Abstract
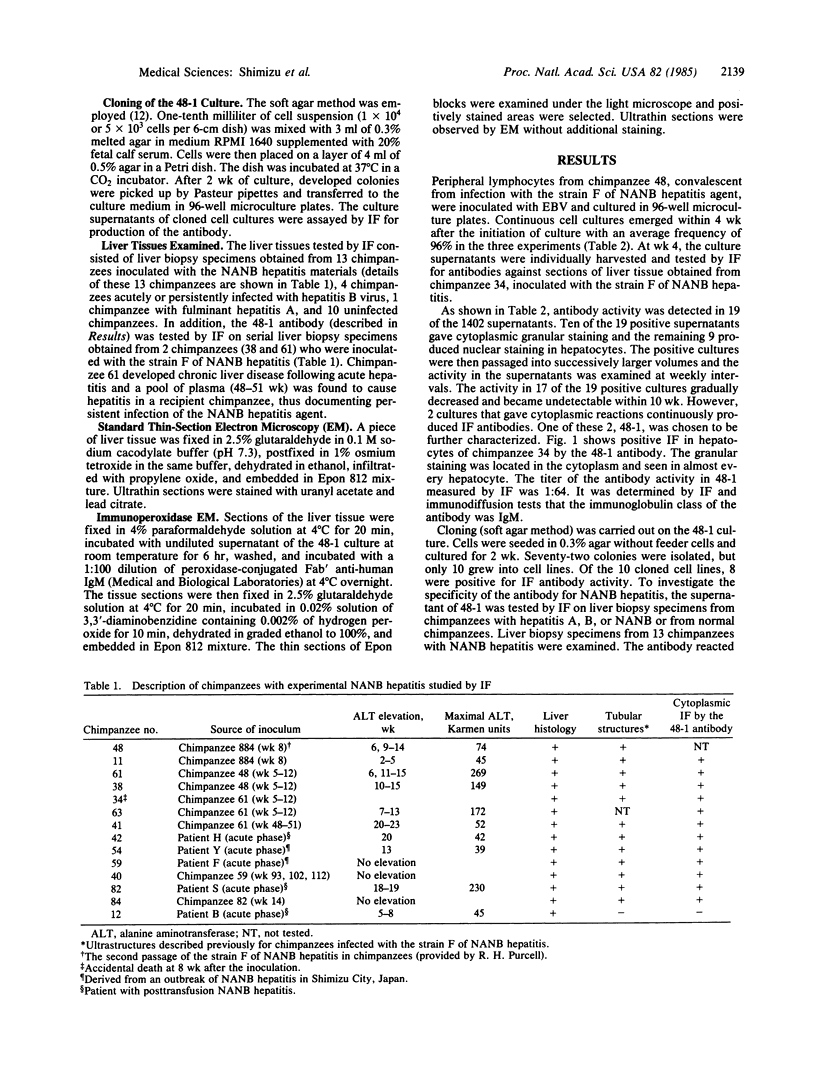
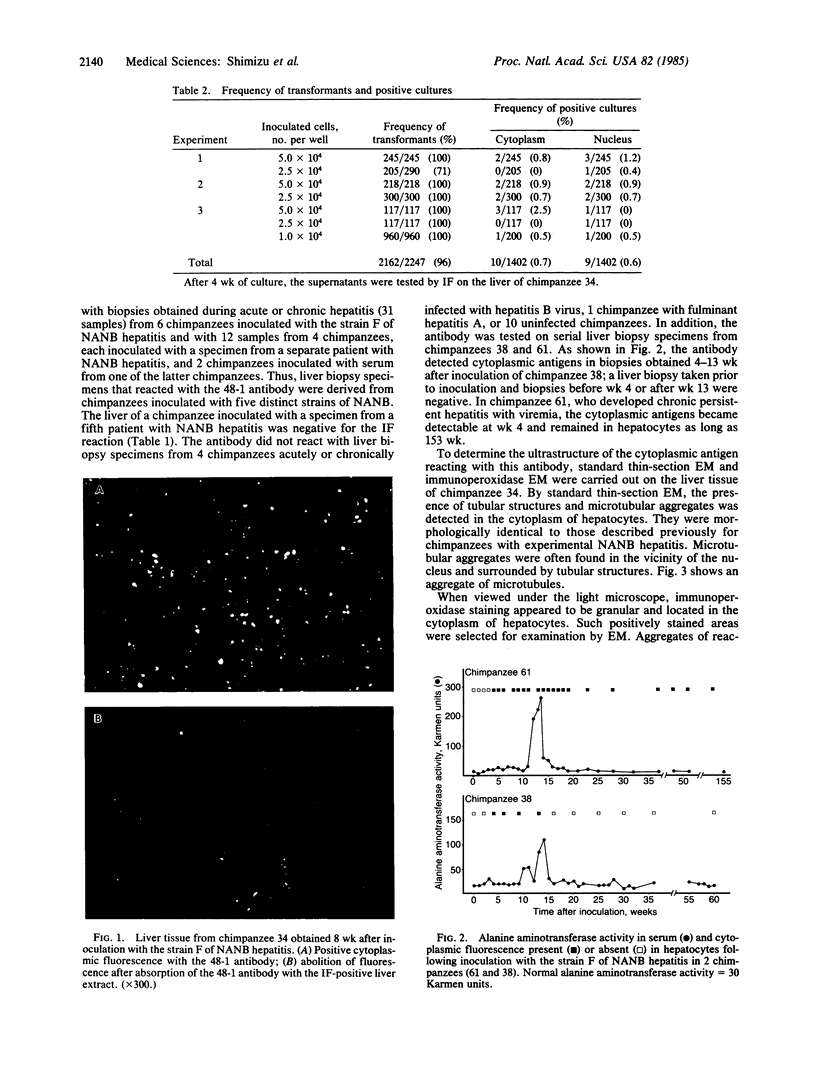
A continuous cell line of chimpanzee lymphocytes producing an antibody specifically associated with non-A, non-B hepatitis (NANB) was established. Peripheral blood lymphocytes of a chimpanzee convalescent from experimental infection with NANB hepatitis were transformed in vitro by Epstein-Barr virus infection into lymphoblastoid cell lines. Supernatants of the cell cultures were screened by immunofluorescence for antibody activity against the liver tissue of a chimpanzee with NANB hepatitis. Nineteen of the 1402 cultures were found to be positive for the activity. Ten of these 19 gave cytoplasmic reactions and the remaining 9 gave nuclear reactions in hepatocytes. One culture (48-1) stably producing the antibody was further characterized. The antibody produced in 48-1 was IgM and gave granular cytoplasmic reactions in hepatocytes. Cloning of 48-1 was performed by the soft agar method and cloned cell lines stably producing the antibody were obtained. The 48-1 antibody reacted with liver biopsy specimens from 12 chimpanzees obtained during the acute or chronic phase of hepatitis caused by five different NANB strains, but not with biopsy specimens from chimpanzees with hepatitis A or B or from normal chimpanzees. In addition, examinations of serial liver biopsy specimens obtained from 2 chimpanzees experimentally infected with NANB hepatitis demonstrated that the antibody reacted with the biopsies obtained during the preacute, acute, and chronic hepatitis, but not with those obtained before inoculation, early incubation period, or during convalescence. The present results indicate the specific association of the antibody with NANB hepatitis. Immunoelectron microscopy revealed that the antibody reacted with the microtubular aggregates identical to those previously described in a patient and chimpanzees with NANB hepatitis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti A., Realdi G., Bortolotti F., Cadrobbi P., Barbieri R., Tremolada F., Ongaro G. Detection by immunofluorescence of an antigen-antibody system in patients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis. Liver. 1981 Sep;1(3):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1981.tb00032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Holland P. V., Popper H. Transmissible agent in non-A, non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1978 Mar 4;1(8062):459–463. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canese M. G., Rizzetto M., Novara R., London W. T., Purcell R. H. Experimental infection of chimpanzees with the HBsAg-associated delta (delta) agent: an ultrastructural study. J Med Virol. 1984;13(1):63–72. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890130108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., Vanstapel M. J., Desmyter J., De Wolf-Peeters C., De Groote G., Colaert J., Mortelmans J., De Groote J., Fevery J., Desmet V. Are nuclear particles specific for non-A, non-B hepatitis? Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):532–544. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Gitnick G. L., Aach R. D., Szmuness W., Mosley J. W., Stevens C. E., Peters R. L., Weiner J. M., Werch J. B., Lander J. J. Non-A, non-B hepatitis transmission in chimpanzees: a project of the transfusion-transmitted viruses study group. Intervirology. 1978;10(1):60–68. doi: 10.1159/000148969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabiri M., Tabor E., Gerety R. J. Antigen-antibody system associated with non-A, non-B hepatitis detected by indirect immunofluorescence. Lancet. 1979 Aug 4;2(8136):221–224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskimies S. Human lymphoblastoid cell line producing specific antibody against Rh-antigen D. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer U., Thomssen R., Legler K., Böttcher U., Gerlich W., Weinmann E., Klinge O. Experimental non-A, non-B hepatitis: four types of cytoplasmic alteration in hepatocytes of infected chimpanzees. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1980;33(3):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF02899184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y. K., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Alter H. J., London W. T. Non-A, non-B hepatitis: ultrastructural evidence for two agents in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Science. 1979 Jul 13;205(4402):197–200. doi: 10.1126/science.451589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spichtin H. P., Gudat F., Schmid M., Pirovino M., Altorfer J., Bianchi L. Microtubular aggregates in human chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis with bridging hepatic necrosis and multinucleated hepatocytic giant cells. Liver. 1982 Dec;2(4):355–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1982.tb00834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G., Koskimies S., Makel O. EB virus-induced B lymphocyte cell lines producing specific antibody. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):420–422. doi: 10.1038/269420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E., Gerety R. J., Drucker J. A., Seeff L. B., Hoofnagle J. H., Jackson D. R., April M., Barker L. F., Pineda-Tamondong G. Transmission of non-A, non-B hepatitis from man to chimpanzee. Lancet. 1978 Mar 4;1(8062):463–466. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E., Mitchell F. D., Goudeau A. M., Gerety R. J. Detection of an antigen-antibody system in serum associated with human non-A, non-B hepatitis. J Med Virol. 1979;4(3):161–169. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya S., Yokoyama S., Yoshie O., Ono Y. Production of diphtheria antitoxin antibody in Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1970–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitvitski L., Trepo C., Prince A. M., Brotman B. Detection of virus-associated antigen in serum and liver of patients with non-A non-B hepatitis. Lancet. 1979 Dec 15;2(8155):1263–1267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Kanamori T., Ono Y. Quantitative analyses of specific B cells for sheep red blood cell, phosphorylcholine, and hepatitis B surface antigen in human B cell populations by polyclonal transformation with Epstein-Barr virus. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1981 Jun;134(2):115–123. doi: 10.1620/tjem.134.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Ono Y. Anti-phosphorylcholine antibody-producing cells in human lymphoblastoid cell lines established by transformation with Epstein-Barr virus. Cell Immunol. 1980 Dec;56(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]