Abstract
Mycobacterium paratuberculosis (National Animal Disease Center strain 18 and American Type Culture Collection strain 19698), the causative agent of Johne Disease (bovine paratuberculosis), contains a major immunoreactive glycopeptidolipid (polar GPL-I) that has been isolated and characterized. (formula; see text) Thus, the glycolipid antigen belongs to the polar mycoside C glycopeptidolipid family present in other mycobacterial species. The distal 2,3-di-O-methyl-alpha-L-fucopyranosyl-(1----3)-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosi de unit, the obvious antigen determinant, appears to be characteristic of M. paratuberculosis. The glycolipid can be recognized readily in isolates of M. paratuberculosis by TLC and its presence may be used as a characteristic marker of the infectious agent. The polar glycopeptidolipid was highly reactive in ELISA against serum from an animal hyperimmunized with M. paratuberculosis strain 18, indicating its basic immunogenicity.
Full text
PDF

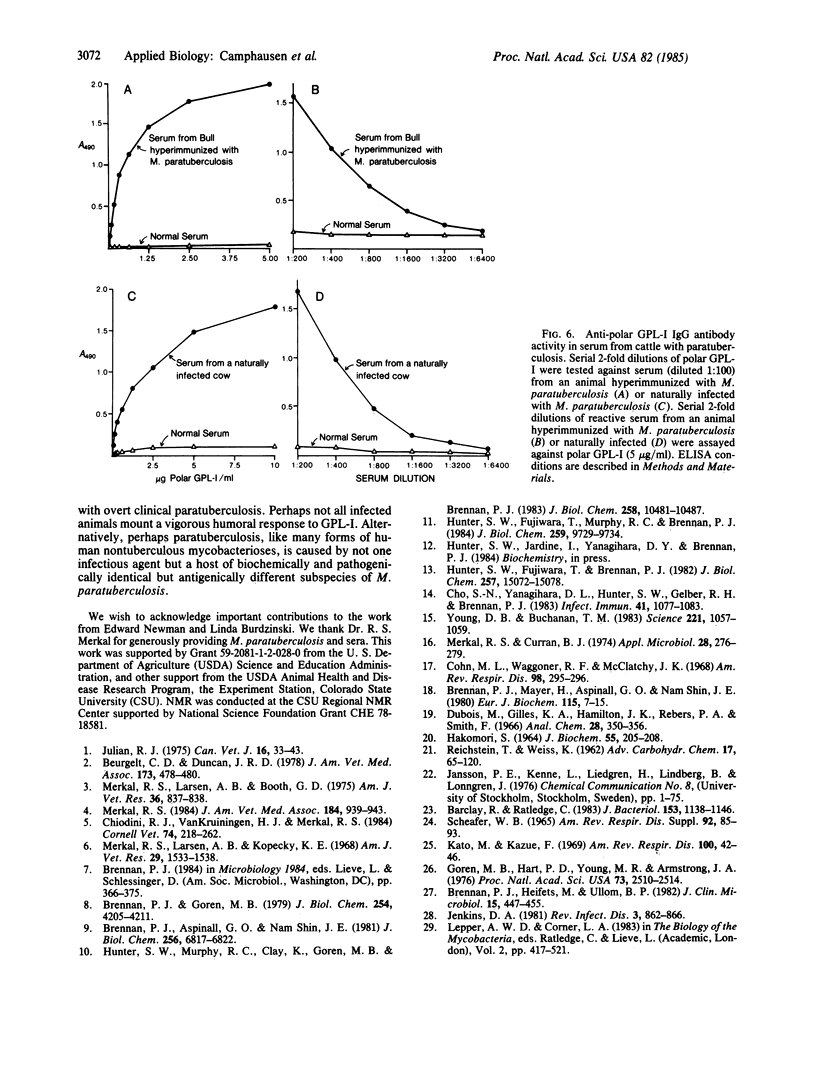
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay R., Ratledge C. Iron-binding compounds of Mycobacterium avium, M. intracellulare, M. scrofulaceum, and mycobactin-dependent M. paratuberculosis and M. avium. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1138–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1138-1146.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Aspinall G. O., Shin J. E. Structure of the specific oligosaccharides from the glycopeptidolipid antigens of serovars in the Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare-Mycobacterium scrofulaceum complex. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6817–6822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Goren M. B. Structural studies on the type-specific antigens and lipids of the mycobacterium avium. Mycobacterium intracellulare. Mycobacterium scrofulaceum serocomplex. Mycobacterium intracellulare serotype 9. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4205–4211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Heifets M., Ullom B. P. Thin-layer chromatography of lipid antigens as a means of identifying nontuberculous mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):447–455. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.447-455.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Mayer H., Aspinall G. O., Nam Shin J. E. Structures of the glycopeptidolipid antigens from serovars in the Mycobacterium avium/Mycobacterium intracellulare/Mycobacterium scrofulaceum serocomplex. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar 16;115(1):7–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buergelt C. D., Duncan J. R. Age and milk production data of cattle culled from a dairy herd with paratuberculosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 1):478–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Ruminant paratuberculosis (Johne's disease): the current status and future prospects. Cornell Vet. 1984 Jul;74(3):218–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S. N., Yanagihara D. L., Hunter S. W., Gelber R. H., Brennan P. J. Serological specificity of phenolic glycolipid I from Mycobacterium leprae and use in serodiagnosis of leprosy. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1077-1083.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn M. L., Waggoner R. F., McClatchy J. K. The 7H11 medium for the cultivation of mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Aug;98(2):295–296. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.98.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., D'Arcy Hart P., Young M. R., Armstrong J. A. Prevention of phagosome-lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages by sulfatides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2510–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Fujiwara T., Brennan P. J. Structure and antigenicity of the major specific glycolipid antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15072–15078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Fujiwara T., Murphy R. C., Brennan P. J. N-acylkansosamine. A novel N-acylamino sugar from the trehalose-containing lipooligosaccharide antigens of Mycobacterium kansasii. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9729–9734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Murphy R. C., Clay K., Goren M. B., Brennan P. J. Trehalose-containing lipooligosaccharides. A new class of species-specific antigens from Mycobacterium. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10481–10487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins P. A. Lipid analysis for the identification of mycobacteria: an appraisal. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):862–866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian R. J. A short review and some observations on Johne's disease with recommendations for control. Can Vet J. 1975 Feb;16(2):33–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Fukushi K. Studies of a biochemical lesion in experimental tuberculosis in mice. X. Mitochondrial swelling induced by cord factor in vivo and accompanying biochemical change. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Jul;100(1):42–46. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Curran B. J. Growth and metabolic characteristics of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):276–279. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.276-279.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Larsen A. B., Booth G. D. Analysis of the effect of inapparent bovine paratuberculosis. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jun;36(6):837–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S., Larsen A. B., Kopecky K. E. Comparison of examination and test methods for early detection of paratuberculous cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Aug;29(8):1533–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkal R. S. Paratuberculosis: advances in cultural, serologic, and vaccination methods. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Apr 15;184(8):939–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Buchanan T. M. A serological test for leprosy with a glycolipid specific for Mycobacterium leprae. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1057–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.6348948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]