Abstract
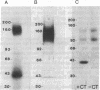
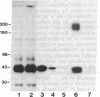
The guanosine 5'-[beta, gamma-imido]triphosphate (p[NH]ppG)-activated adenylate cyclase from rabbit myocardial membranes was purified approximately equal to 60,000-fold to a specific activity of 15 mumol X mg-1 X min-1 by Lubrol PX extraction, affinity chromatography, and gel permeation HPLC. The major purification (greater than 2000-fold) was achieved by affinity chromatography on forskolin-Sepharose, a method previously developed in this laboratory. The final product appeared as two major peptides of Mr 150,000 and 42,000 and one minor peptide of Mr 45,000 when analyzed by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. It is suggested that the Mr 42,000 and 150,000 components represent the alpha-subunit of the stimulatory guanine nucleotide binding regulatory protein (GS) and the catalytic unit, respectively, because upon crosslinking of a reconstituted adenylate cyclase containing the [32P]ADP-ribosylated alpha-subunit of GS (Mr, 42,000), a single radiolabeled product of Mr 190,000 appeared on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels. Further identification is based on the correlation of the Mr 150,000/42,000 bands with enzymatic activity when the purified enzyme was analyzed by various chromatographic procedures.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen T. J., Heideman W., Rosenberg G. B., Storm D. R. Photoaffinity labeling of brain adenylate cyclase preparations with azido[125 I]iodocalmodulin. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2757–2762. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell G. S., Ayers J. S., Hancock W. S., Hearn M. T. A novel method of activation of cross-linked agaroses with 1,1'-carbonyldiimidazole which gives a matrix for affinity chromatography devoid of additional charged groups. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2572–2574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Hewlett E. L., Gilman A. G. Identification of the predominant substrate for ADP-ribosylation by islet activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2072–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt D. R., Asano T., Pedersen S. E., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of catecholamine-stimulated guanosinetriphosphatase activity. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4357–4362. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri Y., Schramm M. Resolution, reconstitution and kinetics of the primary action of a hormone receptor. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):297–300. doi: 10.1038/287297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Hildebrandt J., Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R. Pertussis toxin substrate, the putative Ni component of adenylyl cyclases, is an alpha beta heterodimer regulated by guanine nucleotide and magnesium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4276–4280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Self-assembly in Vitro of the 68,000 molecular weight component of the mammalian neurofilament triplet proteins into intermediate-sized filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Haga K., Gilman A. G. Hydrodynamic properties of the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase from wild type and varient S49 lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5776–5782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanski E., Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Dromerick A. W., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties of the turkey erythrocyte protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12911–12919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M., Bechet J. J., d'Albis A. Disuccinimidyl esters as bifunctional crosslinking reagents for proteins: assays with myosin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 15;102(2):282–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6228–6234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr, Glossmann H. Plasma membrane protein subunit composition. A comparative study by discontinuous electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6335–6338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Smigel M. D., Schleifer L. S., Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Purification of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6516–6520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. GTP-binding proteins in membranes and the control of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7224–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T., Gaugler B., Metzger H. Isolation of homologous and heterologous complexes between catalytic and regulatory components of adenylate cyclase by forskolin-Sepharose. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. Guanine nucleotide-controlled interactions between components of adenylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):85–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Howlett A. C., Ferguson K. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity with resolved components of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6401–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Kempner E. S., Rodbell M. Activation of adenylate cyclase in hepatic membranes involves interactions of the catalytic unit with multimeric complexes of regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5168–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Bleil J. D., Wassarman P. M. Quantitation of nanogram amounts of protein using [3H]dinitrofluorobenzene. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):354–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90850-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Daly J. W., Metzger H., de Souza N. J., Reden J. Structure-activity relationships for activation of adenylate cyclase by the diterpene forskolin and its derivatives. J Med Chem. 1983 Mar;26(3):436–439. doi: 10.1021/jm00357a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorr R. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Purification of the beta-adrenergic receptor. Identification of the hormone binding subunit. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5820–5826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]