Abstract
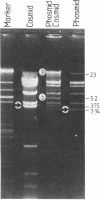
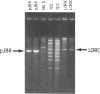
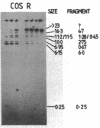
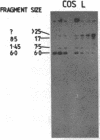
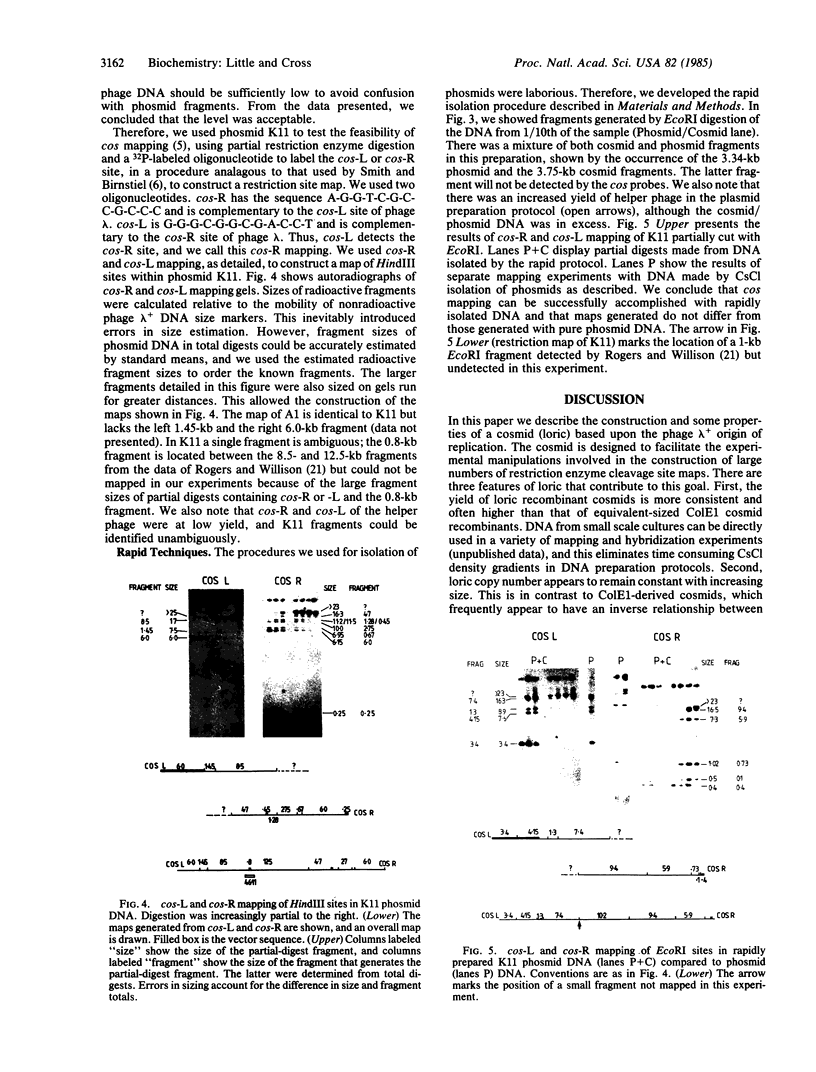
We describe the construction and use of a cosmid vector, loric, which is derived from the phage lambda origin of replication and appears to be more stable than ColE1-derived cosmids. Loric recombinants can be efficiently packaged in vivo to yield 100-300 micrograms of DNA per liter that is linear and has single-stranded cos ends. We call such molecules "phosmids." Phosmid restriction maps can be rapidly generated by labeling either the left or right cos site by annealing on a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide complementary to either cos-L or cos-R. Partial restriction enzyme digestion, agarose gel electrophoresis, and autoradiography are used to size restriction fragments of increasing length, all of which terminate at the labeled cos site. The procedures have been tested by isolating and mapping a region of the H-2 locus of mouse chromosome 17.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod H. R., Artzt K., Bennett D. Rescue of embryonic cells homozygous for a lethal haplotype of the T/t complex: tw12. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Spierer P., Hogness D. S. Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):17–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R. Huntington's disease. Charting the path to the gene. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):404–405. doi: 10.1038/308404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Skalka A. Replication of bacteriophage lambda DNA dependent on the function of host and viral genes. I. Interaction of red, gam and rec. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):185–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Siegele D. A., Rudolph C. F., Frackman S. Cosmid DNA packaging in vivo. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. DNA sequences necessary for packaging of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7456–7460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. F., Treisman R., Bierut L., Seed B., Maniatis T. Plasmid vectors for the rapid isolation and transcriptional analysis of human beta-globin gene alleles. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Dec;1(5):473–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara K. Replication control system in lambda dv. Plasmid. 1981 Jan;5(1):32–52. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Guild G. M., Prestidge L. S., Hogness D. S. A new high-capacity cosmid vector and its use. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Rackwitz H. R., Frischauf A. M., Hohn B., Lehrach H. Selective isolation of cosmid clones by homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4129–4133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Kacich R., Ptashne M. A general method for maximizing the expression of a cloned gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H., Willison K. R. A major rearrangement in the H-2 complex of mouse t haplotypes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):549–552. doi: 10.1038/304549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Jorgensen R. A., Postle K., Reznikoff W. S. The inverted repeats of Tn5 are functionally different. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):795–805. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Parker R. C., Davidson N. Representation of DNA sequences in recombinant DNA libraries prepared by restriction enzyme partial digestion. Gene. 1982 Sep;19(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Purification of genomic sequences from bacteriophage libraries by recombination and selection in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2427–2445. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Theoretical study of the fraction of a long-chain DNA that can be incorporated in a recombinant DNA partial-digest library. Biopolymers. 1982 Sep;21(9):1793–1810. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Weisberg R. Packaging of coliphage lambda DNA. I. The role of the cohesive end site and the gene A protein. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):717–731. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Weisberg R. Packaging of prophage and host DNA by coliphage lambda. Nature. 1975 Jul 10;256(5513):97–103. doi: 10.1038/256097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub F., Thompson E. B. An improved method for preparing large arrays of bacterial colonies containing plasmids for hybridization: in situ purification and stable binding of DNA on paper filters. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]