Abstract
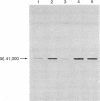
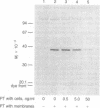
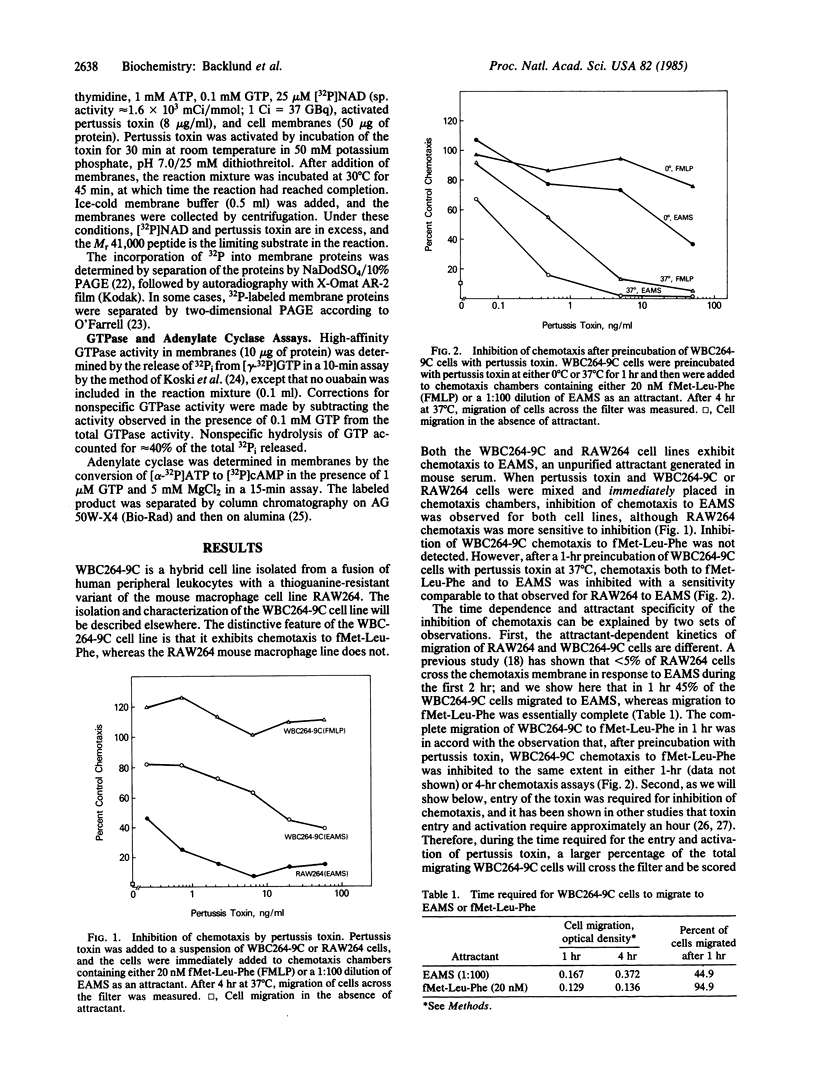
When WBC264-9C cells are preincubated with pertussis toxin, chemotaxis is inhibited and ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein with a subunit Mr 41,000 is observed. Both the inhibition of chemotaxis and the ADP-ribosylation by pertussis toxin display a similar time lag, temperature dependence, and pertussis toxin-concentration dependence. Although the inhibition of chemotaxis and the ADP-ribosylation of the membrane protein are qualitatively correlated, nearly complete inhibition of chemotaxis occurs when there is only partial ADP-ribosylation of the membrane protein. Pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of the Mr 41,000 protein in WBC264-9C membranes is stimulated by GDP, GTP, and to a lesser extent by GMP; the nonhydrolyzable GTP analog guanosine 5'-[beta, gamma-imido]triphosphate has no effect. WBC264-9C membranes have a high-affinity GTPase activity, which is partially inhibited in membranes from pertussis toxin-treated cells. Neither GTPase activity nor adenylate cyclase activity in membranes from WBC264-9C cells is affected by fMet-Leu-Phe, an attractant for these cells. Our results suggest that a guanine nucleotide binding protein may be involved in chemotaxis, but they do not indicate an involvement of adenylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksamit R. R., Backlund P. S., Jr, Cantoni G. L. Chemotaxis and the synthesis of specific proteins are inhibited by 3-deazaadenosine and other adenosine analogs in a mouse macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit R. R., Falk W., Cantoni G. L. Inhibition of chemotaxis by S-3-deazaadenosylhomocysteine in a mouse macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):621–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aksamit R. R., Falk W., Leonard E. J. Chemotaxis by mouse macrophage cell lines. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2194–2199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D. W., Koshland D. E., Jr Evidence for an S-adenosylmethionine requirement in the chemotactic behavior of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):207–223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Hildebrandt J., Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R. Pertussis toxin substrate, the putative Ni component of adenylyl cyclases, is an alpha beta heterodimer regulated by guanine nucleotide and magnesium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4276–4280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Aksamit R. R. Oxidized N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine: effect on the activation of human monocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis and superoxide production. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1471–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop P. A., Oades Z. G., Jesaitis A. J., Painter R. G., Cochrane C. G., Sklar L. A. Evidence for N-formyl chemotactic peptide-stimulated GTPase activity in human neutrophil homogenates. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 23;166(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Smigel M. D., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cyc- and wild type membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3586–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. ADP ribosylation of the specific membrane protein of C6 cells by islet-activating protein associated with modification of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7210–7216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Slow interaction of islet-activating protein with pancreatic islets during primary culture to cause reversal of alpha-adrenergic inhibition of insulin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9580–9588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Lefkowitz R. J., Snyderman R. Guanine nucleotides modulate the binding affinity of the oligopeptide chemoattractant receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):748–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI111045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Lefkowitz R. J., Snyderman R. The oligopeptide chemotactic factor receptor on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes exists in two affinity states. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91130-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Streaty R. A., Klee W. A. Modulation of sodium-sensitive GTPase by partial opiate agonists. An explanation for the dual requirement for Na+ and GTP in inhibitory regulation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14035–14040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Katada T., Amano T., Ui M. Specific uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, of negative signal transduction via alpha-adrenergic, cholinergic, and opiate receptors in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4870–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackin W. M., Huang C. K., Becker E. L. The formylpeptide chemotactic receptor on rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. I. Evidence for two binding sites with different affinities. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1608–1611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Garciá-Sáinz J. A. Pertussis toxin catalyzes the ADP-ribosylation of two distinct peptides, 40 and 41 kDa, in rat fat cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx R. S., McCall C. E., Bass D. A. Chemotaxin-induced changes in cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):284–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.284-286.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade B. D., Kind P. D., Ewell J. B., McGrath P. P., Manclark C. R. In vitro inhibition of murine macrophage migration by Bordetella pertussis lymphocytosis-promoting factor. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):718–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.718-725.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade B. D., Kind P. D., Manclark C. R. Lymphocytosis-promoting factor of Bordetella pertussis alters mononuclear phagocyte circulation and response to inflammation. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):733–739. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.733-739.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Marsh M. L., Kermode J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits the rise in the intracellular concentration of free calcium that is induced by chemotactic factors in rabbit neutrophils: possible role of the "G proteins" in calcium mobilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):644–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91603-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Loss of the inhibitory function of the guanine nucleotide regulatory component of adenylate cyclase due to its ADP ribosylation by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in adipocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3319–3326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. ADP-ribosylation of the specific membrane protein by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, associated with inhibition of a chemotactic peptide-induced arachidonate release in neutrophils. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing biosignaling. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13863–13871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olansky L., Myers G. A., Pohl S. L., Hewlett E. L. Promotion of lipolysis in rat adipocytes by pertussis toxin: reversal of endogenous inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6547–6551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Kredich N. M., Snyderman R. Requirement of S-adenosyl-L-methionine-mediated methylation for human monocyte chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3928–3932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Snyderman R. Transmethylation reactions regulate affinity and functional activity of chemotactic factor receptors on macrophages. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C., Baird S., Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Functional macrophage cell lines transformed by Abelson leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekura R. D., Fish F., Manclark C. R., Meade B., Zhang Y. L. Pertussis toxin. Affinity purification of a new ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14647–14651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Fletcher M. P., Gallin J. I. Adaptation of human neutrophil responsiveness to the chemoattractant N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine. Heterogeneity and/or negative cooperative interaction of receptors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6280–6286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Fischbein L. C., Spilberg I., Atkinson J. P. Induction of a transient elevation in intracellular levels of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphate by chemotactic factors: an early event in human neutrophil activation. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1482–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Increased levels of cyclic adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes after surface stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1077–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI109760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Yamanaka G., Steinberg F., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R., Stryer L., Bourne H. R. ADP-ribosylation of transducin by pertussis toxin blocks the light-stimulated hydrolysis of GTP and cGMP in retinal photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]