Abstract
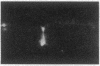
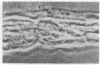
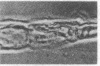
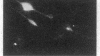
We describe the properties of a monoclonal antibody against the Na+ channel. The antibody, 72.38, competitively inhibited (Ki = 1.5 X 10(-9) M) the binding of an 125I-labeled toxin from the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus (125I-TiTX gamma) to Na+ channels of rat brain membranes. No significant inhibition of binding of a number of other Na+ channel toxins was observed. The inhibition of 125I-TiTX gamma binding also was observed with the solubilized Na+ channel from rat brain membranes (Ki = 2 X 10(-9) M). Antibody 72.38 antagonized 125I-TiTX gamma binding to Na+ channels from different animal species (fish, avian, and mammalian) and from different tissues (electroplax, brain, heart, and muscle). Moreover, 72.38 has been used for immunofluorescence labeling of Na+ channels in rat sciatic nodes of Ranvier and cultured dorsal root ganglion cells. Electrophysiological experiments on rat muscle cells fully confirmed the similarity between TiTX gamma and 72.38 seen in binding experiments. Both produce slow oscillations of the membrane potential accompanied by bursts of action potentials which are due to a selective action on the Na+ channel. TiTX gamma and 72.38 are without effect on the ion selectivity of the Na+ channel, but they both drastically change the voltage-dependence of activation and inactivation of the Na+ channel.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelides K. J., Nutter T. J. Mapping the molecular structure of the voltage-dependent sodium channel. Distances between the tetrodotoxin and Leiurus quinquestriatus quinquestriatus scorpion toxin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11958–11967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Protein components of the purified sodium channel from rat skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Neurochem. 1983 May;40(5):1377–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb13580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barhanin J., Giglio J. R., Léopold P., Schmid A., Sampaio S. V., Lazdunski M. Tityus serrulatus venom contains two classes of toxins. Tityus gamma toxin is a new tool with a very high affinity for studying the Na+ channel. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12553–12558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barhanin J., Pauron D., Lombet A., Norman R. I., Vijverberg H. P., Giglio J. R., Lazdunski M. Electrophysiological characterization, solubilization and purification of the Tityus gamma toxin receptor associated with the gating component of the Na+ channel from rat brain. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):915–920. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01521.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicheportiche R., Balerna M., Lombet A., Romey G., Lazdunski M. Synthesis of new, highly radioactive tetrodotoxin derivatives and their binding properties to the sodium channel. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Mar;104(2):617–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04466.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Levinson S. R. Immunocytochemical localization of sodium channel distributions in the excitable membranes of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6707–6711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vijverberg H. P., Romey G., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. Different functional states of tetrodotoxin sensitive and tetrodotoxin resistant Na+ channels occur during the in vitro development of rat skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Oct;402(2):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00583323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Boheim G., Barhanin J., Pauron D., Lazdunski M. Reconstitution of highly purified saxitoxin-sensitive Na+-channels into planar lipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):509–515. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Catterall W. A. The sodium channel from rat brain. Purification and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1667–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Schmid H., Romey G., Duval D., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. The Ca2+-dependent slow K+ conductance in cultured rat muscle cells: characterization with apamin. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1039–1042. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaimovich E., Ildefonse M., Barhanin J., Rougier O., Lazdunski M. Centruroides toxin, a selective blocker of surface Na+ channels in skeletal muscle: voltage-clamp analysis and biochemical characterization of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombet A., Lazdunski M. Characterization, solubilization, affinity labeling and purification of the cardiac Na+ channel using Tityus toxin gamma. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):651–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombet A., Renaud J. F., Chicheportiche R., Lazdunski M. A cardiac tetrodotoxin binding component: biochemical identification, characterization, and properties. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1279–1285. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiri H., Zeitoun I., Grunhagen H. H., Lev-Ram V., Eshhar Z., Schlessinger J. Monoclonal antibodies associated with sodium channel block nerve impulse and stain nodes of Ranvier. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 17;310(1):168–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Rubly N., Watt D. D. Effect of toxins isolated from the venom of the scorpion Centruroides sculpturatus on the Na currents of the node of Ranvier. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Mar;393(1):56–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00582392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Agnew W. S., Levinson S. R. Principal glycopeptide of the tetrodotoxin/saxitoxin binding protein from Electrophorus electricus: isolation and partial chemical and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):462–470. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Fritz L. C., Raftery M. A., Brockes J. P. Isolation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against the saxitoxin-binding component from the electric organ of the eel Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1673–1677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):813–889. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman R. I., Schmid A., Lombet A., Barhanin J., Lazdunski M. Purification of binding protein for Tityus gamma toxin identified with the gating component of the voltage-sensitive Na+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4164–4168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Fosset M., Samuel D., Ailhaud G. Chick embryo plasma membrane from cardiac muscle and cultured heart cells: isolation procedure and absence of fatty acid-activating enzymes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1977 Feb;9(2):161–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(77)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio S. V., Laure C. J., Giglio J. R. Isolation and characterization of toxic proteins from the venom of the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus. Toxicon. 1983;21(2):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(83)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter J. C., Eddy B., Hall L. M., Fraser C. M. Monoclonal antibodies detect the conservation of muscarinic cholinergic receptor structure from Drosophila to human brain and detect possible structural homology with alpha 1-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):272–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijverberg H. P., Pauron D., Lazdunski M. The effect of Tityus serrulatus scorpion toxin gamma on Na channels in neuroblastoma cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jul;401(3):297–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00582600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Balerna M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Binding of sea anemone toxin to receptor sites associated with gating system of sodium channel in synaptic nerve endings in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1646–1650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]