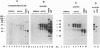Abstract
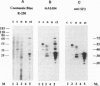
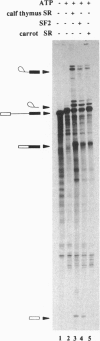
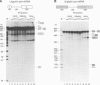
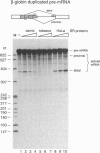
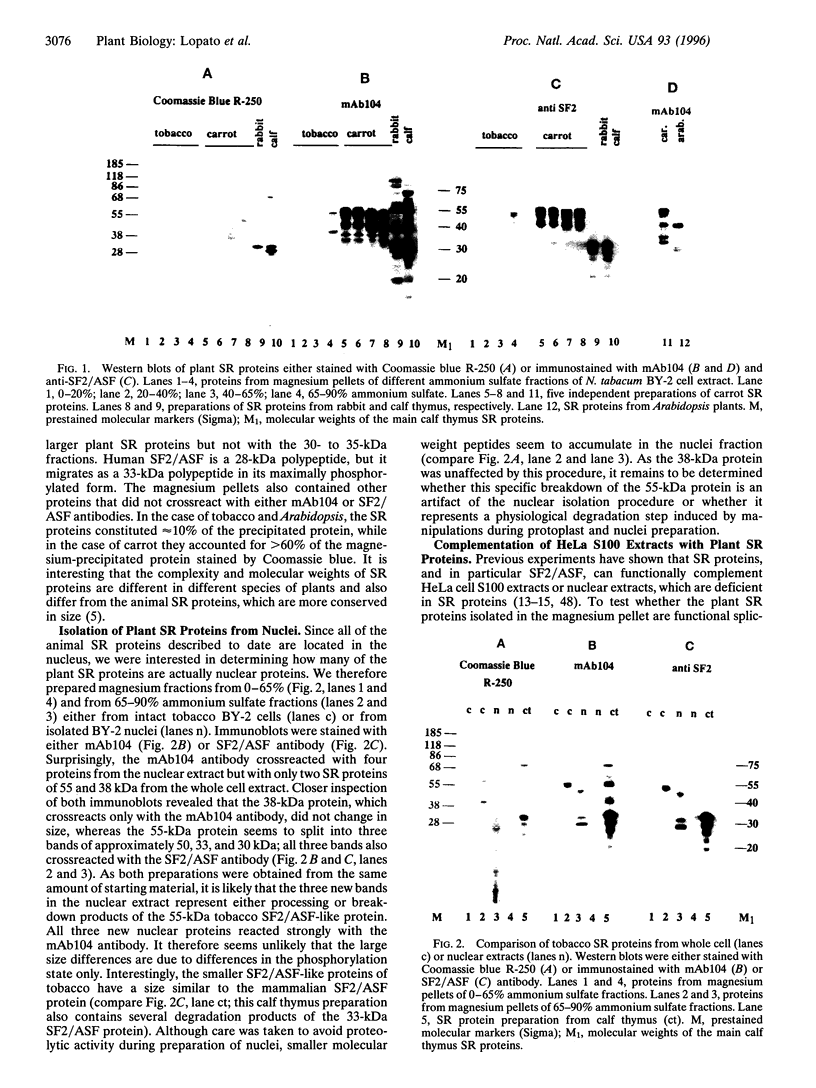
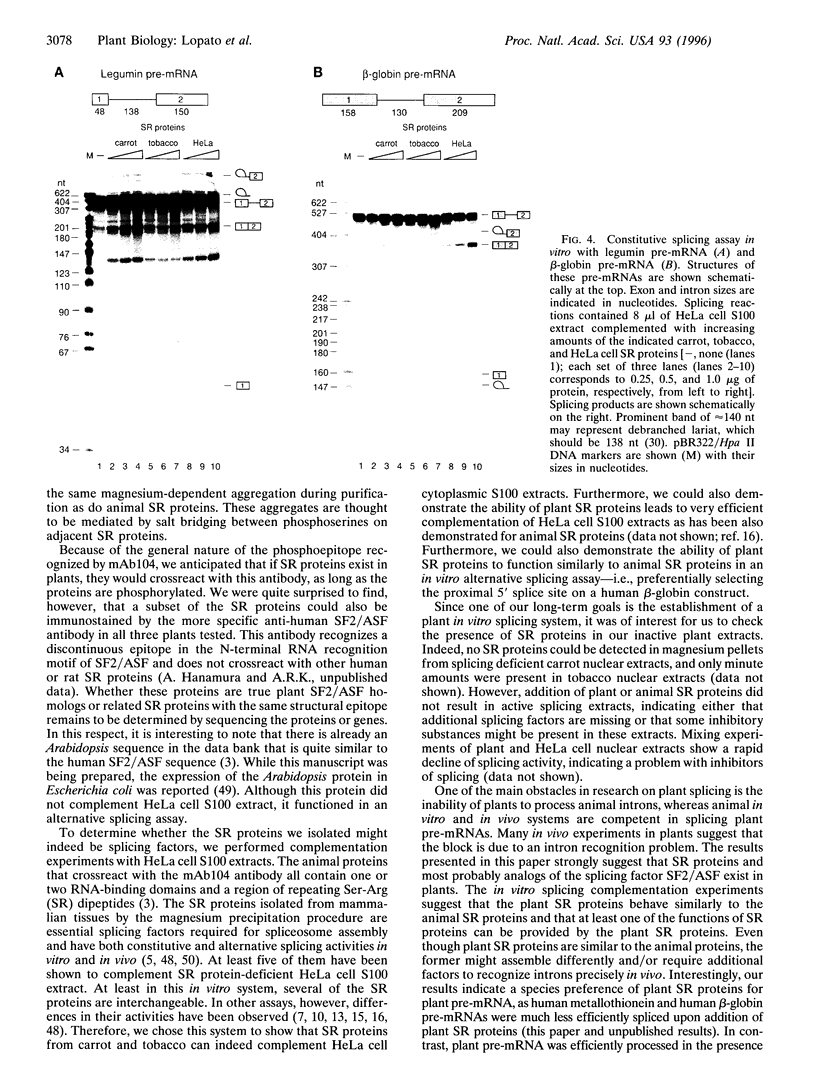
The fact that animal introns are not spliced out in plants suggests that recognition of pre-mRNA splice sites differs between the two kingdoms. In plants, little is known about proteins required for splicing, as no plant in vitro splicing system is available. Several essential splicing factors from animals, such as SF2/ASF and SC-35, belong to a family of highly conserved proteins consisting of one or two RNA binding domain(s) (RRM) and a C-terminal Ser/Arg-rich (SR or RS) domain. These animal SR proteins are required for splice site recognition and spliceosome assembly. We have screened for similar proteins in plants by using monoclonal antibodies specific for a phosphoserine epitope of the SR proteins (mAb1O4) or for SF2/ASF. These experiments demonstrate that plants do possess SR proteins, including SF2/ASF-like proteins. Similar to the animal SR proteins, this group of proteins can be isolated by two salt precipitations. However, compared to the animal SR proteins, which are highly conserved in size and number, SR proteins from Arabidopsis, carrot, and tobacco exhibit a complex pattern of intra- and interspecific variants. These plant SR proteins are able to complement inactive HeLa cell cytoplasmic S1OO extracts that are deficient in SR proteins, yielding functional splicing extracts. In addition, plant SR proteins were active in a heterologous alternative splicing assay. Thus, these plant SR proteins are authentic plant splicing factors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein H., Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. The role of specific protein-RNA and protein-protein interactions in positive and negative control of pre-mRNA splicing by Transformer 2. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birney E., Kumar S., Krainer A. R. Analysis of the RNA-recognition motif and RS and RGG domains: conservation in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Dec 25;21(25):5803–5816. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.25.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Feix G., Frendewey D. Accurate in vitro splicing of two pre-mRNA plant introns in a HeLa cell nuclear extract. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2749–2758. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Simpson C. G., Simpson G. G., Turnbull-Ross A. D., Clark G. P. Plant pre-mRNA splicing and splicing components. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993 Nov 29;342(1301):217–224. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1993.0150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres J. F., Stamm S., Helfman D. M., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative splicing in vivo by overexpression of antagonistic splicing factors. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1706–1709. doi: 10.1126/science.8085156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Isolation of a complementary DNA that encodes the mammalian splicing factor SC35. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):535–538. doi: 10.1126/science.1373910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. The 35-kDa mammalian splicing factor SC35 mediates specific interactions between U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles at the 3' splice site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Mayeda A., Maniatis T., Krainer A. R. General splicing factors SF2 and SC35 have equivalent activities in vitro, and both affect alternative 5' and 3' splice site selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11224–11228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D. Specific commitment of different pre-mRNAs to splicing by single SR proteins. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):82–85. doi: 10.1038/365082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Filipowicz W. Different effects of intron nucleotide composition and secondary structure on pre-mRNA splicing in monocot and dicot plants. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2635–2644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Filipowicz W. The AU-rich sequences present in the introns of plant nuclear pre-mRNAs are required for splicing. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):473–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmuth K., Barta A. In vitro processing of a plant pre-mRNA in a HeLa cell nuclear extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7513–7528. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. G., Mogen B. D., Chu N. M., Chua N. H. The SV40 small t intron is accurately and efficiently spliced in tobacco cells. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Mar;16(3):375–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00023989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohtz J. D., Jamison S. F., Will C. L., Zuo P., Lührmann R., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Manley J. L. Protein-protein interactions and 5'-splice-site recognition in mammalian mRNA precursors. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):119–124. doi: 10.1038/368119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. Purification and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1158–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Mayeda A., Kozak D., Binns G. Functional expression of cloned human splicing factor SF2: homology to RNA-binding proteins, U1 70K, and Drosophila splicing regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90627-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W. Preparation and fractionation of mammalian extracts active in pre-mRNA splicing. Methods Enzymol. 1990;181:3–19. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)81107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar G., Schaal T., Maniatis T., Goodman H. M. Identification of a plant serine-arginine-rich protein similar to the mammalian splicing factor SF2/ASF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7672–7676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Bingham P. M. Arginine/serine-rich domains of the su(wa) and tra RNA processing regulators target proteins to a subnuclear compartment implicated in splicing. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou H., McCullough A. J., Schuler M. A. 3' splice site selection in dicot plant nuclei is position dependent. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4485–4493. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Taha S., Walbot V. Nuclear pre-mRNA processing in higher plants. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1994;47:149–193. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Walbot V. Addition of A- and U-rich sequence increases the splicing efficiency of a deleted form of a maize intron. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Feb;24(3):449–463. doi: 10.1007/BF00024113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Helfman D. M., Krainer A. R. Modulation of exon skipping and inclusion by heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 and pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2/ASF. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2993–3001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Ohshima Y. Short donor site sequences inserted within the intron of beta-globin pre-mRNA serve for splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4484–4491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Zahler A. M., Krainer A. R., Roth M. B. Two members of a conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins are involved in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1301–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough A. J., Lou H., Schuler M. A. Factors affecting authentic 5' splice site selection in plant nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1323–1331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. RNA-RNA interactions in the spliceosome: unraveling the ties that bind. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Murphy C., Gall J. G. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes a phosphorylated epitope stains lampbrush chromosome loops and small granules in the amphibian germinal vesicle. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2217–2223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S. K., Ackerman E. J. Ribozymes correctly cleave a model substrate and endogenous RNA in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17106–17109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson C. G., Brown J. W. Efficient splicing of an AU-rich antisense intron sequence. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Jan;21(2):205–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00019937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson G. G., Vaux P., Clark G., Waugh R., Beggs J. D., Brown J. W. Evolutionary conservation of the spliceosomal protein, U2B''. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5213–5217. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waigmann E., Barta A. Processing of chimeric introns in dicot plants: evidence for a close cooperation between 5' and 3' splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):75–81. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebauer K., Herrero J. J., Filipowicz W. Nuclear pre-mRNA processing in plants: distinct modes of 3'-splice-site selection in plants and animals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2042–2051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Maniatis T. Specific interactions between proteins implicated in splice site selection and regulated alternative splicing. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1061–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90316-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Neugebauer K. M., Lane W. S., Roth M. B. Distinct functions of SR proteins in alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):219–222. doi: 10.1126/science.8385799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V. L., Spritz R. A. Splicing of plant pre-mRNAs in animal systems and vice versa. Gene. 1987;56(2-3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]