Abstract
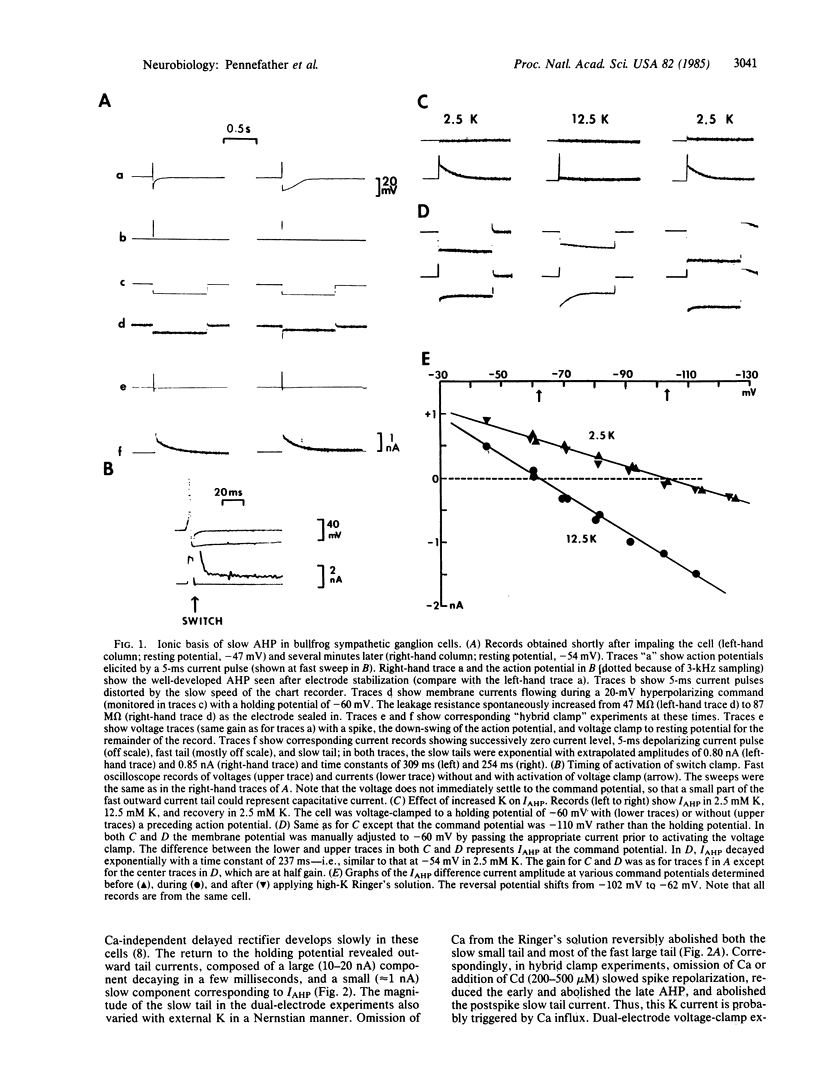
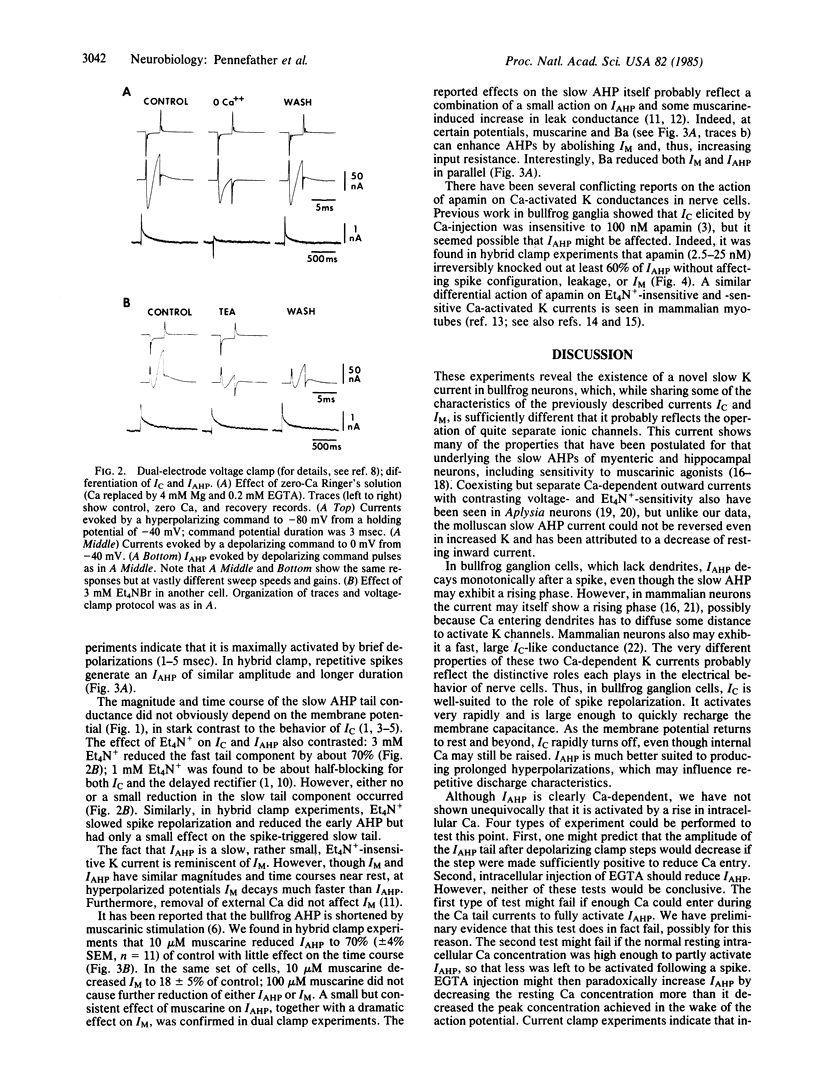
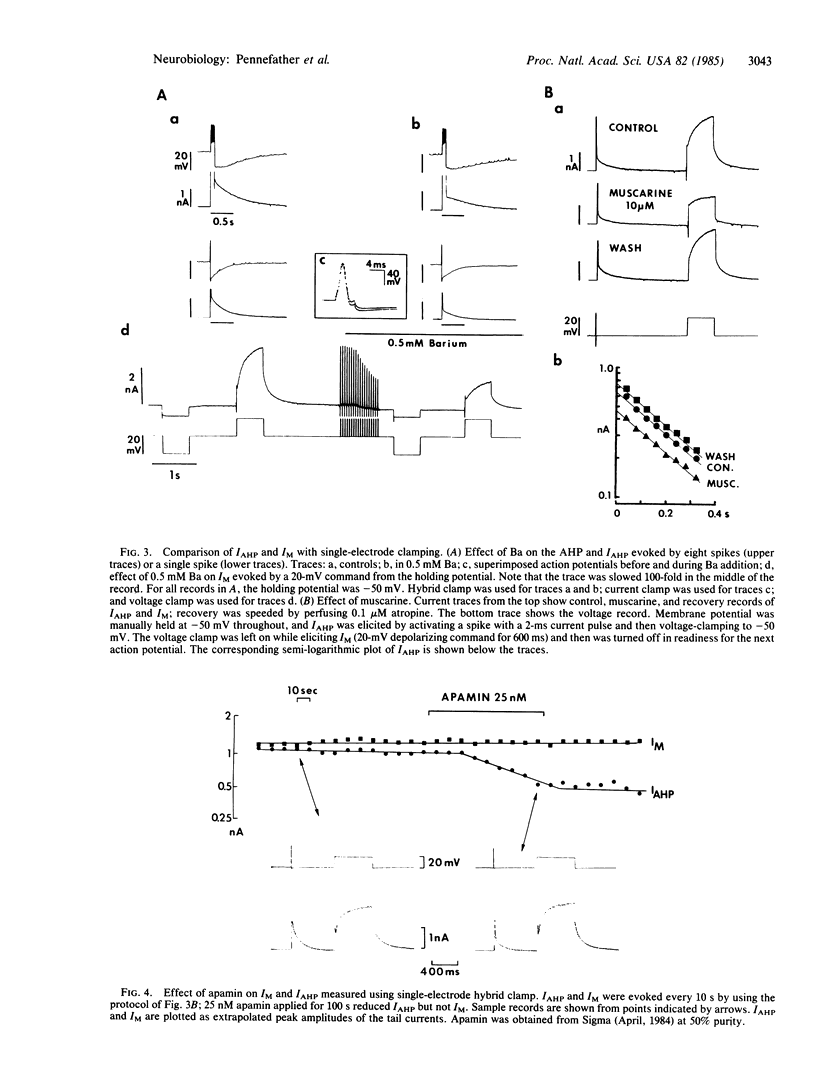
Healthy bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells often show a two-component afterhyperpolarization (AHP). Both components can be reduced or abolished by adding Ca-channel blockers or by removing external Ca. Application of a single electrode "hybrid clamp"--i.e., switching from current- to voltage-clamp at the peak of the AHP, reveals that the slow AHP component is generated by a small, slow, monotonically decaying outward current, which we call IAHP. IAHP is blocked by Ca-removal or by apamin and is a pure K current. It is slightly sensitive to muscarine and to tetraethylammonium ion but is much less so than muscarine-sensitive (IM) and fast Ca-dependent (IC) K currents. It also can be recorded in dual-electrode voltage-clamp experiments, where it is seen as a slow, small component of the outward tail current that follows brief depolarizations to 0 mV or beyond. IC is seen as an early, fast, large component of the same tail current. Both components are blocked by Ca removal, but only the IC component is blocked by low doses of tetraethylammonium ion. Thus, bullfrog ganglion cells exhibit two quite distinct Ca-dependent K currents, which differ in size, voltage-sensitivity, kinetics, and pharmacology. These two currents also play quite separate roles in shaping the action potential.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F., Dribin L. B. Calcium-dependent slow potassium conductance in rat skeletal myotubes. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90450-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Ion conductance and selectivity of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Jul;84(1):1–23. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A., Adams P. R. Ca-activated potassium current in vertebrate sympathetic neurons. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Potassium channels in myelinated nerve. Selective permeability to small cations. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):669–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Koketsu K. Analysis of the slow excitatory postsynaptic potential in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1976;26(6):651–669. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.26.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Morita K., Nohmi M. Origin of calcium ions involved in the generation of a slow afterhyperpolarization in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Nov;399(3):194–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00656714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Weight F. F. Action potential repolarization may involve a transient, Ca2+-sensitive outward current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):185–188. doi: 10.1038/300185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tokimasa T. Depression of calcium-dependent potassium conductance of guinea-pig myenteric neurones by muscarinic agonists. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:253–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Lazdunski M. The coexistence in rat muscle cells of two distinct classes of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with different pharmacological properties and different physiological functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T. Muscarinic agonists depress calcium-dependent gK in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 Apr;10(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



