Abstract
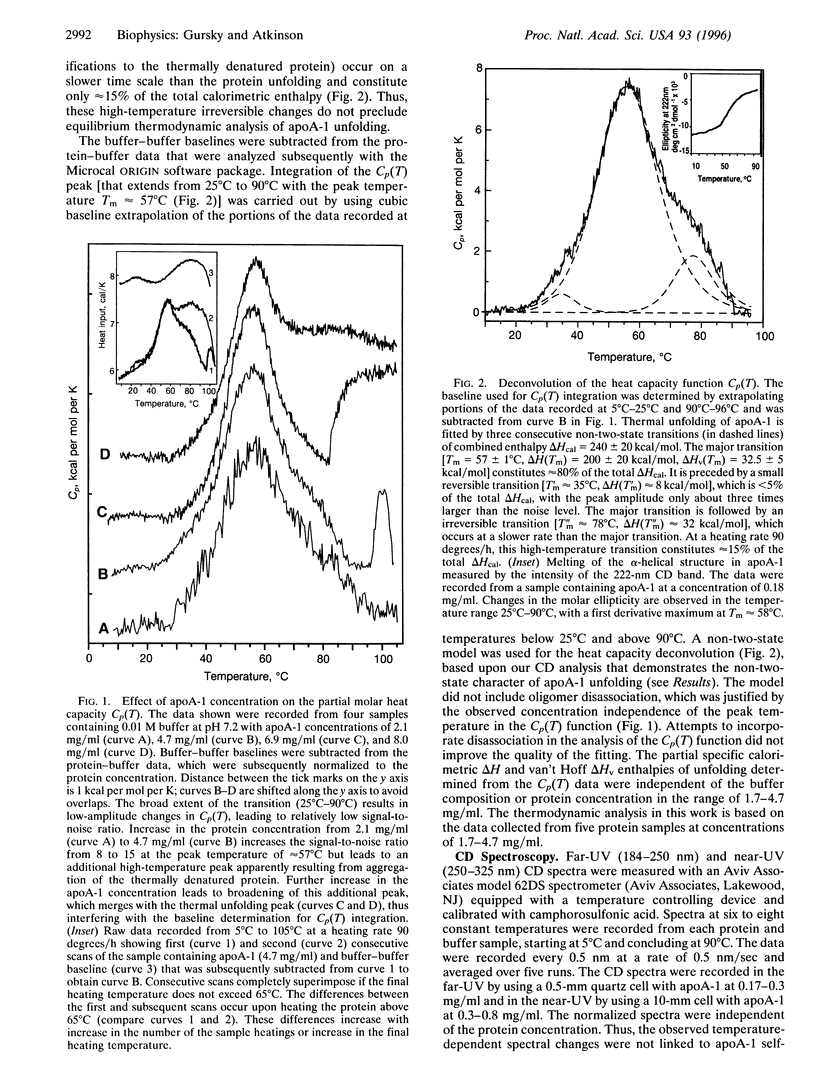
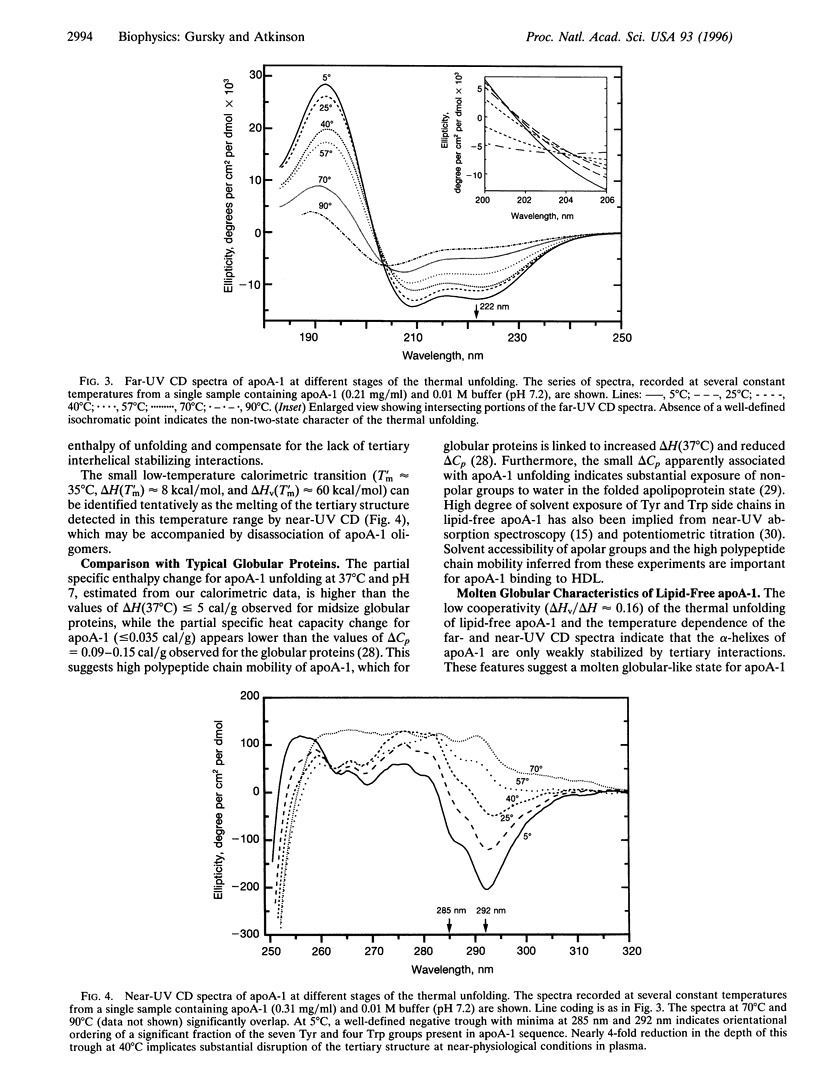
Apolipoprotein A-1 (apoA-1) in complex with high-density lipoprotein is critically involved in the transport and metabolism of cholesterol and in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. We reexamined the thermal unfolding of lipid-free apoA-1 in low-salt solution at pH approximately 7, by using differential scanning calorimetry and circular dichroism. At protein concentrations <5 mg/ml, thermal unfolding of apoA-1 is resolved as an extended peak (25 degrees C-90 degrees C) that can be largely accounted for by a single reversible non-two-state transition with midpoint Tm 57 +/- 1 degree C, calorimetric enthalpy deltaH(Tm)= 200 +/- 20 kcal/mol (1 kcal = 4.18 kJ), van't Hoff enthalpy deltaHv(Tm) approximately 32.5 kcal/mol, and cooperativity deltaHv(Tm)/deltaH(Tm) approximately 0.16. The enthalpy deltaH(Tm) can be accounted for by melting of the alpha-helical structure that is inferred by CD to constitute approximately 60% of apoA-1 amino acids. Farand near-UV CD spectra reveal noncoincident melting of the secondary and tertiary structural elements and indicate a well-defined secondary structure but a largely melted tertiary structure for apoA-1 at approximately 37 degrees C and pH 7. This suggests a molten globular-like state for lipid-free apoA-1 under near-physiological conditions. Our results suggest that in vivo lipid binding by apoA-1 may be mediated via the molten globular apolipoprotein state in plasma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson D., Small D. M. Recombinant lipoproteins: implications for structure and assembly of native lipoproteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:403–456. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbeau D. L., Jonas A., Teng T., Scanu A. M. Asymmetry of apolipoprotein A-I in solution as assessed from ultracentrifugal, viscometric, and fluorescence polarization studies. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):362–369. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiter D. R., Kanost M. R., Benning M. M., Wesenberg G., Law J. H., Wells M. A., Rayment I., Holden H. M. Molecular structure of an apolipoprotein determined at 2.5-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 22;30(3):603–608. doi: 10.1021/bi00217a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Fairwell T., LaRue A., Ronan R., Houser A., Bronzert T. J. The amino acid sequence of human APOA-I, an apolipoprotein isolated from high density lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelli W. P., Doyle J. T., Gordon T., Hames C. G., Hjortland M. C., Hulley S. B., Kagan A., Zukel W. J. HDL cholesterol and other lipids in coronary heart disease. The cooperative lipoprotein phenotyping study. Circulation. 1977 May;55(5):767–772. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.55.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Immunochemical heterogeneity of human plasma high density lipoproteins. Identification with apolipoprotein A-I- and A-II-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2982–2993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. M., Benedek G. B., Carey M. C. Self-association of human apolipoproteins A-I and A-II and interactions of apolipoprotein A-I with bile salts: quasi-elastic light scattering studies. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8116–8125. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Evidence for a lipoprotein carrier in human plasma catalyzing sterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts and its relationship to lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3911–3914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire E. Thermodynamics of partly folded intermediates in proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:141–165. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.24.060195.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne J., Brewer B., Jr, Edelhoch H. The molecular properties of ApoA-I from human high density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2411–2416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handel T. M., Williams S. A., DeGrado W. F. Metal ion-dependent modulation of the dynamics of a designed protein. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):879–885. doi: 10.1126/science.8346440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynie D. T., Freire E. Structural energetics of the molten globule state. Proteins. 1993 Jun;16(2):115–140. doi: 10.1002/prot.340160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Wald J. H., Toohill K. L., Krul E. S., Kézdy K. E. Apolipoprotein A-I structure and lipid properties in homogeneous, reconstituted spherical and discoidal high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22123–22129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Isolation and characterization of the human apolipoprotein A-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. H., Tanimura M., Luo C. C., Datta S., Chan L. The apolipoprotein multigene family: biosynthesis, structure, structure-function relationships, and evolution. J Lipid Res. 1988 Mar;29(3):245–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Repeated helical pattern in apolipoprotein-A-I. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):465–466. doi: 10.1038/267465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte R. T., Atkinson D. Conformational analysis of apolipoprotein A-I and E-3 based on primary sequence and circular dichroism. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1221–1239. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81698-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Khechinashvili N. N. A thermodynamic approach to the problem of stabilization of globular protein structure: a calorimetric study. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 5;86(3):665–684. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L., Makhatadze G. I. Heat capacity of proteins. II. Partial molar heat capacity of the unfolded polypeptide chain of proteins: protein unfolding effects. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 20;213(2):385–391. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L. Stability of proteins. Proteins which do not present a single cooperative system. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:1–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalov P. L. Stability of proteins: small globular proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:167–241. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A. Conformational stability of the polypeptide components of human high density serum lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):6013–6015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosseneu M., Soetewey F., Lievens M. J., Vercaemst R., Peeters H. Ionization behaviour of native apolipoproteins and of their complexes with lecithin. 1. Calorimetric and potentiometric titration of the native apoA-I protein and of the apoA-I protein-dimyristoyl lecithin complex. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep 15;79(1):251–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz J. M., Marqusee S., Baldwin R. L., York E. J., Stewart J. M., Santoro M., Bolen D. W. Calorimetric determination of the enthalpy change for the alpha-helix to coil transition of an alanine peptide in water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2854–2858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jones M. K., De Loof H., Brouillette C. G., Venkatachalapathi Y. V., Anantharamaiah G. M. The amphipathic helix in the exchangeable apolipoproteins: a review of secondary structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1992 Feb;33(2):141–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks D. L., Lund-Katz S., Phillips M. C. The charge and structural stability of apolipoprotein A-I in discoidal and spherical recombinant high density lipoprotein particles. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25839–25847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Shipley G. G., Small D. M. Conformational and thermodynamic properties of apo A-1 of human plasma high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3749–3755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Small D. M., Shipley G. G., Lees R. S. Apoprotein stability and lipid-protein interactions in human plasma high density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4940–4942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetterau J. R., Jonas A. Effect of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicle curvature on the reaction with human apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10961–10966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wardell M. R., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Agard D. A. Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1817–1822. doi: 10.1126/science.2063194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



