Abstract
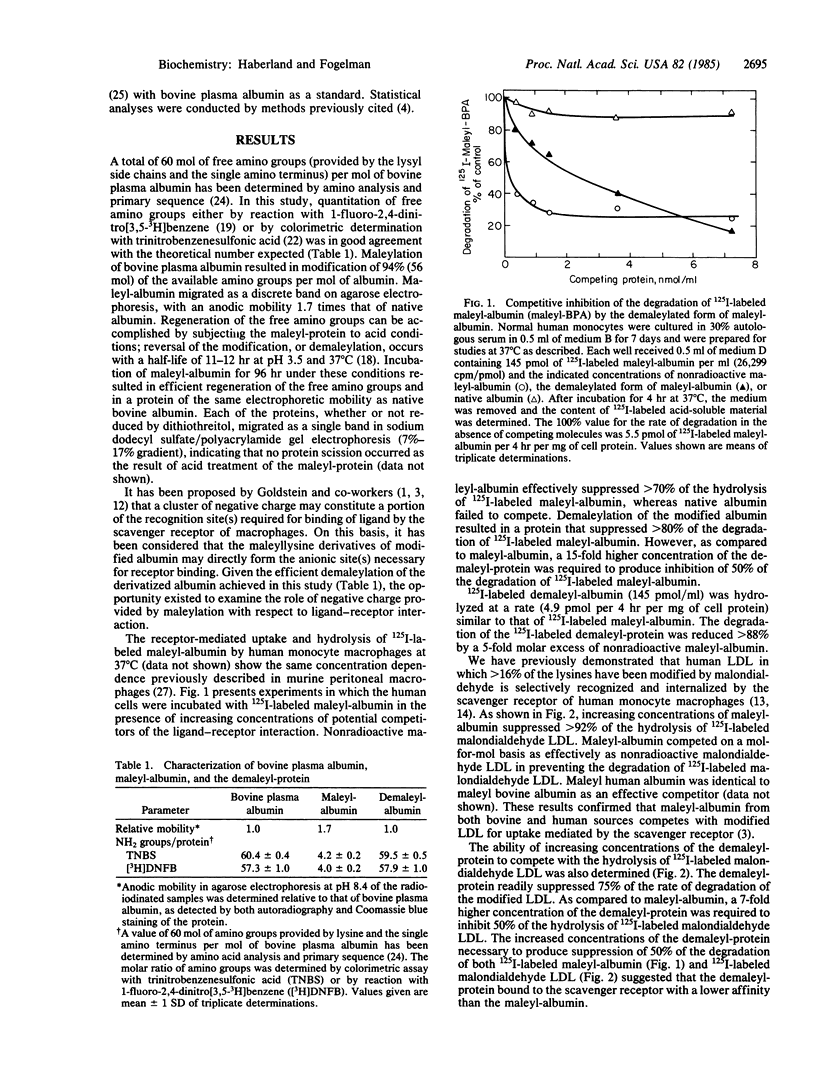
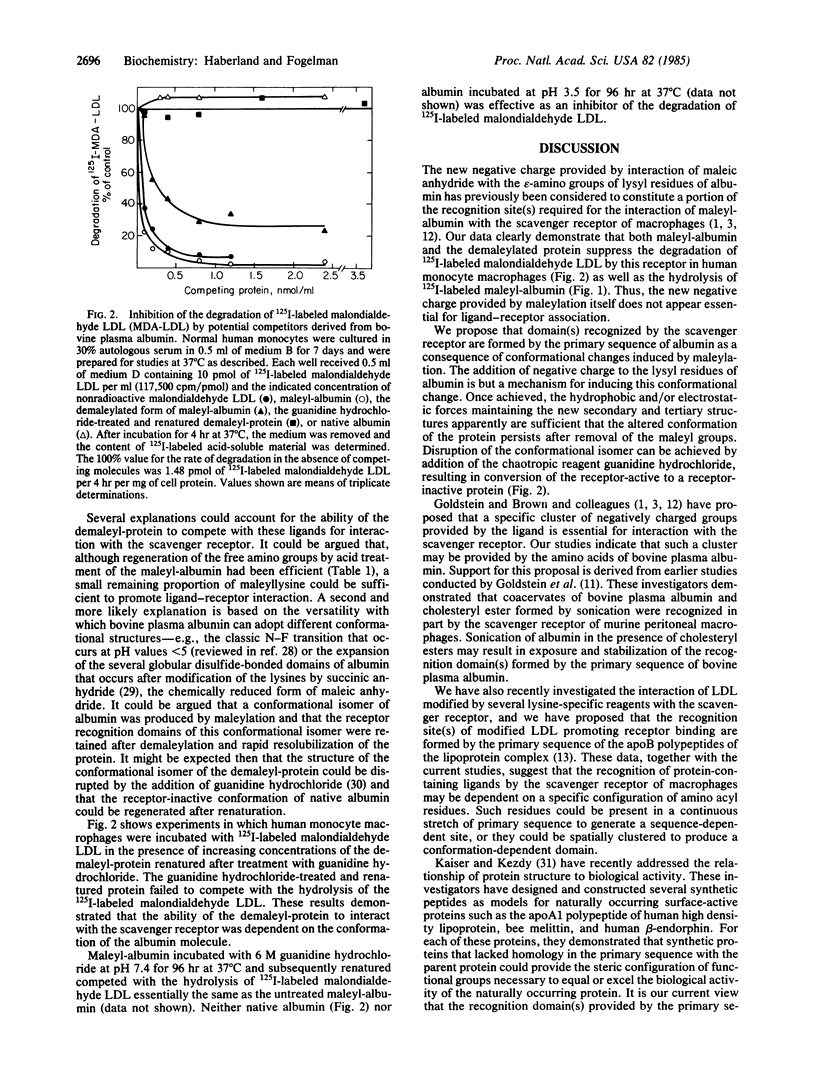
Maleyl bovine plasma albumin competed on an equimolar basis with malondialdehyde low density lipoprotein (LDL) in suppressing the lysosomal hydrolysis of 125I-labeled malondialdehyde LDL mediated by the scavenger receptor of human monocyte macrophages. Maleyl bovine plasma albumin, in which 94% of the amino groups were modified, exhibited an anodic mobility in agarose electrophoresis 1.7 times that of the native protein. Incubation of maleyl bovine plasma albumin at pH 3.5 regenerated the free amino groups and restored the protein to the same electrophoretic mobility as native albumin. The demaleylated protein suppressed 75% of the hydrolysis of 125I-labeled malondialdehyde LDL and greater than 80% of 125I-labeled maleyl bovine plasma albumin. The ability of the demaleylated protein to compete was abolished after treatment with guanidine hydrochloride. Although ligands recognized by the scavenger receptor typically are anionic, we propose that addition of new negative charge achieved by maleylation, rather than directly forming the receptor binding site(s), induces conformational changes in albumin as a prerequisite to expression of the recognition domain(s). The altered conformation of the modified protein apparently persists after removal of the maleyl groups. We conclude that the primary sequence of albumin, rather than addition of new negative charge, provides the recognition determinant(s) essential for interaction of maleyl bovine plasma albumin with the scavenger receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Falck J. R., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The scavenger cell pathway for lipoprotein degradation: specificity of the binding site that mediates the uptake of negatively-charged LDL by macrophages. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):67–81. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. The cholesteryl ester cycle in macrophage foam cells. Continual hydrolysis and re-esterification of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9344–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Edmond J., Seager J., Popják G. Abnormal induction of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in leukocytes from subjects with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2045–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Haberland M. E., Seager J., Hokom M., Edwards P. A. Factors regulating the activities of the low density lipoprotein receptor and the scavenger receptor on human monocyte-macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1981 Sep;22(7):1131–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Seager J., Hokom M., Edwards P. A. Separation of and cholesterol synthesis by human lymphocytes and monocytes. J Lipid Res. 1979 Mar;20(3):379–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Shechter I., Seager J., Hokom M., Child J. S., Edwards P. A. Malondialdehyde alteration of low density lipoproteins leads to cholesteryl ester accumulation in human monocyte-macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2214–2218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Hoff H. F., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Stimulation of cholesteryl ester synthesis in macrophages by extracts of atherosclerotic human aortas and complexes of albumin/cholesteryl esters. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):210–226. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Chemical evaluation of conformational differences in native and chemically modified proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90442-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland M. E., Fogelman A. M., Edwards P. A. Specificity of receptor-mediated recognition of malondialdehyde-modified low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1712–1716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland M. E., Olch C. L., Folgelman A. M. Role of lysines in mediating interaction of modified low density lipoproteins with the scavenger receptor of human monocyte macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11305–11311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of biologically modified low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):149–159. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of low density lipoprotein previously incubated with cultured endothelial cells: recognition by receptors for acetylated low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6499–6503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V., Johnson W. J., Adams D. O. Selective diminution of the binding of mannose by murine macrophages in the late stages of activation. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5129–5135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. J., Pizzo S. V., Imber M. J., Adams D. O. Receptors for maleylated proteins regulate secretion of neutral proteases by murine macrophages. Science. 1982 Nov 5;218(4572):574–576. doi: 10.1126/science.6289443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Secondary structures of proteins and peptides in amphiphilic environments. (A review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1137–1143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Spencer M. Structural studies and organic ligand-binding properties of bovine plasma albumin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6134–6148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. B., Oh S. Y. Altered metabolism (in vivo and in vitro) of plasma lipoproteins after selective chemical modification of lysine residues of the apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):743–750. doi: 10.1172/JCI109518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F. The free amino groups of insulin. Biochem J. 1945;39(5):507–515. doi: 10.1042/bj0390507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter I., Fogelman A. M., Haberland M. E., Seager J., Hokom M., Edwards P. A. The metabolism of native and malondialdehyde-altered low density lipoproteins by human monocyte-macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1981 Jan;22(1):63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. C., Jr, Reynolds J. A. Molecular weight and hydrodynamic properties of apolipoprotein B in guanidine hydrochloride and sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1639–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


