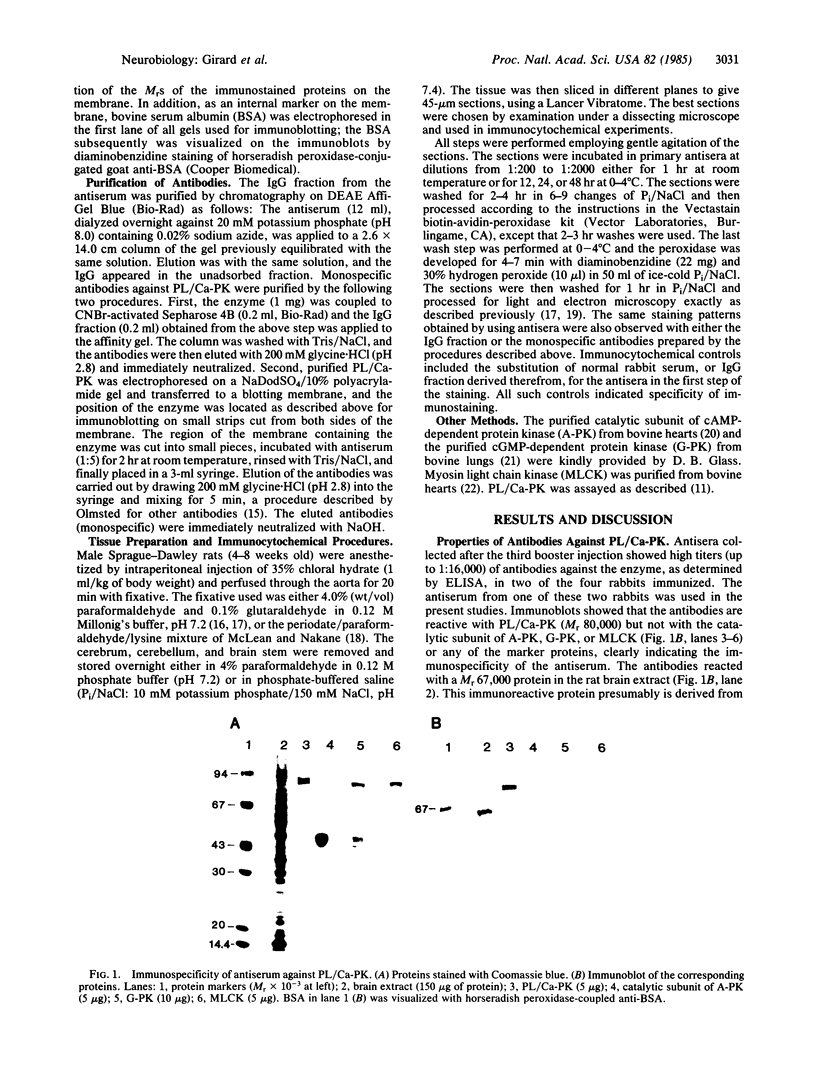
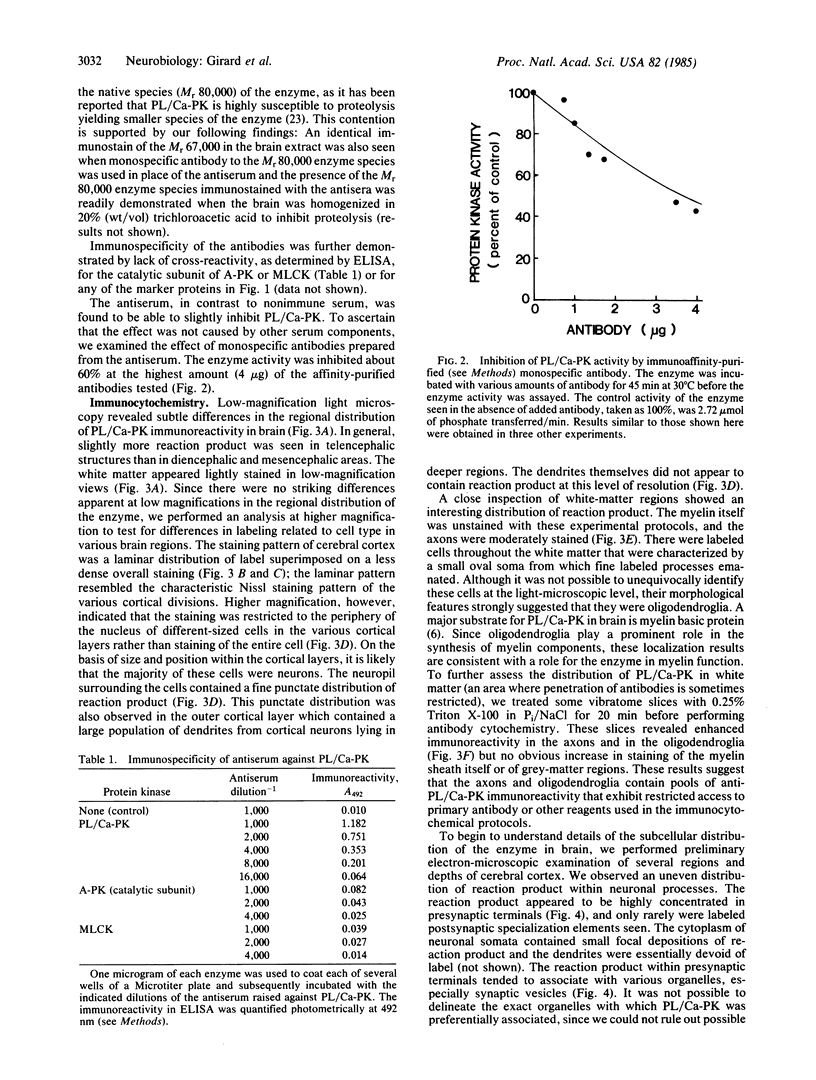
Abstract
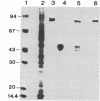
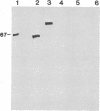
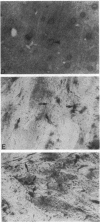
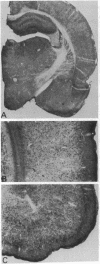
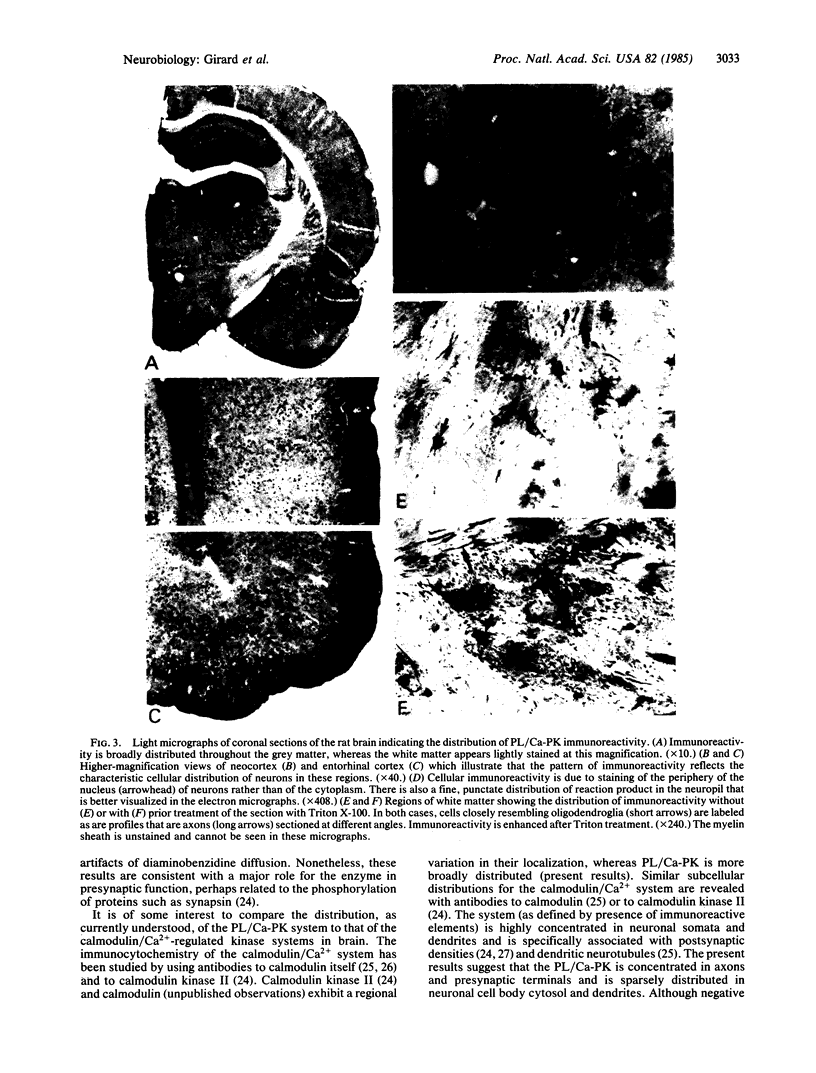
Antisera against phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) were raised in rabbits. Immunospecificity of the polyclonal antibodies, as determined by immunoblot and ELISA, was shown by their reactivity to the enzyme but not to other protein kinases or any of many other proteins tested. Immunocytochemical localization of the kinase in rat brains revealed that although the enzyme was distributed broadly in different brain regions, it was highly restricted to the periphery of the nucleus of neurons in cerebral cortex and to axons and cells strongly resembling oligodendroglia in white-matter regions. Initial electron microscopy of cerebral cortex revealed that the enzyme was highly concentrated in the presynaptic terminals, and only rarely were labeled postsynaptic specialization elements seen. It is suggested that the discrete localization of the enzyme, which is distinct from that of the calmodulin/Ca2+-dependent system, may be related to certain biological and functional aspects of brain that are regulated by Ca2+ at the level of protein phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bechtel P. J., Beavo J. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of catalytic subunit of skeletal muscle adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2691–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng T. P., Byrd F. I., Whitaker J. N., Wood J. G. Immunocytochemical localization of coated vesicle protein in rodent nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):624–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Comparison of the substrate specificity of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate- and guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. Kinetic studies using synthetic peptides corresponding to phosphorylation sites in histone H2B. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9728–9738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grab D. J., Berzins K., Cohen R. S., Siekevitz P. Presence of calmodulin in postsynaptic densities isolated from canine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8690–8696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Kajikawa N., Shiota M., Nishizuka Y. Proteolytic activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by calcium-dependent neutral protease. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1156–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Mazzei G. J. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase: a major protein phosphorylation system. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 May;35(2-3):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Localization of calmodulin in rat cerebellum by immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):473–480. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., McGuinness T. L., Greengard P. Immunocytochemical localization of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5604–5608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Raynor R. L., Fritz R. B., Kuo J. F. Purification to homogeneity, characterization and monoclonal antibodies of phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from spleen. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):435–443. doi: 10.1042/bj2090435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. S., Chou C. H., Kibler R. F., Kuo J. F. Basic protein in brain myelin is phosphorylated by endogenous phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. J Neurochem. 1982 Nov;39(5):1397–1404. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. S., Chou C. H., Mazzei G. J., Dembure P., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+ -dependent protein kinase preferentially phosphorylates serine-115 of bovine myelin basic protein. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1257–1264. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Filburn C. R. Affinity chromatography of protein kinase C-phorbol ester receptor on polyacrylamide-immobilized phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12311–12314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Vallet B., Autric F., Demaille J. G. Purification and characterization of bovine cardiac calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12136–12144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. I. Purification and general properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Wallace R. W., Whitaker J. N., Cheung W. Y. Immunocytochemical localization of calmodulin and a heat-labile calmodulin-binding protein (CaM-BP80) in basal ganglia of mouse brain. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):66–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]