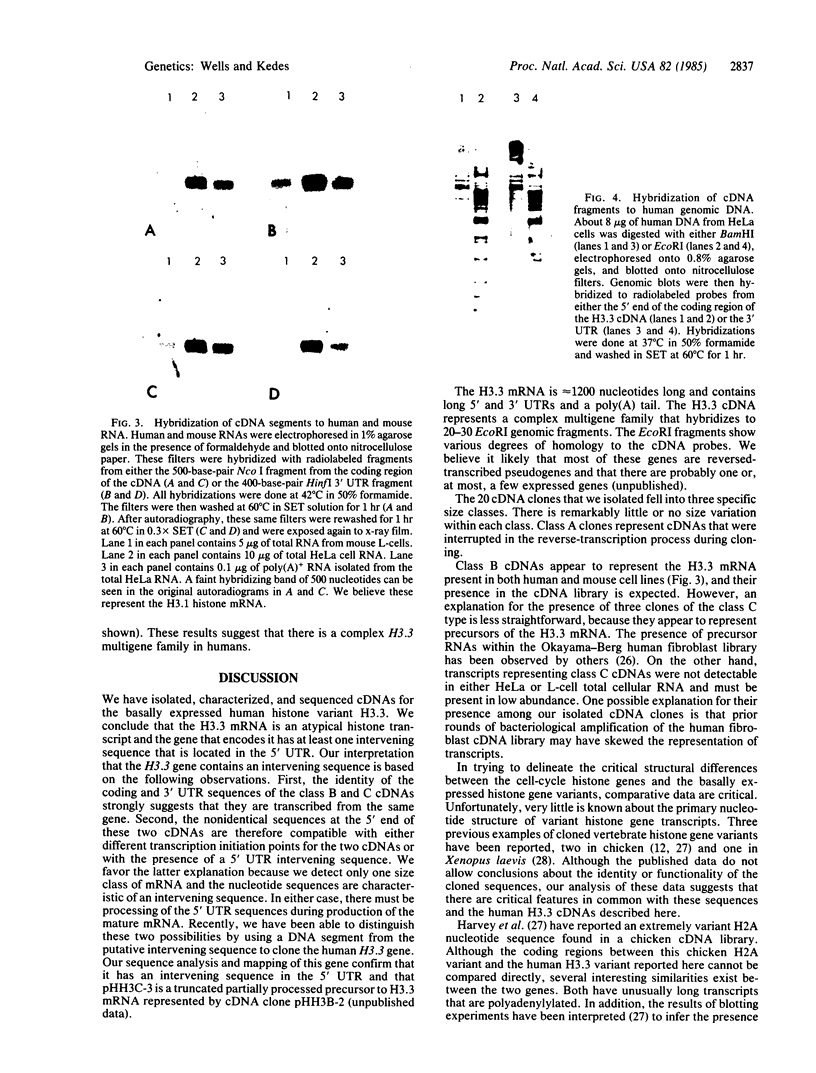
Abstract
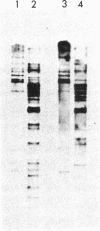
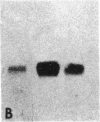
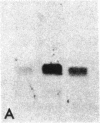
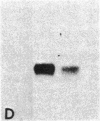
We have isolated and sequenced full-length cDNA clones encoding the human basally expressed H3.3 histone from a human fibroblast cDNA library. Several features of this atypical cDNA distinguish it and its gene from the well-characterized cell-cycle regulated histone genes and their RNA transcripts. The H3.3 mRNA is approximately equal to 1200 bases long, contains unusually long 5' and 3' untranslated regions, and has a 3' polyadenylylated terminus. In addition, we have isolated and characterized a cDNA clone that is a precursor to the H3.3 mRNA and contains an intervening sequence interrupting its 5' untranslated region. Hybridization of subsegments of the cDNA to human genomic DNA reveals a complex multigene family. The differences in the structures of basal and cell-cycle histone genes suggest a model to explain the differences in their expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birchmeier C., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of authentic 3' termini of an H2A mRNA in vivo is dependent on a short inverted DNA repeat and on spacer sequences. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Dodgson J. B. Histone genes are clustered but not tandemly repeated in the chicken genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2856–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B. A chicken histone H3 gene contains intervening sequences. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):434–436. doi: 10.1038/297434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin S. G., Zweidler A. Non-allelic variants of histones 2a, 2b and 3 in mammals. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):273–275. doi: 10.1038/266273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Whiting J. A., Coles L. S., Krieg P. A., Wells J. R. H2A.F: an extremely variant histone H2A sequence expressed in the chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2819–2823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Formation of the 3' end of histone mRNA by post-transcriptional processing. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):203–206. doi: 10.1038/308203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Cohn R., Kedes L., Mohun T. Expression and organization of histone genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:239–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Ivarie R. Asymmetrical distribution of CpG in an 'average' mammalian gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7865–7877. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohe Y., Iwai K. Human spleen histone H3. Isolation and amino acid sequence. J Biochem. 1981 Oct;90(4):1205–1211. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old R. W., Woodland H. R. Histone genes: not so simple after all. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):624–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti I., Fragapane P., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E., Amaldi F., Bozzoni I. Characterization of histone genes isolated from Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis genomic libraries. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7543–7559. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Chiu I. M., Pan C. J., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H., Marzluff W. F. Isolation of two clusters of mouse histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4078–4082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde P., Stoppelli M. P., Galeffi P., Di Nocera P., Blasi F. Identification and primary sequence of an unspliced human urokinase poly(A)+ RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4727–4731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Tsai S., Bonner W. M. Changes in histone H3 composition and synthesis pattern during lymphocyte activation. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3868–3873. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Tsai S., Bonner W. M. Patterns of histone variant synthesis can distinguish G0 from G1 cells. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong R., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7409–7425. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]