Abstract
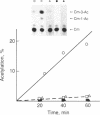
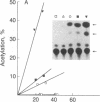
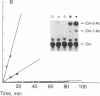
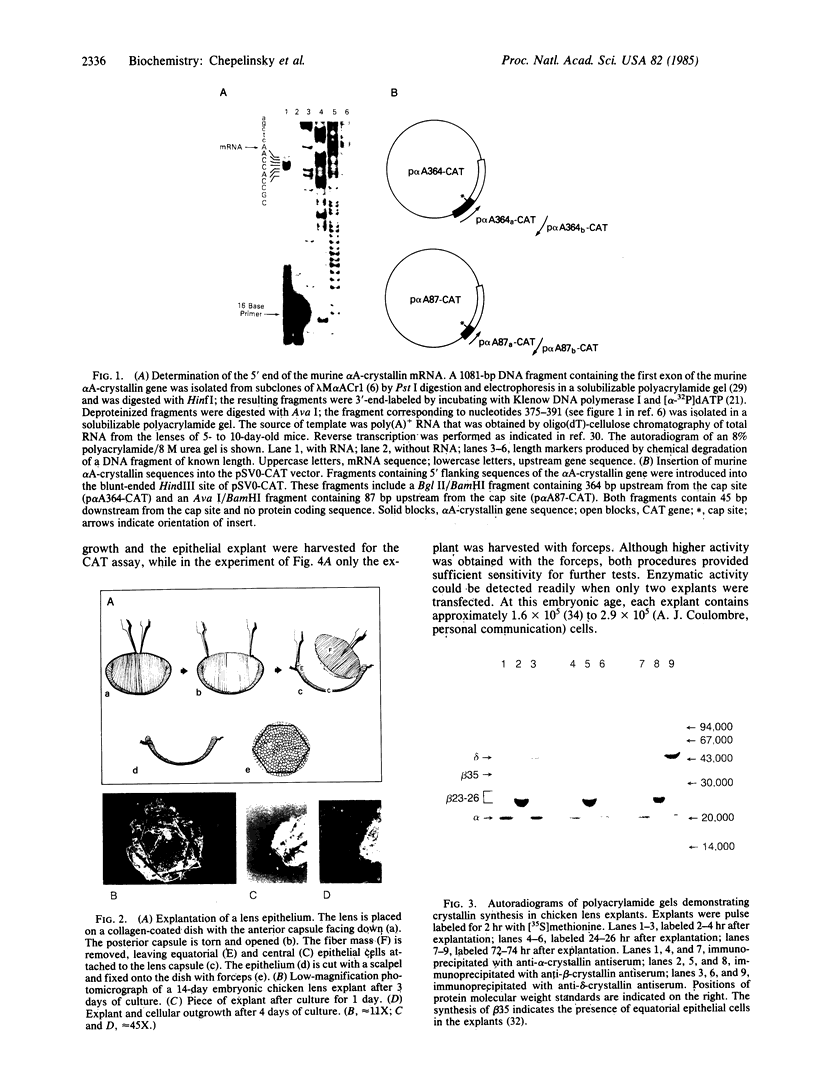
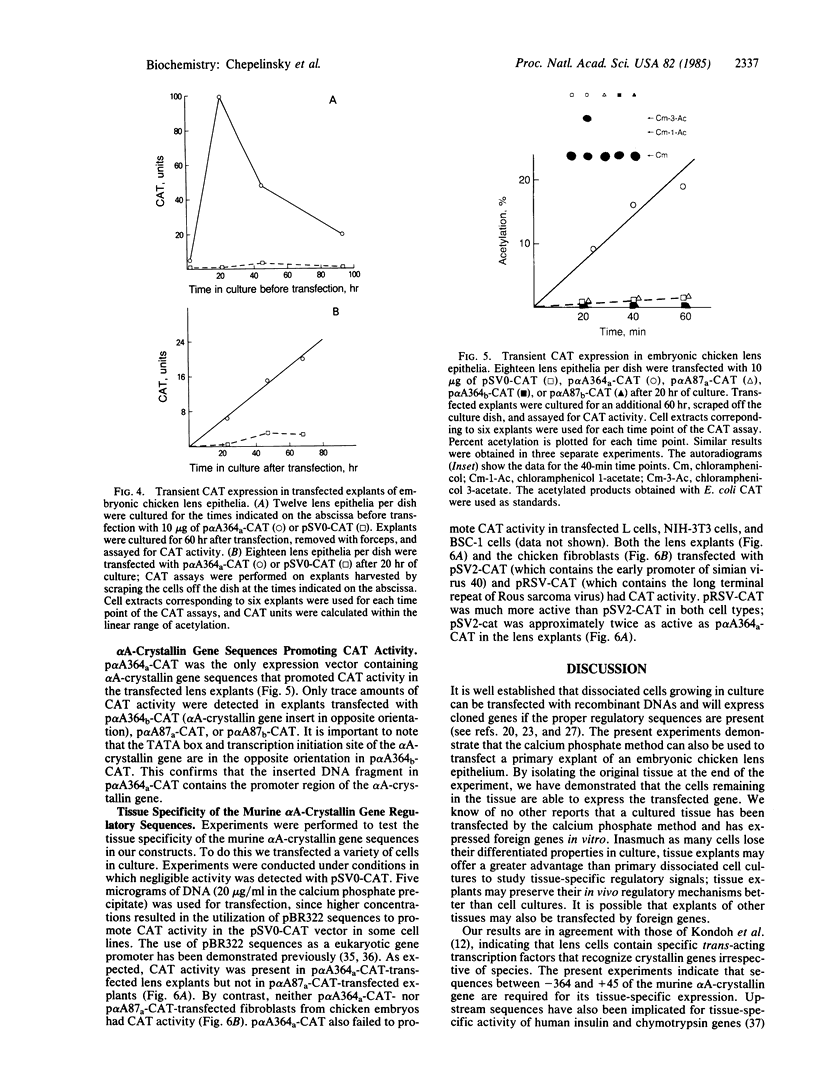
We have developed a system using explanted embryonic chicken lens epithelia to express foreign recombinant genes containing crystallin DNA regulatory sequences introduced by calcium phosphate transfection. Optimal results were obtained with lens epithelia from 14-day embryos transfected 1 day after explantation and assayed 3 days later. When DNA sequences (-364 to +45) of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene were inserted in the pSVO-CAT expression vector of Gorman et al. [Gorman, C. M., Moffat, L. F. & Howard, B. H. (1982) Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 1044-1051] in the same orientation as in the crystallin gene, they promoted chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT; EC 2.3.1.28) activity in the transfected epithelia. Sequences 87 to 364 base pairs upstream from the murine gene cap site were required for CAT gene expression. These crystallin gene regulatory sequences did not promote CAT expression in primary cultures of embryonic chicken fibroblasts or other nonlens cells. By contrast, the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus and the early promoter of simian virus 40 promoted CAT activity in lens and nonlens cells. Our experiments thus demonstrate that the explanted embryonic chicken lens epithelium is an advantageous recipient for identifying lens-cell-specific regulatory sequences of crystallin genes and implicate a DNA region upstream of the "TATA box" for regulation of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene. These experiments also suggest that explanted epithelia from other tissues may be useful for studying the expression of foreign genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Parks L. A., Coon H. G. Culture of hormone-dependent functional epithelial cells from rat thyroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H. Lens proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;12(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238209105849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Folsom V., Tonegawa S. Cell type-specific enhancer element associated with a mouse MHC gene, E beta. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):594–597. doi: 10.1038/310594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Spacer DNA sequences upstream of the T-A-T-A-A-A-T-A sequence are essential for promotion of H2A histone gene transcription in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7102–7106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. N. Use of solubilizable acrylamide disulfide gels for isolation of DNA fragments suitable for sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. J., Dilley K. J. Structural proteins of the mammalian lens: a review with emphasis on changes in development, aging and cataract. Exp Eye Res. 1976 Jan;22(1):1–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inana G., Piatigorsky J., Norman B., Slingsby C., Blundell T. Gene and protein structure of a beta-crystallin polypeptide in murine lens: relationship of exons and structural motifs. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):310–315. doi: 10.1038/302310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. E., DeFeo D., Piatigorsky J. Initial studies on cultured embryonic chick lens epithelial cells infected with a temperature-sensitive Rous sarcoma virus. Vision Res. 1981;21(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(81)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative RNA splicing of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene: protein-coding information within an intron. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Yasuda K., Okada T. S. Tissue-specific expression of a cloned chick delta-crystallin gene in mouse cells. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):440–442. doi: 10.1038/301440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenstra J. A., Hukkelhoven M. W., Groeneveld A. A., Smits R. A., Weterings P. J., Bloemendal H. Gene expression of transformed lens cells. Exp Eye Res. 1982 Dec;35(6):549–554. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(82)80069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok S., Tsui L. C., Shinohara T., Piatigorsky J., Gold R., Breitman M. Analysis of the mouse gamma-crystallin gene family: assignment of multiple cDNAs to discrete genomic sequences and characterization of a representative gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4517–4529. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse D. S., Haynes J. R., VanLeeuwen D., Schon E. A., Cleary M. L., Shapiro S. G., Lingrel J. B., Roeder R. G. Transcription of the beta-like globin genes and pseudogenes of the goat in a cell-free system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4339–4354. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menko A. S., Klukas K. A., Johnson R. G. Chicken embryo lens cultures mimic differentiation in the lens. Dev Biol. 1984 May;103(1):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstone L. M., Piatigorsky J. Rates of protein synthesis in explanted embryonic chick lens epithelia: differential stimulation of delta-crystallin synthesis. Dev Biol. 1975 Mar;43(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstone L. M., Zelenka P., Piatigorsky J. Delta-crystallin mRNA in chick lens cells: mRNA accumulates during differential stimulation of delta-crystallin synthesis in cultured cells. Dev Biol. 1976 Feb;48(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moormann R. J., den Dunnen J. T., Mulleners L., Andreoli P., Bloemendal H., Schoenmakers J. G. Strict co-linearity of genetic and protein folding domains in an intragenically duplicated rat lens gamma-crystallin gene. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 25;171(4):353–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson J. M., Fuller G. M. In vitro synthesis of rat fibrinogen: identification of preA alpha, preB beta, and pre gamma polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):303–307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson J. M., Piatigorsky J. Sequence of a complete chicken delta-crystallin cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrer H., Beebe D. C., Piatigorsky J. Beta-crystallin mRNAs: differential distribution in the developing chicken lens. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker B. A., Stark G. R. Regulation of simian virus 40 transcription: sensitive analysis of the RNA species present early in infections by virus or viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):360–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.360-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persons B. J., Modak S. P. The pattern of DNA synthesis in the lens epithelium and the annular pad during development and growth of the chick lens. Exp Eye Res. 1970 Jan;9(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(70)80069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Delta crystallins and their nucleic acids. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;59(1-2):33–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00231304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Lens crystallins and their gene families. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):620–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90254-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Lens differentiation in vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features. Differentiation. 1981;19(3):134–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J., Rothschild S. S. Loss during development of the ability of chick embryonic lens cells to elongate in culture: inverse relationship between cell division and elongation. Dev Biol. 1972 Jun;28(2):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J., Webster H. D., Craig S. P. Protein synthesis and ultrastructure during the formation of embryonic chick lens fibers in vivo and in vitro. Dev Biol. 1972 Feb;27(2):176–189. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Promotion of specific in vitro transcription by excised "TATA" box sequences inserted in a foreign nucleotide environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3941–3958. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonneau L., Hervé B., Jacquemin E., Courtois Y. State of differentiation of bovine epithelial lens cells in vitro. Modulation of the synthesis and of the polymerization of specific proteins (crystallins) and non-specific proteins in relation to cell divisions. Exp Cell Res. 1983 May;145(2):433–446. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K., Nakajima N., Isobe T., Okada T. S., Shimura Y. The nucleotide sequence of a complete chicken delta-crystallin cDNA. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1397–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Venrooij W. J., Groeneveld A. A., Bloemendal H., Benedetti E. L. Cultured calf lens epithelium. I. Methods of cultivation and characteristics of the cultures. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Jun;18(6):517–526. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]