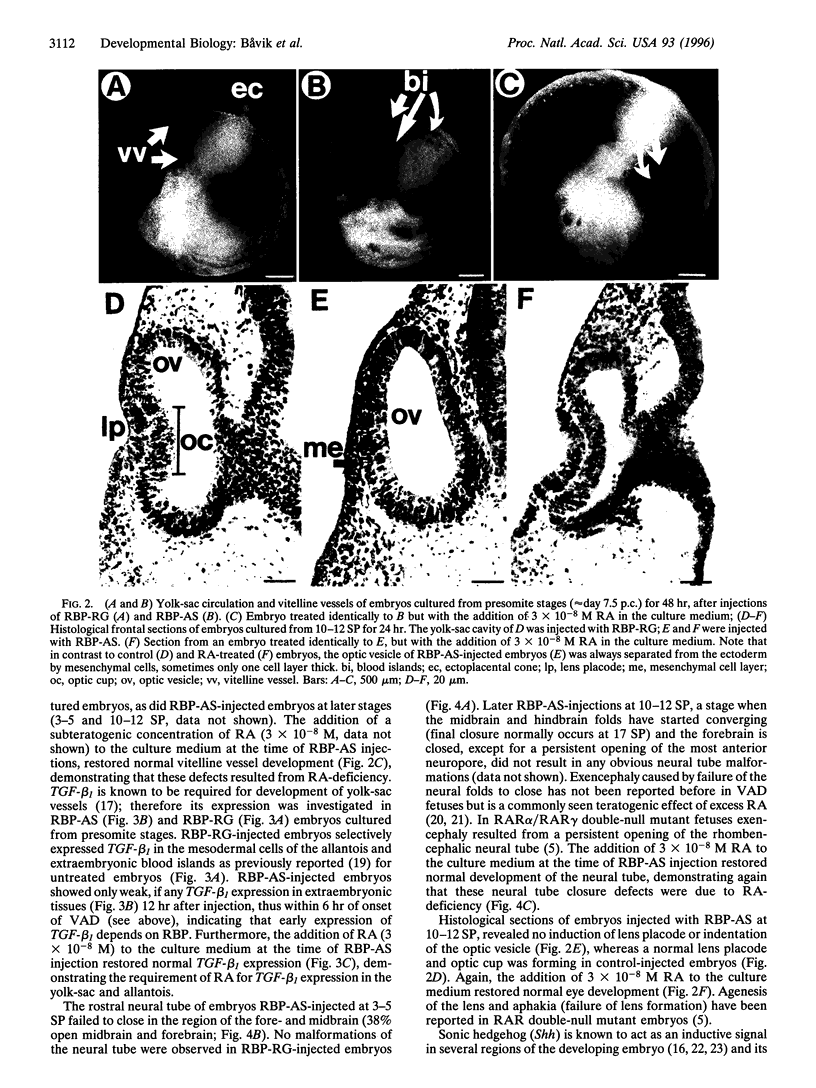
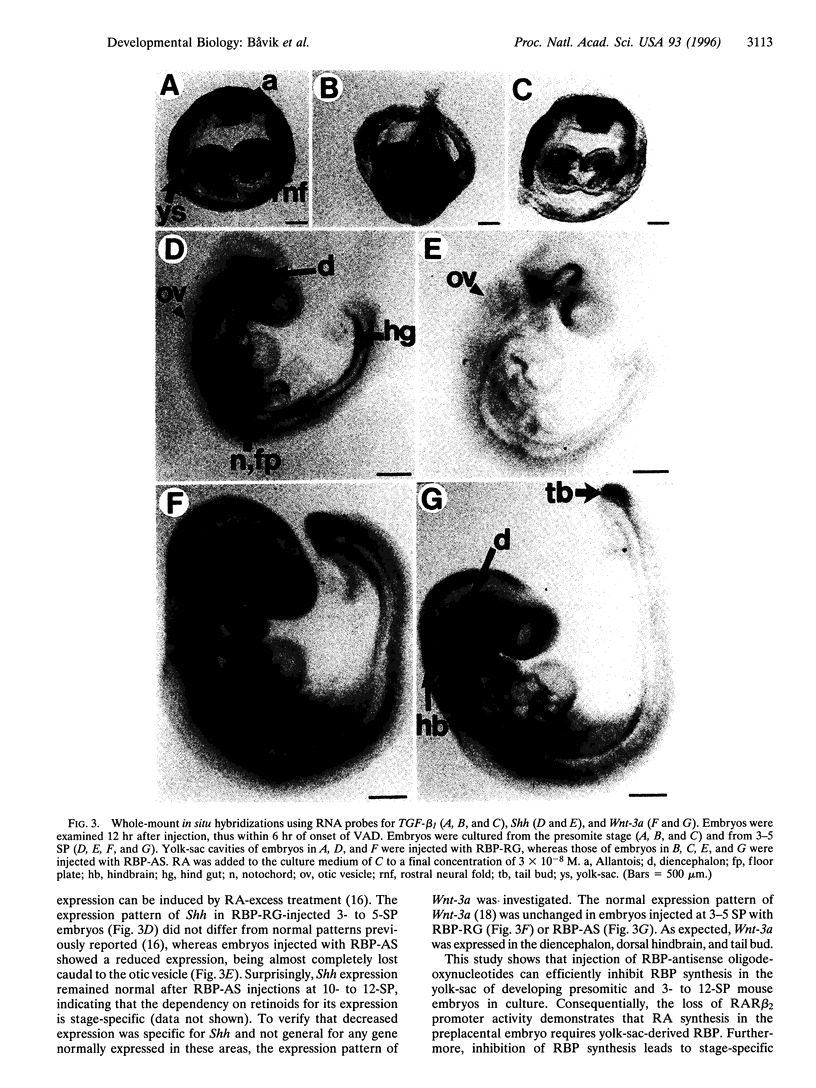
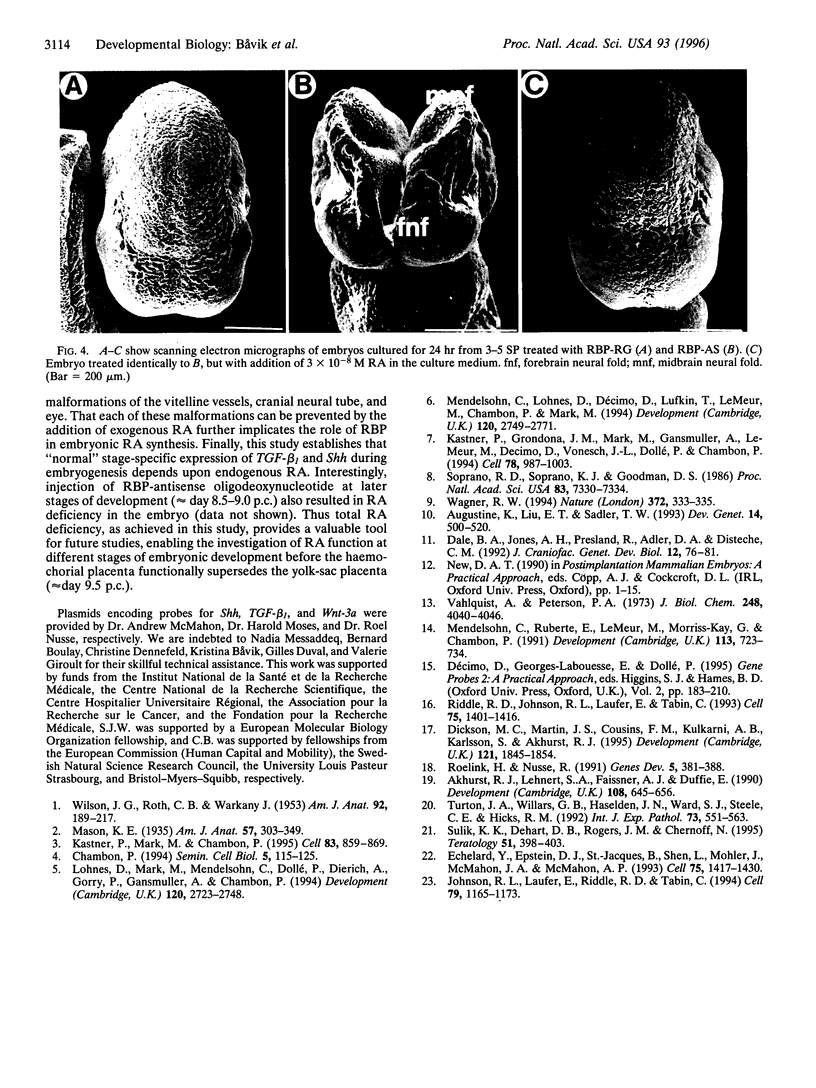
Abstract
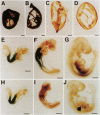
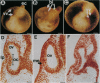
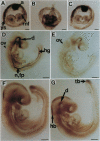
Presomitic and 3- to 12-somite pair cultured mouse embryos were deprived of retinoic acid (RA) by yolk-sac injections of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides for retinol binding protein (RBP). Inhibition of yolk-sac RBP synthesis was verified by immunohistochemistry, and the loss of activity of a lacZ-coupled RA-sensitive promoter demonstrated that embryos rapidly became RA-deficient. This deficiency resulted in malformations of the vitelline vessels, cranial neural tube, and eye, depending upon the stage of embryonic development at the time of antisense injection. Addition of RA to the culture medium at the time of antisense injection restored normal development implicating the role of RBP in embryonic RA synthesis. Furthermore, the induced RA deficiency resulted in early down-regulation of developmentally important genes including TGF-beta1 and Shh.
Full text
PDF
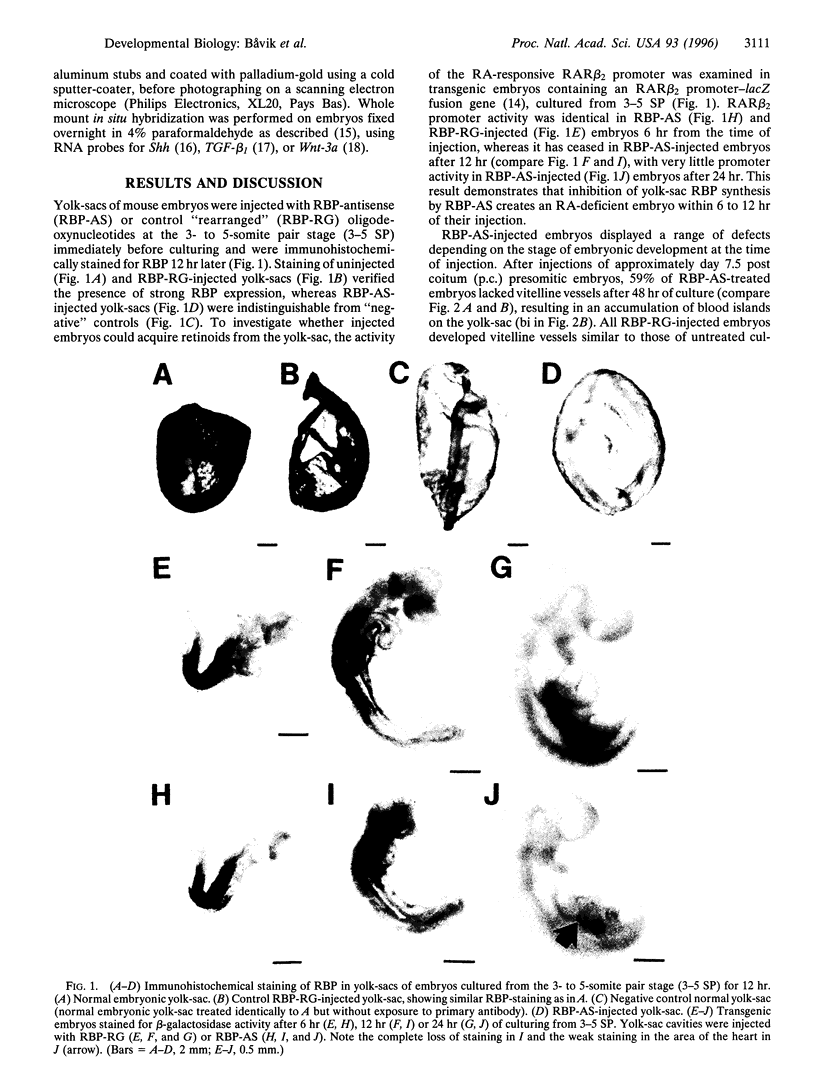
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhurst R. J., Lehnert S. A., Faissner A., Duffie E. TGF beta in murine morphogenetic processes: the early embryo and cardiogenesis. Development. 1990 Apr;108(4):645–656. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine K., Liu E. T., Sadler T. W. Antisense attenuation of Wnt-1 and Wnt-3a expression in whole embryo culture reveals roles for these genes in craniofacial, spinal cord, and cardiac morphogenesis. Dev Genet. 1993;14(6):500–520. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020140611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambon P. The retinoid signaling pathway: molecular and genetic analyses. Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;5(2):115–125. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B. A., Jones A. H., Presland R., Adler D. A., Disteche C. M. Chromosomal localization of the retinol binding protein gene and its elimination as a candidate gene for the repeated epilation (Er) mutation in mice. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1992 Apr-Jun;12(2):76–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson M. C., Martin J. S., Cousins F. M., Kulkarni A. B., Karlsson S., Akhurst R. J. Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor-beta 1 knock out mice. Development. 1995 Jun;121(6):1845–1854. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.6.1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echelard Y., Epstein D. J., St-Jacques B., Shen L., Mohler J., McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P. Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1417–1430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Laufer E., Riddle R. D., Tabin C. Ectopic expression of Sonic hedgehog alters dorsal-ventral patterning of somites. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1165–1173. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Grondona J. M., Mark M., Gansmuller A., LeMeur M., Decimo D., Vonesch J. L., Dollé P., Chambon P. Genetic analysis of RXR alpha developmental function: convergence of RXR and RAR signaling pathways in heart and eye morphogenesis. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):987–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohnes D., Mark M., Mendelsohn C., Dollé P., Dierich A., Gorry P., Gansmuller A., Chambon P. Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development (I). Craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities in RAR double mutants. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2723–2748. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Lohnes D., Décimo D., Lufkin T., LeMeur M., Chambon P., Mark M. Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development (II). Multiple abnormalities at various stages of organogenesis in RAR double mutants. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2749–2771. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Ruberte E., LeMeur M., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Developmental analysis of the retinoic acid-inducible RAR-beta 2 promoter in transgenic animals. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):723–734. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle R. D., Johnson R. L., Laufer E., Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1401–1416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelink H., Nusse R. Expression of two members of the Wnt family during mouse development--restricted temporal and spatial patterns in the developing neural tube. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):381–388. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano D. R., Soprano K. J., Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein and transthyretin mRNA levels in visceral yolk sac and liver during fetal development in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7330–7334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulik K. K., Dehart D. B., Rogers J. M., Chernoff N. Teratogenicity of low doses of all-trans retinoic acid in presomite mouse embryos. Teratology. 1995 Jun;51(6):398–403. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420510605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turton J. A., Willars G. B., Haselden J. N., Ward S. J., Steele C. E., Hicks R. M. Comparative teratogenicity of nine retinoids in the rat. Int J Exp Pathol. 1992 Oct;73(5):551–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahlquist A., Peterson P. A. Combination of specific antibodies with the human vitamin A-transporting protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):4040–4046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON J. G., ROTH C. B., WARKANY J. An analysis of the syndrome of malformations induced by maternal vitamin A deficiency. Effects of restoration of vitamin A at various times during gestation. Am J Anat. 1953 Mar;92(2):189–217. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000920202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. W. Gene inhibition using antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):333–335. doi: 10.1038/372333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]