Abstract
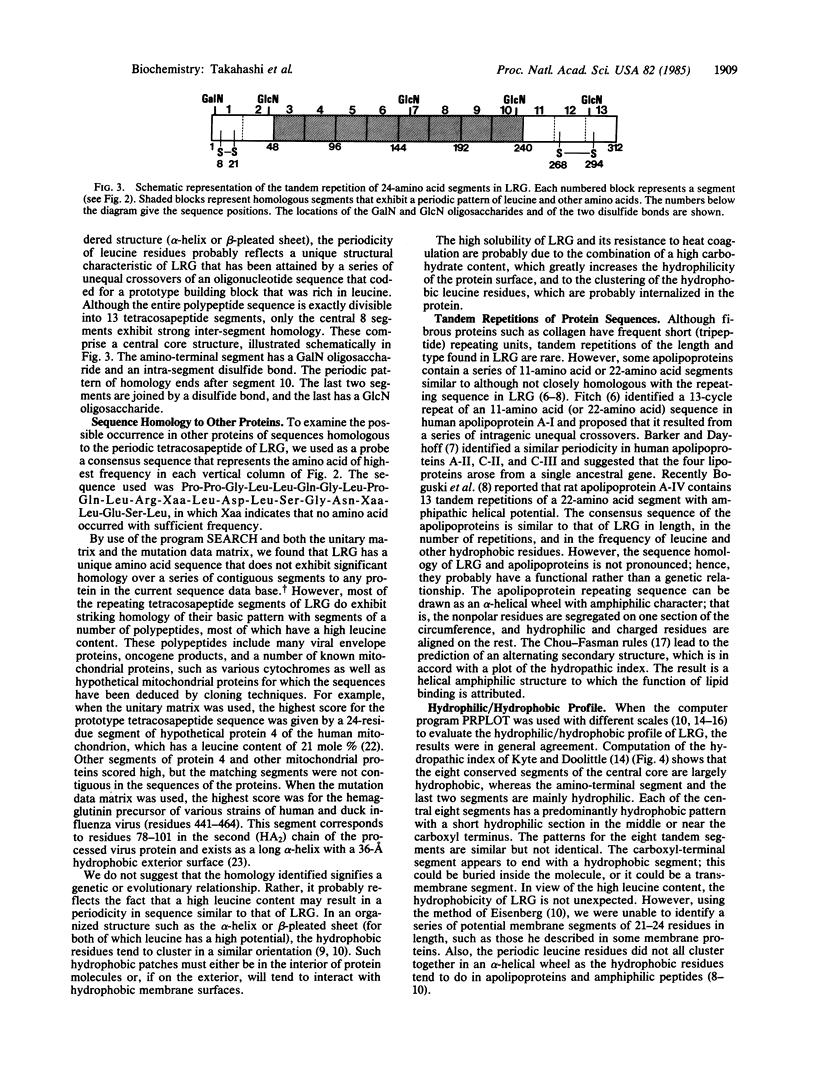
The complete primary structure of the 3.1S leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein (LRG) present in human plasma has been determined. This protein (Mr approximately 45,000) consists of a single polypeptide chain with one galactosamine and four glucosamine oligosaccharides attached. The polypeptide has two intrachain disulfide bonds and contains 312 amino acid residues of which 66 are leucine. The amino acid sequence can be exactly divided into 13 segments of 24 residues each, eight of which exhibit a periodic pattern in the occurrence of leucine, proline, and asparagine. The consensus sequence for the repeating tetracosapeptide unit is Pro-Xaa-Xaa-Leu-Leu-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-X aa-Xaa-Leu-Xaa-Xaa-Leu-Xaa-Leu-Xaa-Xaa-Asn-Xaa-Leu-Xaa-Xaa-Leu. This periodicity suggests that the unique structure of LRG arose from a series of unequal crossovers of a precursor oligonucleotide sequence that encoded a building block rich in leucine. Overall, the amino acid sequence of LRG is not significantly homologous to the continuous sequence of any protein in the current data base. However, the consensus tetracosapeptide sequence shows strong homology to segments of many mitochondrial proteins, viral envelope proteins, and oncogene proteins that have a high leucine content and transmembrane domains. Tandem repetition of similar segments also occurs in apolipoproteins that have amphipathic helical potential. Prediction of the secondary structure by the Chou-Fasman rules and calculation of the hydrophilic/hydrophobic profile by several methods confirm the tandem repetition of largely hydrophobic structural units; these begin with a beta-turn that leads into an organized structure with alpha-helical or beta-sheet potential. These structural characteristics and the homology to mitochondrial proteins and apolipoproteins suggest that LRG is a membrane-derived or membrane-associated protein containing a series of domains capable of bipolar surface orientation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Rao J. K., Hargrave P. A. Structural prediction of membrane-bound proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., Dayhoff M. O. Evolution of lipoproteins deduced from protein sequence data. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1977;57(4):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(77)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., Elshourbagy N., Taylor J. M., Gordon J. I. Rat apolipoprotein A-IV contains 13 tandem repetitions of a 22-amino acid segment with amphipathic helical potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. Phylogenies constrained by the crossover process as illustrated by human hemoglobins and a thirteen-cycle, eleven-amino-acid repeat in human apolipoprotein A-I. Genetics. 1977 Jul;86(3):623–644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt H., Baudner S. Isolierung und Charakterisierung eines bisher unbekannten leucinreichen 3.1S-alpha2-Glykoproteins aus Humanserum. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Jun;358(6):639–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis A. S. Cleavage at aspartic acid. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:324–332. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Secondary structures of proteins and peptides in amphiphilic environments. (A review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1137–1143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma beta 2-glycoprotein I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortel T. L., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Structural model of human ceruloplasmin based on internal triplication, hydrophilic/hydrophobic character, and secondary structure of domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of human hemopexin, the heme-binding protein of serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):73–77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Structure of human hemopexin: O-glycosyl and N-glycosyl sites and unusual clustering of tryptophan residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2021–2025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R., Andersson L., Cullis P. M., Southgate C. C. Affinities of amino acid side chains for solvent water. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):849–855. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



