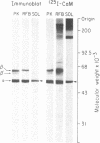
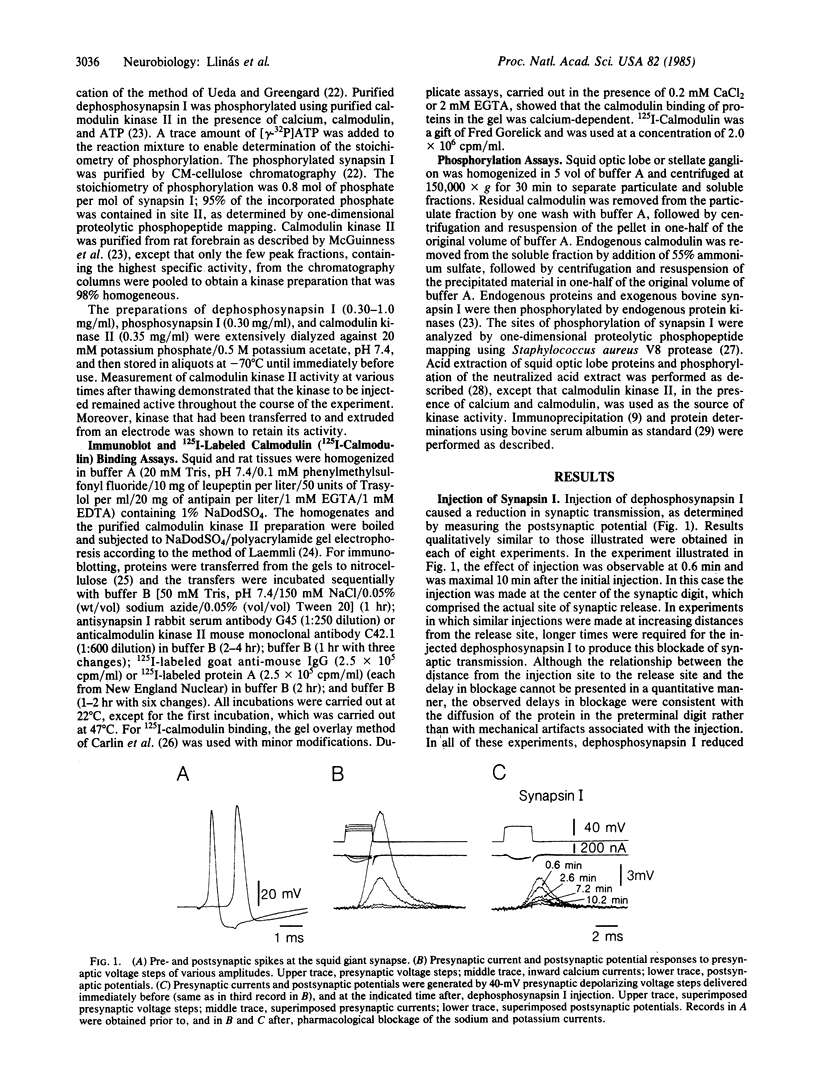
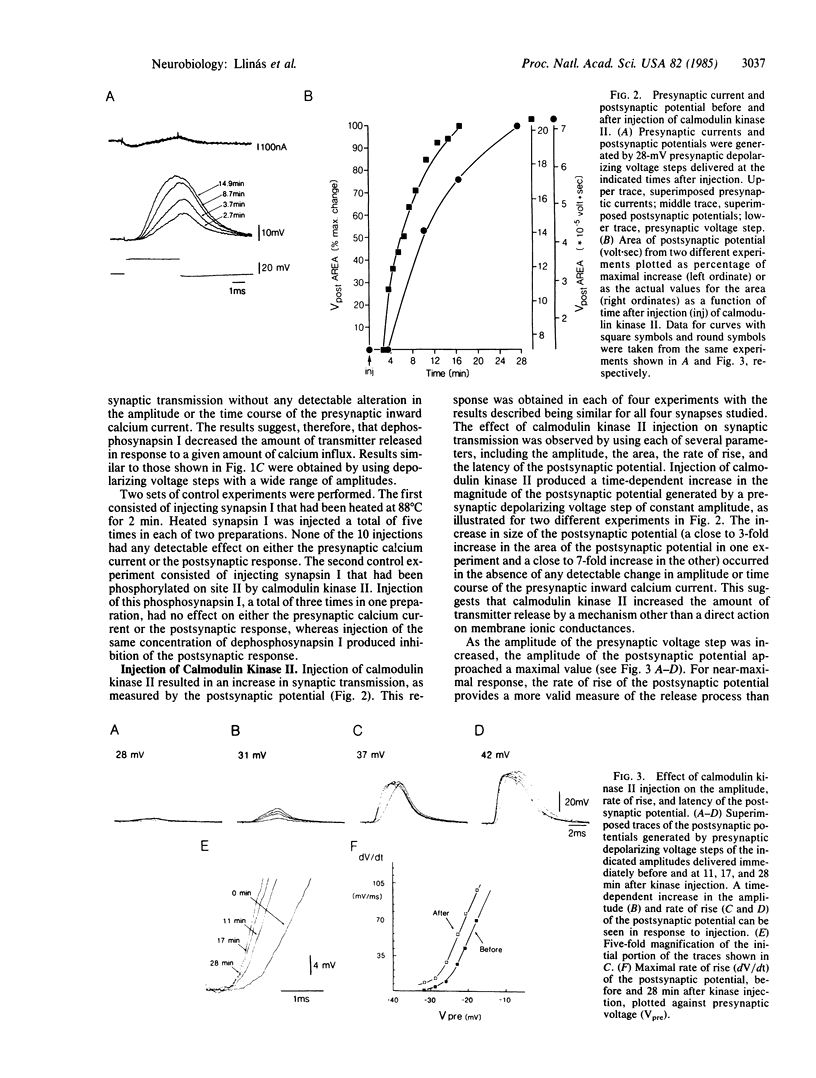
Abstract
Synapsin I and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II were pressure-injected into the preterminal digit of the squid giant synapse to test directly the possible regulation of neurotransmitter release by these substances. Neurotransmitter release was determined by measuring the amplitude, rate of rise, and latency of the postsynaptic potential generated in response to presynaptic depolarizing steps under voltage clamp conditions. Injection of dephosphosynapsin I decreased the amplitude and rate of rise of the postsynaptic potential, whereas injection of either phosphosynapsin I or heat-treated dephosphosynapsin I was without effect. Conversely, injection of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, which phosphorylates synapsin I on site II, increased the rate of rise and amplitude and decreased the latency of the postsynaptic potential. The effects of these proteins were observed without any detectable change in the initial phase of the presynaptic calcium current. A synapsin I-like protein and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II were demonstrated by biochemical and immunochemical techniques to be present in squid nervous tissue. The data support the hypothesis that synapsin I regulates the availability of synaptic vesicles for release; we propose that calcium entry into the nerve terminal activates calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, which phosphorylates synapsin I on site II, dissociating it from the vesicles and thereby removing a constraint in the release process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlin R. K., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Function of a calmodulin in postsynaptic densities. III. Calmodulin-binding proteins of the postsynaptic density. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):449–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Harris S. M., Jr, Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Synapsin I (Protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. II. Its specific association with synaptic vesicles demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in agarose-embedded synaptosomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1355–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRiemer S. A., Kaczmarek L. K., Lai Y., McGuinness T. L., Greengard P. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphorylation in the nervous system of Aplysia. J Neurosci. 1984 Jun;4(6):1618–1625. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-06-01618.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Greengard P. Neurotransmitter- and neuromodulator-dependent alterations in phosphorylation of protein I in slices of rat facial nucleus. J Neurosci. 1981 Feb;1(2):192–203. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-02-00192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Greengard P. Serotonin stimulates phosphorylation of protein I in the facial motor nucleus of rat brain. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):76–79. doi: 10.1038/289076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarizing agents and cyclic nucleotides regulate the phosphorylation of specific neuronal proteins in rat cerebral cortex slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H. Molecular biology of learning: modulation of transmitter release. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):433–443. doi: 10.1126/science.6289442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B. Experimental approaches to understanding the role of protein phosphorylation in the regulation of neuronal function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:493–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarization-induced phosphorylation of specific proteins, mediated by calcium ion influx, in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2764–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents in squid giant synapse. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):289–321. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84898-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Relationship between presynaptic calcium current and postsynaptic potential in squid giant synapse. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):323–351. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84899-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Simon S. M. Transmission by presynaptic spike-like depolarization in the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2415–2419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness T. L., Lai Y., Greengard P. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Isozymic forms from rat forebrain and cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1696–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness T. L., Lai Y., Greengard P., Woodgett J. R., Cohen P. A multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Similarities between skeletal muscle glycogen synthase kinase and a brain synapsin I kinase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 14;163(2):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80846-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I in nerve terminals: selective association with small synaptic vesicles. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1209–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.6438799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Dopamine and depolarizing agents regulate the state of phosphorylation of protein I in the mammalian superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7479–7483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Nerve impulses increase the phosphorylation state of protein I in rabbit superior cervical ganglion. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):452–454. doi: 10.1038/296452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation in the brain. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):583–588. doi: 10.1038/305583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintar J. E., Levitt P., Salach J. I., Weyler W., Rosenberg M. B., Breakefield X. O. Specificity of antisera prepared against pure bovine MAO-B. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 3;276(1):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsou K., Greengard P. Regulation of phosphorylation of proteins I, IIIa, and IIIb in rat neurohypophysis in vitro by electrical stimulation and by neuroactive agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6075–6079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Aswad D. W., Greengard P. A dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):69–71. doi: 10.1038/301069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. I. Regional and cellular distribution in the rat brain. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):84–98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00084.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]