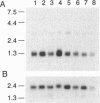
Abstract
Hsubc9, a human gene encoding a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, has been cloned. The 18-kDa HsUbc9 protein is homologous to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes Hus5 of Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Ubc9 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Hsubc9 gene complements a ubc9 mutation of S. cerevisiae. It has been mapped to chromosome 16p13.3 and is expressed in many human tissues, with the highest levels in testis and thymus. According to the Ga14 two-hybrid system analysis, HsUbc9 protein interacts with human recombination protein Rad51. A mouse homolog, Mmubc9, encodes an amino acid sequence that is identical to the human protein. In mouse spermatocytes, MmUbc9 protein, like Rad51 protein, localizes in synaptonemal complexes, which suggests that Ubc9 protein plays a regulatory role in meiosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley T., Plug A. W., Xu J., Solari A. J., Reddy G., Golub E. I., Ward D. C. Dynamic changes in Rad51 distribution on chromatin during meiosis in male and female vertebrates. Chromosoma. 1995 Oct;104(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00352222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly V., Lamb J., Sung P., Prakash S., Prakash L. Specific complex formation between yeast RAD6 and RAD18 proteins: a potential mechanism for targeting RAD6 ubiquitin-conjugating activity to DNA damage sites. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):811–820. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel P., Chien C. T., Sternglanz R., Fields S. Elimination of false positives that arise in using the two-hybrid system. Biotechniques. 1993 Jun;14(6):920–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson F. E., Stasiak A., West S. C. Purification and characterization of the human Rad51 protein, an analogue of E. coli RecA. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5764–5771. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. K. RecA homologs Dmc1 and Rad51 interact to form multiple nuclear complexes prior to meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1081–1092. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:643–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Johnson P., Sommer T., Jentsch S., Hochstrasser M. Multiple ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes participate in the in vivo degradation of the yeast MAT alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90426-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W., Milne G. T., Weaver D. T. Homotypic and heterotypic protein associations control Rad51 function in double-strand break repair. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2552–2562. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser M., Pisetsky D., Warren R., McCarty G., Moses M. A new method for the cytological analysis of autoantibody specificities using whole-mount, surface-spread meiotic nuclei. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90494-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feilotter H. E., Hannon G. J., Ruddell C. J., Beach D. Construction of an improved host strain for two hybrid screening. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1502–1503. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C. DNA double-strand breaks and the RAD50-RAD57 genes in Saccharomyces. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Apr;4(2):73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Golub E. I., Reddy G., Radding C. M., Ward D. C. Nuclear foci of mammalian Rad51 recombination protein in somatic cells after DNA damage and its localization in synaptonemal complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2298–2302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. L., Firmenich A. A., Berg P. Complex formation in yeast double-strand break repair: participation of Rad51, Rad52, Rad55, and Rad57 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer W. D. The search for the right partner: homologous pairing and DNA strand exchange proteins in eukaryotes. Experientia. 1994 Mar 15;50(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF01924005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M. Ubiquitin, proteasomes, and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi K., Li B., Bartel P., Fields S. Use of the two-hybrid system to identify the domain of p53 involved in oligomerization. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1693–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennissen H. P. Ubiquitin and the enigma of intracellular protein degradation. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jul 1;231(1):1–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. The ubiquitin-conjugation system. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:179–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. D., Symington L. S. Functional differences and interactions among the putative RecA homologs Rad51, Rad55, and Rad57. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):4843–4850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.9.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B., Fields S. Identification of mutations in p53 that affect its binding to SV40 large T antigen by using the yeast two-hybrid system. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):957–963. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Ward D. C. Oligonucleotide probes for the analysis of specific repetitive DNA sequences by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Oct;1(7):535–539. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne G. T., Weaver D. T. Dominant negative alleles of RAD52 reveal a DNA repair/recombination complex including Rad51 and Rad52. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1755–1765. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. Cyclin ubiquitination: the destructive end of mitosis. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Yu X., Shinohara A., Egelman E. H. Similarity of the yeast RAD51 filament to the bacterial RecA filament. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1896–1899. doi: 10.1126/science.8456314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried T., Baldini A., Rand T. C., Ward D. C. Simultaneous visualization of seven different DNA probes by in situ hybridization using combinatorial fluorescence and digital imaging microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1388–1392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekelsky J. J., Hawley R. S. The bond between sisters. Cell. 1995 Oct 20;83(2):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Futcher B., Jentsch S. Role of a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in degradation of S- and M-phase cyclins. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):78–81. doi: 10.1038/373078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Ogawa T. Rad51 protein involved in repair and recombination in S. cerevisiae is a RecA-like protein. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90447-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasawa M., Shinohara A., Hotta Y., Ogawa H., Ogawa T. Localization of RecA-like recombination proteins on chromosomes of the lily at various meiotic stages. Genes Dev. 1995 Apr 15;9(8):925–934. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.8.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon H. J., Carbon J. Genetic and biochemical interactions between an essential kinetochore protein, Cbf2p/Ndc10p, and the CDC34 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):4835–4842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.9.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Khodairy F., Enoch T., Hagan I. M., Carr A. M. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe hus5 gene encodes a ubiquitin conjugating enzyme required for normal mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1995 Feb;108(Pt 2):475–486. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]