G. Cleavage at Asn-Gly bonds with hydroxylamine. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:132–145. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botts J., Takashi R., Torgerson P., Hozumi T., Muhlrad A., Mornet D., Morales M. F. On the mechanism of energy transduction in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2060–2064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botts J., Ue K., Hozumi T., Samet J. Consequences of reacting the thiols of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5157–5163. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Wolf I., Tarcsafalvi A., Gergely J., Sréter F. A. Location of SH-1 and SH-2 in the heavy chain segment of heavy meromyosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):793–799. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Kielley W. W. Troponin-tropomyosin complex. Column chromatographic separation and activity of the three, active troponin components with and without tropomyosin present. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4742–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka T. Direct cross-linking of three domains in the myosin head. J Biochem. 1984 Jul;96(1):269–272. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi T. Structure and function of myosin subfragment 1 as studied by tryptic digestion. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):799–804. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh T., Imae S., Morita F. Binding of F-actin to a region between SH1 and SH2 groups of myosin subfragment-1 which may determine the high affinity of acto-subfragment-1 complex at rigor. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):447–454. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower N. S., Kosower E. M., Newton G. L., Ranney H. M. Bimane fluorescent labels: labeling of normal human red cells under physiological conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3382–3386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. P., Bertrand R., Audemard E., Kassab R., Walzthöny D., Wallimann T. The interaction of skeletal myosin subfragment 1 with the polyanion, heparin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 3;143(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structure of the actin-myosin interface. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):301–306. doi: 10.1038/292301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. The limited tryptic cleavage of chymotryptic S-1: an approach to the characterization of the actin site in myosin heads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Ue K., Morales M. F. Proteolysis and the domain organization of myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):736–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Ue K. Proteolysis and structure of skeletal muscle actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3680–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):653–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope B. J., Wagner P. D., Weeds A. G. Heterogeneity of myosin heavy chains in subfragment-1 isoenzymes rabbit skeletal myosin. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):470–473. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E. Sulfhydryl modification and labeling of myosin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):84–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S. A., Estes J. E. Detection of conformational changes in actin by proteolytic digestion: evidence for a new monomeric species. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 15;104(4):777–792. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Location of SH1 and SH2 along a heavy chain of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3281–3285. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. W., Elzinga M. The sequence of the NH2-terminal 204-residue fragment of the heavy chain of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13100–13110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Active site trapping of nucleotides by crosslinking two sulfhydryls in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Chemical modification of myosin by active-site trapping of metal-nucleotides with thiol crosslinking reagents. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]