Abstract
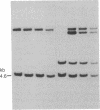
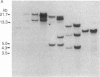
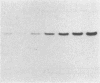
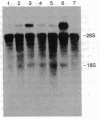
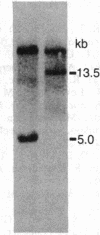
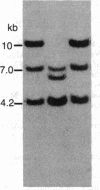
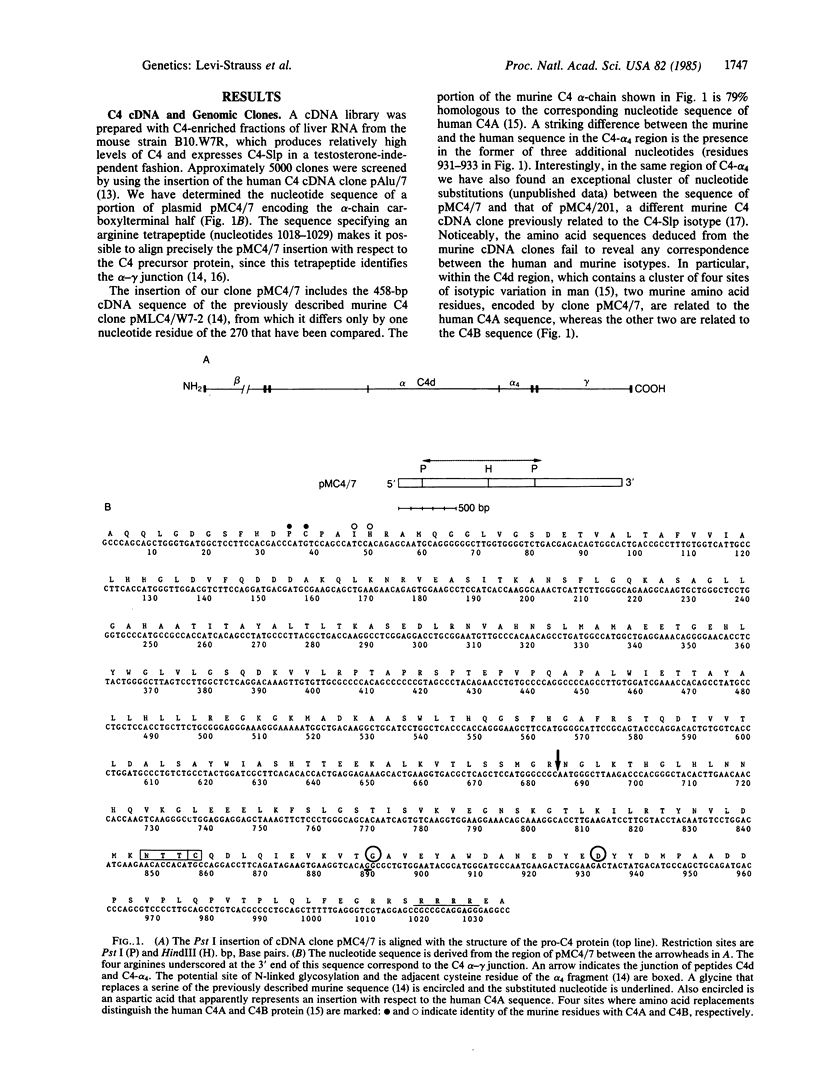
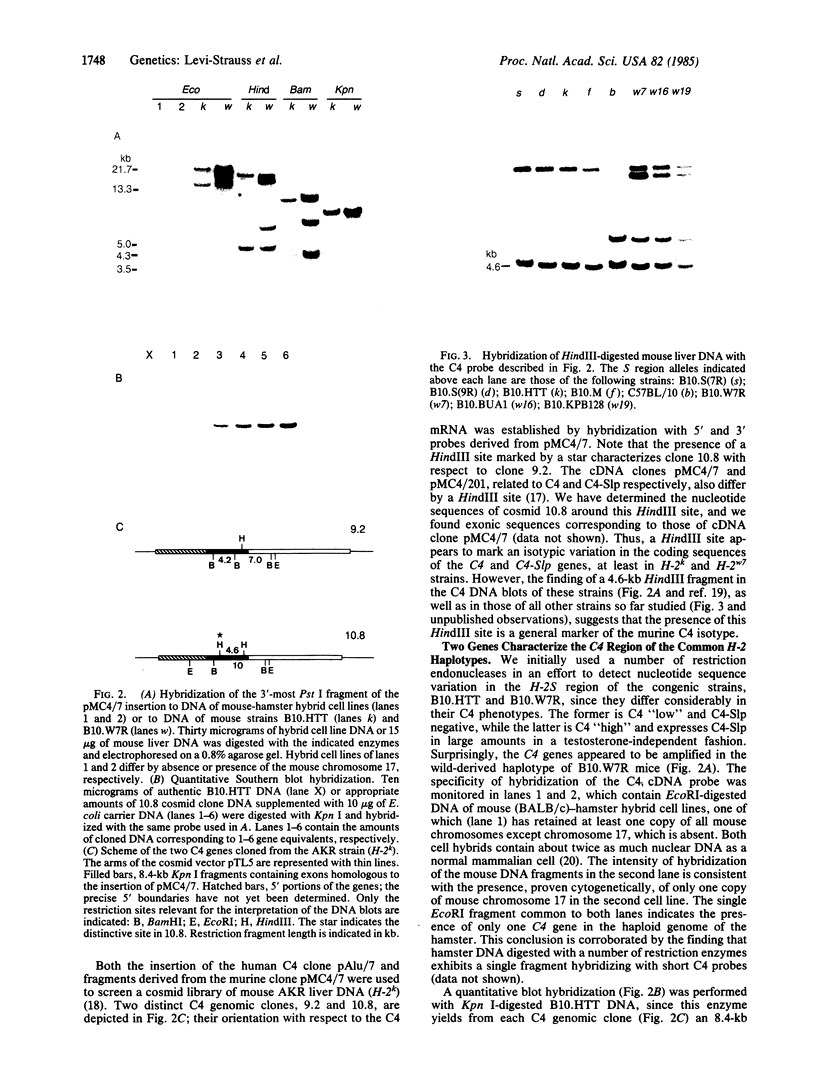
Mouse liver cDNA clones related to the C4 and C4-Slp isoforms of the fourth component of complement differ by few nucleotide changes within a region of substantial divergence from human C4. It is suggested that the mouse C4 gene duplication is an evolutionarily recent event with respect to the time of mammalian radiation. This conclusion is reinforced by the presence of a single C4 gene in the Syrian hamster. Most H-2 haplotypes, including those characterized by an undetectable C4-Slp protein, possess two C4 gene copies which, in contrast to the neighboring factor B, show a marked restriction site polymorphism. The genetic variation of this region is emphasized by the presence in the mouse of a rare "polymorphism" for C4 gene number. Multiple C4-related gene copies characterize those exceptional wild-derived H-2 haplotypes, H-2w7, H-2w16, and H-2w19, that determine the expression of the C4-Slp protein in female animals.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J. P., Karp D. R., Seeskin E. P., Killion C. C., Rosa P. A., Newell S. L., Shreffler D. C. H-2 S region determined polymorphic variants of the C4, Slp, C2, and B complement proteins: a compilation. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(6):617–623. doi: 10.1007/BF00372032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter-Suermann D., Krönke M., Brade V., Hadding U. Inherited polymorphism of guinea pig factor B and C4: evidence for genetic linkage between the C4 and Bf loci. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1822–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. J., Shreffler D. C. Female expression of the H-2-linked sex-limited protein (Slp) due to non-H-2 genes. Immunogenetics. 1980;10(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01561549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. Cloning of a human complement component C4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):264–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curman B., Ostberg L., Sandberg L., Malmheden-Eriksson I., Stålenheim G., Rask L., Peterson P. A. H-2 linked Ss protein is C4 component of complement. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):243–245. doi: 10.1038/258243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V. Murine sex-limited protein (Slp) antigenic sites in human complement component C4. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(4):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00372466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Shreffler D. C. Characterization of a constitutive variant of the murine serum protein allotype, Slp. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1507–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp D. R., Atkinson J. P., Shreffler D. C. Genetic variation in glycosylation of the fourth component of murine complement. Association with hemolytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7330–7335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Grennan D., Martin A., Demant P. Identification of Ss protein as murine C4. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):242–243. doi: 10.1038/258242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meo T., Krasteff T., Shreffler D. C. Immunochemical characterization of murine H-2 controlled Ss (serum substance) protein through identification of its human homologue as the fourth component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson J., Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V. cis-Interacting genes in the S region of the murine major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):306–308. doi: 10.1038/289306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell S. L., Shreffler D. C., Atkinson J. P. Biosynthesis of C4 by mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Characterization of an in vitro culture system and comparison of C4 synthesis by "low" vs "high" C4 strains. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Shreffler D. C., Sepich D. S., Lilly S. P. cDNA clone spanning the alpha-gamma subunit junction in the precursor of the murine fourth complement component (C4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5061–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Holm I., Rougeon F. The mouse Rn locus: S allele of the renin regulator gene results from a single structural gene duplication. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Mollenhauer E., Démant P., Rittner C. A molecular basis for the two locus model of human complement component C4. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):854–856. doi: 10.1038/298854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackstein R., Colten H. R., Woods D. E. Phylogenetic conservation of a class III major histocompatibility complex antigen, factor B. Isolation and nucleotide sequencing of mouse factor B cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14693–14697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C., Atkinson J. P., Chan A. C., Karp D. R., Killion C. C., Ogata R. T., Rosa P. A. The C4 and Slp genes of the complement region of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):395–403. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Malissen M., Hood L., Orn A., Maki R. A., Dastoornikoo G. R., Stephan D., Gibb E., Romaniuk R. Tracts of high or low sequence divergence in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2995–3003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02246.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szpirer C., Szpirer J. A mouse hepatoma cell line which secretes several serum proteins including albumin and alpha-foetoprotein. Differentiation. 1975 Oct 16;4(2):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1975.tb01446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymura J. M., Wabl M. R., Klein J. Mouse mitochondrial superoxide dismutase locus is on chromosome 17. Immunogenetics. 1981;14(3-4):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00342192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Lévi-Strauss M., Duponchel C., Meo T. Sequence heterogeneity of murine complementary DNA clones related to the C4 and C4-Slp isoforms of the fourth complement component. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):389–394. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Colten H. R. Use of a cDNA clone for the fourth component of human complement (C4) for analysis of a genetic deficiency of C4 in guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5387–5391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]