Abstract
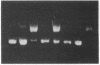
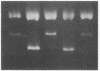
We isolated mutant strains of the facultative anaerobe Salmonella typhimurium that grow either aerobically or anaerobically. Strict anaerobic mutants contained a defective DNA topoisomerase I gene (topI), while strict aerobic mutants contained a defective DNA gyrase subunit A gene (gyrA, also nalA). Topoisomerase I activity was detected in cell-free extracts of strict aerobic mutants but not of strict anaerobic mutant strains, whereas gyrase activity was detected in extracts of strict anaerobic mutants but not of strict aerobic mutants. Furthermore, extracts of wild-type cells, cultured under vigorous aerobic condition, contain topoisomerase I activity but no significant gyrase activity. In contrast, the extracts of anaerobically cultured wild-type cells contain gyrase activity but no significant topoisomerase I activity. Sucrose gradient centrifugation with ethidium bromide showed that chromosomal DNA in strict aerobic mutants and aerobically grown wild-type cells was relaxed, while the chromosomal DNA of strict anaerobic mutants and anaerobically grown wild-type cells was more supercoiled. Aerobic cultures of wild type and strict aerobic mutants produced both superoxide dismutase and catalase, whereas anaerobic cultures of wild type and strict anaerobic mutants did not. These results lead us to conclude that activity of topoisomerase I, associated with relaxation of chromosomal DNA, is necessary for expression of genes required for aerobic growth, whereas activity of gyrase, associated with supercoiling of chromosomal DNA, is necessary for expression of genes required for anaerobic growth.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boling M., Adler H., Masker W. Restoration of viability to an Escherichia coli mutant deficient in the 5'----3' exonuclease of DNA polymerase I. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):706–710. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.706-710.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Sternglanz R., Reynolds A. E., Wright A. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants have compensatory mutations in DNA gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Snyder M. Superhelical Escherichia coli DNA: relaxation by coumermycin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 5;120(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E., Margolin P. Suppression of promoter mutations by the pleiotropic supx mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;117(2):91–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00267607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. M. DNA supercoiling and gene expression. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):686–687. doi: 10.1038/307686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:147–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBLITH S. A., PROCTOR B. E. Photometric determination of catalase activity. J Biol Chem. 1950 Dec;187(2):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Menzel R., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Friedman D. I. Regulation of DNA supercoiling in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):763–767. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A. C., Stocker B. A. Genetics of sensitivity of Salmonella species to colicin M and bacteriophages T5, T1, and ES18. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1214–1223. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1214-1223.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. T., Wimpenny J. W., Hughes D. E., Mossman M. R. Regulation of metabolism in facultative bacteria. I. Structural and functional changes in Escherichia coli associated with shifts between the aerobic and anaerobic states. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory E. M., Fridovich I. Induction of superoxide dismutase by molecular oxygen. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):543–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.543-548.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Kanegasaki S. Smooth specific phage adsorption: endorhamnosidase activity of tail parts of P22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Escherichia coli mutants thermosensitive for deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase subunit A: effects on deoxyribonucleic acid replication, transcription, and bacteriophage growth. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):424–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.424-435.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo T. T., Stocker B. A. ES18, a general transducing phage for smooth and nonsmooth Salmonella typhimurium. Virology. 1970 Nov;42(3):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S., Marklund G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):469–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Gellert M. Regulation of the genes for E. coli DNA gyrase: homeostatic control of DNA supercoiling. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otter R., Cozzarelli N. R. Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:171–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbye K. M., Margolin P. Role of the supX gene in ultraviolet light-induced mutagenesis in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):170–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.170-178.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss G. J., Manes S. H., Drlica K. Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I mutants: increased supercoiling is corrected by mutations near gyrase genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90402-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, Edition VI. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):410–453. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.410-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanzey B. Modulation of gene expression by drugs affecting deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.40-47.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann J. P., Jones D. T., Woods D. R. UV light induction of proteins in Bacteroides fragilis under anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):44–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.44-47.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. R., Pruss G. J., Manes S. H., Burg L., Drlica K. DNA supercoiling in gyrase mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):397–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.397-403.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternglanz R., DiNardo S., Voelkel K. A., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y., Becherer K., Zumstein L., Wang J. C. Mutations in the gene coding for Escherichia coli DNA topoisomerase I affect transcription and transposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2747–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Burgi E. On the structure of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):127–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D., LEDERBERG J. Genetic exchange in Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1952 Nov;64(5):679–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.5.679-699.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]