Abstract
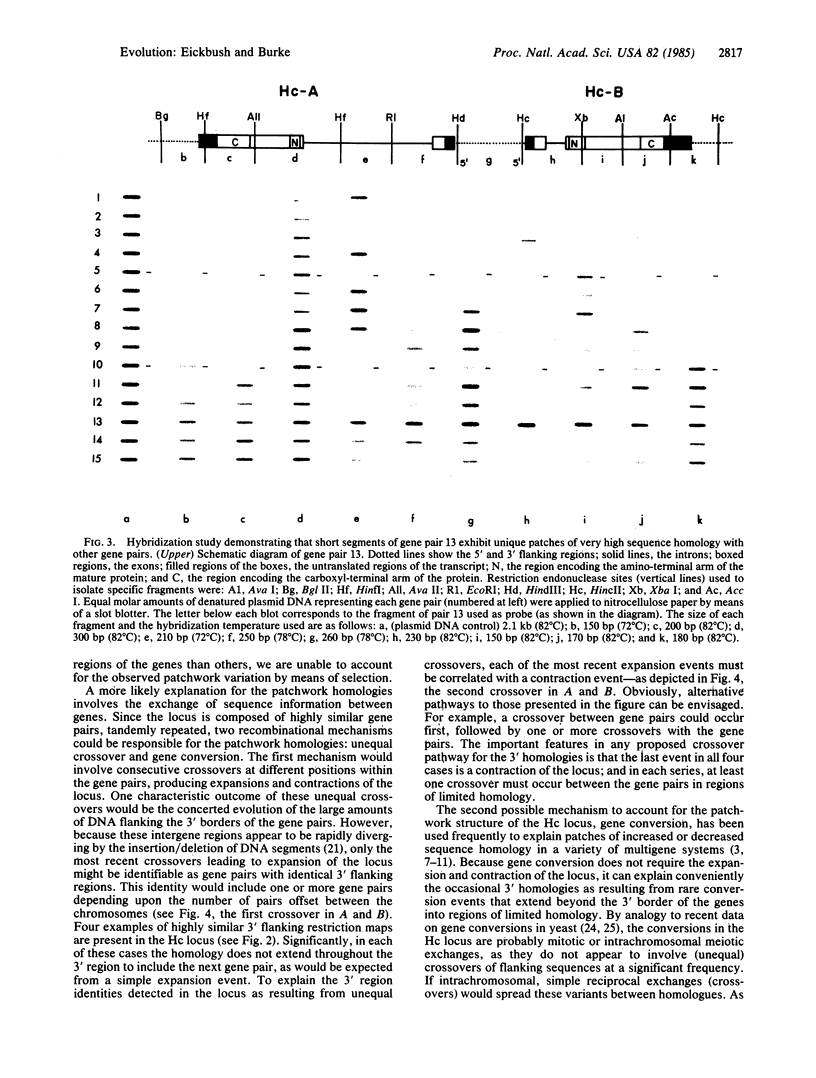
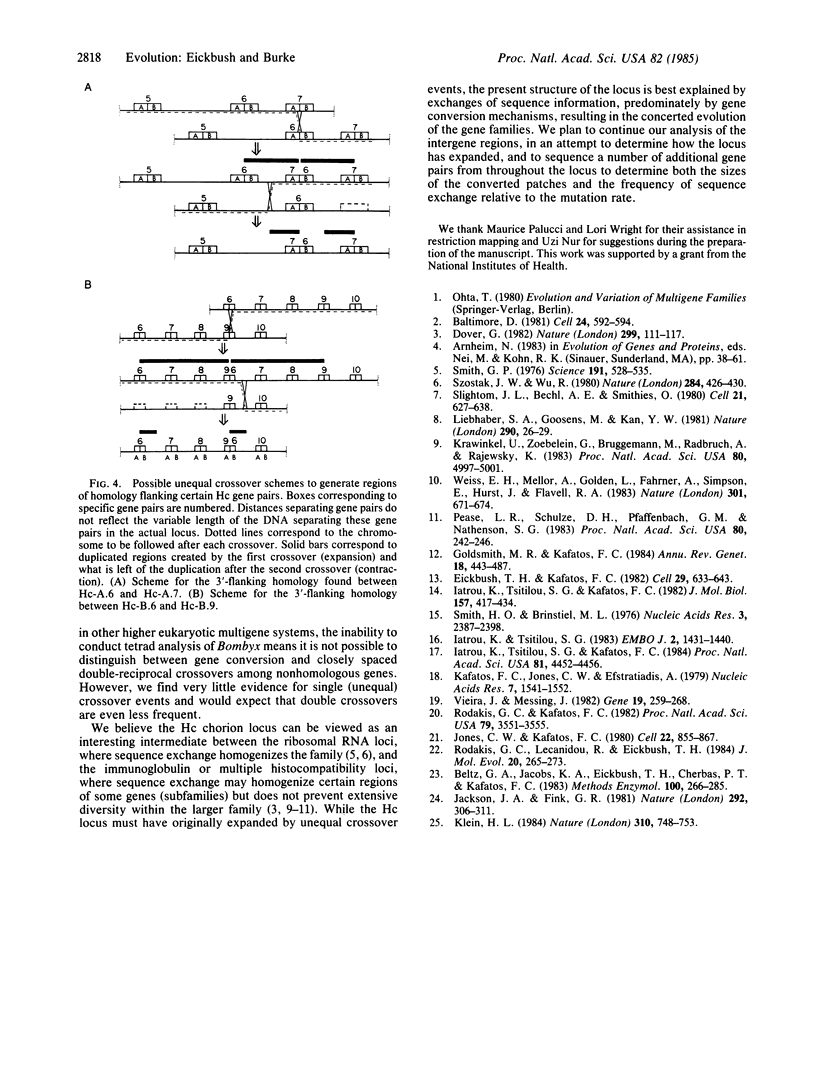
The late chorion locus of Bombyx mori, containing paired members from two multigene families, has been analyzed in detail. The 15 gene pairs, irregularly spaced over 140 kilobases, exhibit an identical structure and a high overall sequence homology, while the flanking DNA (intergene regions) varies considerably. Segments of DNA of 150-300 base pairs from a reference gene pair were used as probes in a series of DNA hybridization experiments. It was found that the sequence variants within the locus are in a "patchwork" arrangement. Each gene pair contains a unique pattern of regions or "patches" that are highly homologous to the reference gene pair, interspersed with regions exhibiting less homology. We suggest that phenotypic selection is unable to account for the observed patchwork patterns; rather, sequence exchange between genes must be postulated. The nature of the DNA flanking the gene pairs would suggest that most of this sequence exchange is by means of gene conversion rather than unequal crossover events.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltz G. A., Jacobs K. A., Eickbush T. H., Cherbas P. T., Kafatos F. C. Isolation of multigene families and determination of homologies by filter hybridization methods. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:266–285. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Kafatos F. C. A walk in the chorion locus of Bombyx mori. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. R., Kafatos F. C. Developmentally regulated genes in silkmoths. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:443–487. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Tsitilou S. G. Coordinately expressed chorion genes of Bombyx mori: is developmental specificity determined by secondary structure recognition? EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1431–1440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Tsitilou S. G., Kafatos F. C. DNA sequence transfer between two high-cysteine chorion gene families in the silkmoth Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4452–4456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Tsitilou S. G., Kafatos F. C. Developmental classes and homologous families of chorion genes in Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):417–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90469-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. A., Fink G. R. Gene conversion between duplicated genetic elements in yeast. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):306–311. doi: 10.1038/292306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Kafatos F. C. Structure, organization and evolution of developmentally regulated chorion genes in a silkmoth. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):855–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90562-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. L. Lack of association between intrachromosomal gene conversion and reciprocal exchange. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):748–753. doi: 10.1038/310748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Zoebelein G., Brüggemann M., Radbruch A., Rajewsky K. Recombination between antibody heavy chain variable-region genes: evidence for gene conversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4997–5001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Goossens M., Kan Y. W. Homology and concerted evolution at the alpha 1 and alpha 2 loci of human alpha-globin. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):26–29. doi: 10.1038/290026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease L. R., Schulze D. H., Pfaffenbach G. M., Nathenson S. G. Spontaneous H-2 mutants provide evidence that a copy mechanism analogous to gene conversion generates polymorphism in the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):242–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodakis G. C., Kafatos F. C. Origin of evolutionary novelty in proteins: how a high-cysteine chorion protein has evolved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3551–3555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodakis G. C., Lecanidou R., Eickbush T. H. Diversity in a chorion multigene family created by tandem duplications and a putative gene-conversion event. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(3-4):265–273. doi: 10.1007/BF02104732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Wu R. Unequal crossing over in the ribosomal DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):426–430. doi: 10.1038/284426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Mellor A., Golden L., Fahrner K., Simpson E., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. The structure of a mutant H-2 gene suggests that the generation of polymorphism in H-2 genes may occur by gene conversion-like events. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):671–674. doi: 10.1038/301671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




