Abstract
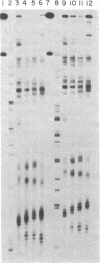
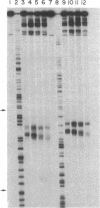
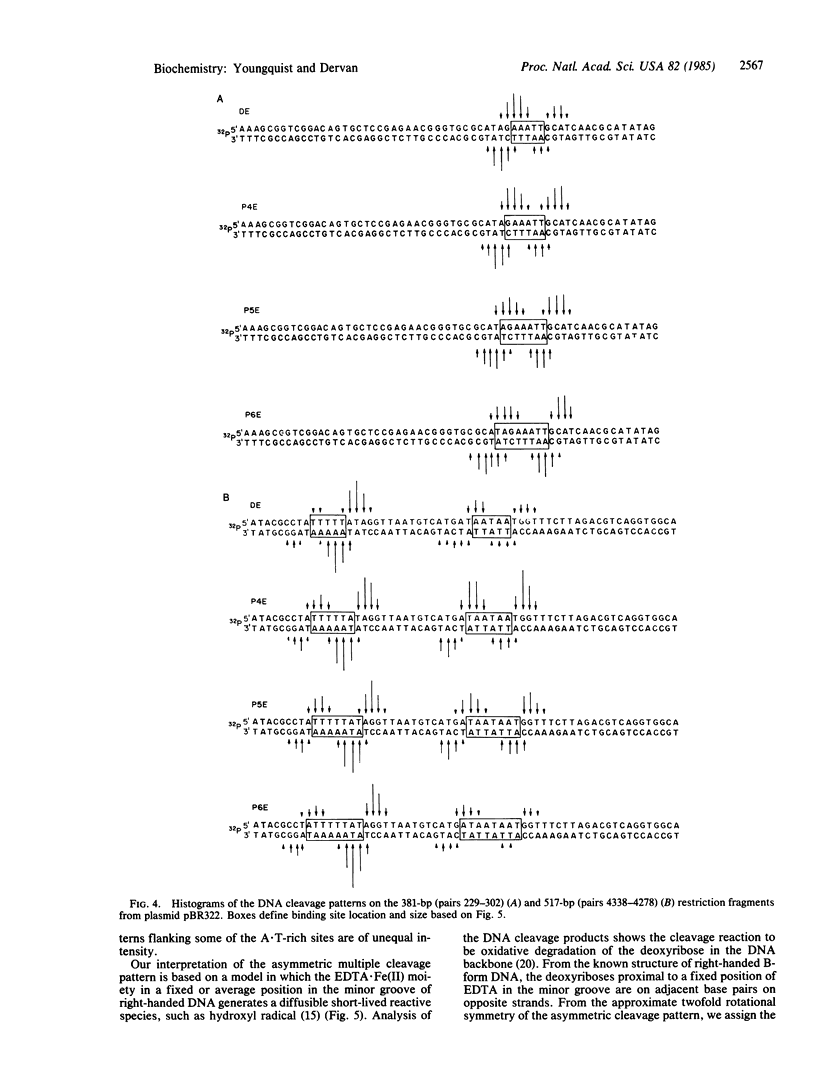
Four homologous oligopeptide-EDTA molecules, tri-, tetra, penta-, and hexa(N-methylpyrrolecarboxamide)-EDTA, in the presence of Fe(II), O2, and dithiothreitol, cleave 32P-end-labeled restriction fragments from plasmid pBR322 DNA at common locations rich in A X T base pairs that differ in the size of the binding site. From analysis of the cleavage patterns visualized by high-resolution denaturing gel electrophoresis, the oligopeptides with three, four, five, and six N-methylpyrrolecarboxamide units, containing four, five, six, and seven amide NHs, bind sites of A X T-rich DNA consisting of five, six, seven, and eight contiguous base pairs, respectively. The general rule of n amides affording binding site sizes of n + 1 base pairs is consistent with the oligopeptides binding in the minor groove of right-handed DNA, with the amide NH groups forming bridges between the adjacent N-3 and O-2 atoms of adenine or thymine on opposite strands of the DNA helix.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Yoon C., Goodsell D., Pjura P., Dickerson R. E. The molecular origin of DNA-drug specificity in netropsin and distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1376–1380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krylov A. S., Grokhovsky S. L., Zasedatelev A. S., Zhuze A. L., Gursky G. V., Gottikh B. P. Quantitative estimation of the contribution of pyrrolcarboxamide groups of the antibiotic distamycin A into specificity of its binding to DNA AT pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):289–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck G., Zimmer C., Reinert K. E., Arcamone F. Specific interactions of distamycin A and its analogs with (A-T) rich and (G-C) rich duplex regions of DNA and deoxypolynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2655–2670. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Blumenfeld K. S., Breslauer K. J. Calorimetric and spectroscopic investigation of drug-DNA interactions. I. The binding of netropsin to poly d(AT). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2857–2870. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D. Theoretical calculations of the helix-coil transition of DNA in the presence of large, cooperatively binding ligands. Biopolymers. 1976 Jul;15(7):1345–1375. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Canuel L. L. Netropsin-poly(dA-dT) complex in solution: structure and dynamics of antibiotic-free base pair regions and those centered on bound netropsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5207–5211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W. Revised sequence of the tetracycline-resistance gene of pBR322. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P. G., Dervan P. B. Distamycin and penta-N-methylpyrrolecarboxamide binding sites on native DNA. A comparison of methidiumpropyl-EDTA-Fe(II) footprinting and DNA affinity cleaving. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Mar;1(5):1133–1147. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P. G., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific double-strand cleavage of DNA by penta-N-methylpyrrolecarboxamide-EDTA X Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6834–6837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Map of distamycin, netropsin, and actinomycin binding sites on heterogeneous DNA: DNA cleavage-inhibition patterns with methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5470–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewska K., Lavery R., Pullman B. Theoretical studies of the selective binding to DNA of two non-intercalating ligands: netropsin and SN 18071. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8825–8839. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Luck G., Birch-Hirschfeld E., Weiss R., Arcamone F., Guschlbauer W. Chain length-dependent association of distamycin-type oligopeptides with A X T and G X C pairs in polydeoxynucleotide duplexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 13;741(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]