ABSTRACT
The fungal pathogen Candida albicans causes macrophage death and escapes, but the molecular mechanisms remained unknown. Here we used live-cell imaging to monitor the interaction of C. albicans with macrophages and show that C. albicans kills macrophages in two temporally and mechanistically distinct phases. Early upon phagocytosis, C. albicans triggers pyroptosis, a proinflammatory macrophage death. Pyroptosis is controlled by the developmental yeast-to-hypha transition of Candida. When pyroptosis is inactivated, wild-type C. albicans hyphae cause significantly less macrophage killing for up to 8 h postphagocytosis. After the first 8 h, a second macrophage-killing phase is initiated. This second phase depends on robust hyphal formation but is mechanistically distinct from pyroptosis. The transcriptional regulator Mediator is necessary for morphogenesis of C. albicans in macrophages and the establishment of the wild-type surface architecture of hyphae that together mediate activation of macrophage cell death. Our data suggest that the defects of the Mediator mutants in causing macrophage death are caused, at least in part, by reduced activation of pyroptosis. A Mediator mutant that forms hyphae of apparently wild-type morphology but is defective in triggering early macrophage death shows a breakdown of cell surface architecture and reduced exposed 1,3 β-glucan in hyphae. Our report shows how Candida uses host and pathogen pathways for macrophage killing. The current model of mechanical piercing of macrophages by C. albicans hyphae should be revised to include activation of pyroptosis by hyphae as an important mechanism mediating macrophage cell death upon C. albicans infection.
IMPORTANCE
Upon phagocytosis by macrophages, Candida albicans can transition to the hyphal form, which causes macrophage death and enables fungal escape. The current model is that the highly polarized growth of hyphae results in macrophage piercing. This model is challenged by recent reports of C. albicans mutants that form hyphae of wild-type morphology but are defective in killing macrophages. We show that C. albicans causes macrophage cell death by at least two mechanisms. Phase 1 killing (first 6 to 8 h) depends on the activation of the pyroptotic programmed host cell death by fungal hyphae. Phase 2 (up to 24 h) is rapid and depends on robust hyphal formation but is independent of pyroptosis. Our data provide a new model for how the interplay between fungal morphogenesis and activation of a host cell death pathway mediates macrophage killing by C. albicans hyphae.
INTRODUCTION
Candida albicans is a human commensal but is also an important human pathogen responsible for more than 400,000 cases of invasive disease per year, from which the mortality is high (1). A key virulence attribute for this organism is the ability to undergo developmental transitions that result in morphological plasticity. The budding yeast state is associated with commensalism, while the developmental transition to hyphal growth is generally related to disease (2). Hyphae are linked to the ability of C. albicans to evade phagocytic digestion by macrophages (3, 4). Signals within the phagocytic environment trigger the developmental transition to hyphae, resulting in the escape of hyphae at the expense of the host cell (3). Generally, yeast-form cells fail to cause damage and to escape from macrophages (4, 5). The current model is that the highly polarized growth of hyphae enables physical destruction of the macrophage by piercing of the fungal filaments through the macrophage plasma membrane (3). Challenging this model are findings that dissociate the ability of C. albicans to grow as hyphae from the ability to escape from macrophages (5, 6).
In addition to the morphological and size differences, a main distinguishing feature of yeast and hyphal cells is the structure of the cell wall (7–9). The C. albicans cell wall is made of glucose polymers 1,3 and 1,6 β-glucans, chitin, and a range of mannosylated proteins that decorate the cell surface. The differential expression and exposure of cell wall components are thought to be a major factor in how immune cells discriminate yeast from invasive hyphal forms (reviewed in reference 7). For example, differences between yeast and hyphae in β-glucan exposure have been proposed to lead to differential engagements with the cell surface pathogen recognition receptor (PRR) dectin-1 (10). Dectin-1 triggers proinflammatory interleukin-1β (IL-1β) expression via Syk kinase signaling, and activation of a cytoplasmic inflammasome that contains NLRP3, ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a carboxy-terminal CARD) and caspase-1 results in cleavage of pro-IL-1β to its bioactive form (11–14). Other pathogen recognition receptors also contribute to this pathway (12–14). Intracellular hyphae, but not yeast forms, induce caspase-1-dependent IL-1β secretion, although it remains unknown how the NLRP3/ASC inflammasome is activated under these conditions (12, 15). Intriguingly, dectin-1 signaling in some C. albicans isolates has been linked to a noncanonical inflammasome in which caspase-8, rather than caspase-1, was proposed to cleave and thereby activate IL-1β (14). That and other studies (16) suggest that C. albicans can adjust the composition of its cell wall during the course of infection to modulate innate immune responses. Indeed, a recent study suggested that factors additional to hyphal morphology lead to production of IL-1β (6).
Inflammasomes that induce IL-1β secretion can also trigger programmed cell death. In the case of caspase-1 activation, macrophages undergo a proinflammatory form of cell death termed pyroptosis. Other programmed cell death pathways, such as the canonical apoptosis and ordered necrosis, which depends on receptor-interacting kinases Rip1 and Rip3 (reviewed in reference 17), have also been shown to protect against viral and bacterial infections by either eliminating the replicative niche of the pathogens or exposing them to the immune system (18, 19). However, the timing of these pathways may be critical, as some microbial pathogens, including Salmonella, induce caspase-1- and Rip3-dependent cell death to trigger escape from macrophages and dissemination from the site of infection (20–22). Cell death pathways have mostly been studied in the context of bacterial and viral infections, and there is only limited evidence indicating whether they play a role in fungal disease (23, 24).
Here we show that C. albicans kills macrophages by inducing pyroptotic programmed cell death at early times post-phagocytosis (the first 8 h under our experimental conditions). Hyphal morphogenesis is important for induction of pyroptosis, and our data suggest that proper hyphal cell surface architecture mediates early macrophage killing and fungal escape. Pyroptosis-independent macrophage killing by Candida also occurs, particularly at later stages post-phagocytosis, and this requires robust hyphal morphogenesis. Activation of pyroptosis in response to Candida might serve to augment proinflammatory responses, but C. albicans might in addition hijack activation of this programmed cell death pathway to escape from macrophages and thus evade the innate immune response. These two scenarios are not mutually exclusive and offer an explanation for the paradoxical role of hyphal forms in C. albicans pathogenesis, whereby hyphae are both the virulent form of the pathogen and the form that triggers host immune responses.
RESULTS
C. albicans kills macrophages by triggering pyroptosis.
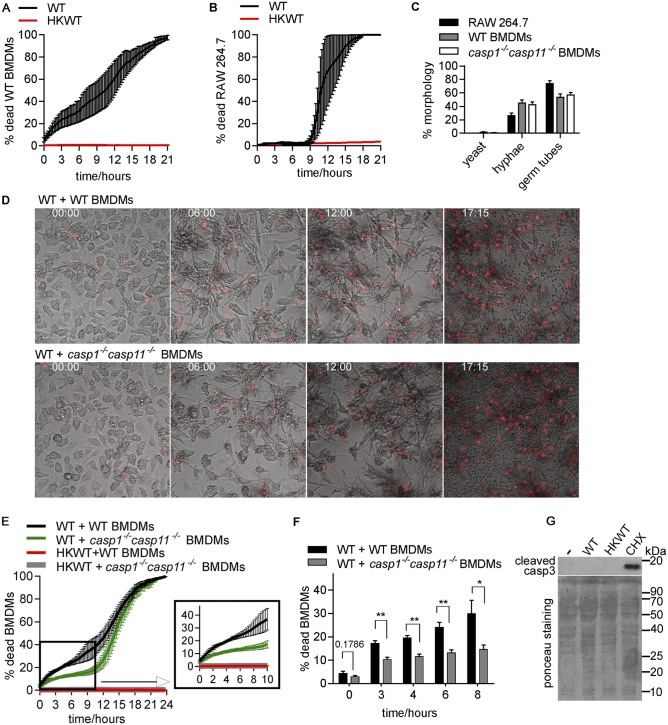
To understand the mechanism by which C. albicans kills macrophages, we devised a time-lapse microscopy assay whereby C. albicans is incubated with macrophages in the presence of the membrane-impermeable dye propidium iodide (PI). This allowed detailed determination of macrophage cell death rates as percentages of PI-positive cells over time (images were taken every 15 min over 21 to 24 h). C. albicans was coincubated with bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) for 1 h (at a multiplicity of infection [MOI] of 1 macrophage to 6 Candida cells), followed by washing of the nonphagocytosed cells and monitoring of macrophage cell death. Thus, the assay monitors the consequences of the interactions between phagocytosed (intracellular) Candida cells and macrophages. A detailed description of the assay is provided in Materials and Methods in the supplemental material. In agreement with other studies (25), BMDM cell death rates were about 20% to 30% within 6 h post-infection with C. albicans (Fig. 1A). During this time, C. albicans formed extended filaments that were clearly extruding from host cells (Fig. 1D; see also Video S1 in the supplemental material). At later times, C. albicans induced a second phase of macrophage killing, which lasted up to 21 h post-infection and resulted in a complete collapse of the host cell culture (Fig. 1A; see also Video S1). Both phases were dependent on live C. albicans, as heat-killed cells failed to induce any death, despite almost wild-type infection rates (Fig. 1A; for rates of infection by heat-killed cells, see Fig. 2A).
FIG 1 .
C. albicans triggers pyroptotic macrophage cell death. (A) Wild-type (WT) C. albicans was incubated with wild-type BMDMs at MOI 1:6 (macrophage:Candida), and macrophage cell death was monitored over time. Shown are averages and standard errors of the means (SEM) of the results from two independent biological experiments. HKWT, heat-killed wild-type C. albicans cells (yeast morphology). (B) Experiments were performed as described for panel A except that the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line was used. Averages and SEM are shown (n = 2). (C) Yeast and filamentous forms were counted from images from the live-cell microscopy experiments described for panels B and E at 30 min after the 1-h coincubation. A total of 100 phagocytosed Candida cells were counted for each of the independent biological experiments and classified as yeast, germ tubes, or hyphae. Values shown are means ± SEM (n = 2 for the RAW 264.7 cells and n = 3 for BMDMs). (D) Images corresponding to selected time points (h) from the live-cell microscopy of wild-type C. albicans infecting wild-type or casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs. (E) Wild-type C. albicans was incubated with wild-type or casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs. Averages and SEM of the results of 4 independent experiments are shown. These data and the data in the graph in panel F are the same as those determined in the wild-type Candida control experiments represented in Fig. 3. They are shown here separately for clarity of the results. (F) Graphs show means and SEM for percentages of macrophage cell death at selected time points from the curves shown in panel E. **, P <0.01; *, P <0.05. Representative live-cell microscopy movies from the macrophage-killing experiments represented in this figure are shown in Videos S1 to S3 in the supplemental material. (G) BMDMs were infected with live or heat-killed wild-type (HKWT) Candida at MOI 1:6 (macrophage:Candida) or treated with cycloheximide (CHX; 50 µg/ml) for 3 h, and the generation of cleaved caspase 3 was detected by immune blotting. Loading was visualized by Ponceau staining. Cycloheximide treatment served as a positive control.
FIG 2 .
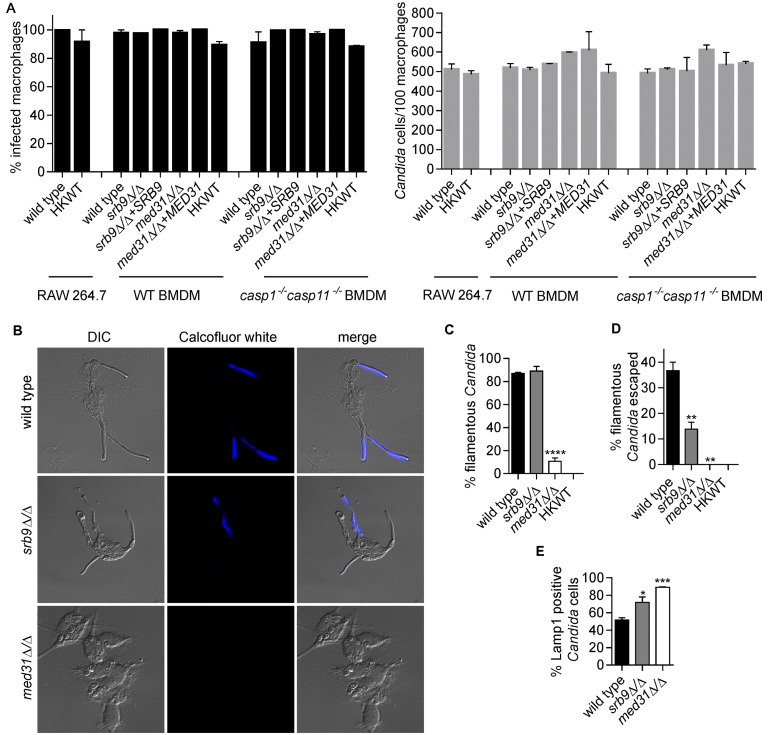
Mediator regulates morphogenesis and escape of C. albicans from macrophages. (A) Percentages of infected macrophages and numbers of Candida cells/100 macrophages were determined from images from the live-cell microscopy experiments represented in Fig. 1B and 3. Three independent biological experiments were performed for BMDMs and two for the RAW 264.7 cell line, and a total of 200 macrophages were counted in each of the experiments. Values are means ± SEM. HKWT, heat-killed wild-type cells. (B and C) Wild-type C. albicans and med31∆/∆ and srb9∆/∆ strains were used to infect wild-type BMDMs, and fungal cell morphology was assessed by microscopy and quantified at 3 h postphagocytosis by counting at least 200 cells/strain. Averages and SEM of the results of 3 independent experiments are shown. ****, P ≤ 0.0001. DIC, differential interference contrast. (D) Percentages of escaped C. albicans hyphae and calcofluor white (CW)-stained hyphae were determined by counting total cells in macrophages from bright-field images (see images in panel B). CW stains only fungal cells that are outside the macrophages, while the phagocytosed cells are protected. At least 200 cells/strain were counted. Data represent averages and SEM (n = 3). **, P ≤ 0.01. (E) Association of C. albicans with late phagosomes in wild-type BMDMs was monitored by immunofluorescence by staining for the phagosomal marker Lamp1. Lamp1-positive C. albicans cells were scored by microscopy (images are shown in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material) at the 2-h time point (following the 1-h coincubation). Three independent experiments were performed, and at least 50 Candida cells were counted in each. Averages and SEM are shown. *, P <0.05; ***, P <0.001.
In contrast to BMDMs, the RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cell line was resistant to C. albicans killing in the first 8 to 9 h post-infection (Fig. 1B). Filamentation (the appearance of hyphal filaments and germ tubes) in RAW 264.7 cells was similar to what we observed in BMDMs (Fig. 1C; also compare Videos S1 and S2 in the supplemental material). The levels of phagocytosis of Candida cells were also similar between BMDMs and RAW 264.7 macrophages (Fig. 2A). Hyphae eventually escaped from RAW 264.7 cells, followed by rapid killing of the entire host culture within the next 7 to 8 h (Fig. 1B). Therefore, efficient killing of macrophages by Candida hyphae in phase 1 might require a host factor that is inactive in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
RAW 264.7 macrophages lack the inflammasome component ASC, which is required for caspase-1 activation (26), and could thus be defective in activation of pyroptosis. To probe directly for the role of pyroptosis in C. albicans-mediated killing of macrophages, we utilized BMDMs derived from casp1−/− casp11−/− mutant mice (27). As shown in Fig. 1E and F, casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs were more resistant to killing by C. albicans within the first 8 to 10 h. Phagocytosis of C. albicans by casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDM was similar to that seen with wild-type BMDMs, and fungal hyphae formed normally (Fig. 1C and 2A), suggesting that lower rates of macrophage cell death are not caused by lower uptake or changes to the morphogenesis of Candida in the mutant BMDMs. Instead, these data show that C. albicans triggers pyroptotic macrophage death during the first phase post-infection. The second phase of macrophage killing by C. albicans hyphae was not defective in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs, as a rapid macrophage-killing phase was seen starting at 10 to 12 h (Fig. 1D and 1E; see also Video S3 in the supplemental material). We note that, even in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs, some macrophage cell death was observed early upon infection (Fig. 1E and F), indicating that C. albicans utilizes mechanisms additional to pyroptosis to cause macrophage death. However, we found no evidence of activation of caspase 3 by C. albicans early post-infection (Fig. 1G), suggesting that the canonical apoptotic pathway was not triggered in phase 1 under our experimental conditions.
Mediator as a new regulator of C. albicans-macrophage interactions.
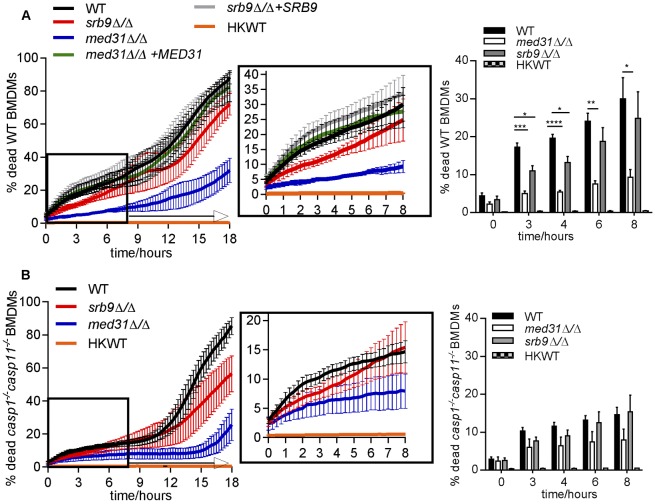
We have previously shown that the subunits of the Mediator complex, a central transcriptional regulator, control morphogenesis and cell wall integrity in C. albicans (28). The mutant deleted for the Mediator MED31 subunit infected BMDMs similarly to wild-type C. albicans (Fig. 2A), but was delayed in filamentation and was primarily in yeast form at 3 h post-phagocytosis (Fig. 2B and C). Filamentous structures were starting to form at later time points, and filaments were visible at 4 to 5 h post-infection (see Video S4 in the supplemental material). This finding is in agreement with our previous data determined in vitro and in the worm infection model that showed that the med31∆/∆ mutant is impaired in filamentation (28). Consistent with the morphogenesis defect, the med31∆/∆ mutant was severely impaired in early escape from macrophages (as judged by microscopy using calcofluor white staining of externalized hyphae) (Fig. 2B and D) and remained associated with the late phagosomal marker Lamp1 for prolonged times (Fig. 2E; images are shown in Fig. S1). The med31∆/∆ mutant is impaired for fitness in vitro (28), but was able to survive long-term in BMDMs, although it failed to multiply efficiently at 13.5 h post-infection (see Fig. S2D; we note that, for the data determined at 13.5 h in our assay, we do not differentiate between phagocytosed and escaped Candida cells that were replicating in the media). Consistent with the morphogenesis and macrophage escape defects, the med31∆/∆ mutant induced low levels of macrophage cell death within 8 to 10 h post-infection (Fig. 3A). Notably, this mutant consistently induced higher macrophage cell death rates than heat-killed wild-type yeast cells (see graph in Fig. 3A). After 18 h, macrophage cell death rates increased to about 30%, and by 24 h, the med31∆/∆ mutant caused an average macrophage cell death rate of 62.5% (Fig. 3A and data not shown). The increased ability of the mutant to cause macrophage death at later time points was most likely due to the eventual formation of filaments. Complementation of the med31∆/∆ mutant with the plasmid containing the MED31 gene restored macrophage death to wild-type levels (Fig. 3A).
FIG 3 .
Roles of Mediator and Candida morphogenesis in pyroptosis-dependent and -independent macrophage death. (A and B) Wild-type C. albicans, the med31∆/∆ and srb9∆/∆ mutants, and the complemented strains were used to infect wild-type (A) or casp1−/− casp11−/− (B) BMDMs, as described for Fig. 1. The controls for these experiments with wild-type C. albicans were the same as those described for Fig. 1E and F. Each of the experiments was performed with the wild type and with both mutants of C. albicans, infecting wild-type or casp1−/− casp11−/− mutant BMDMs, all assayed together to allow direct comparisons of the effects of host and pathogen mutations. The wild-type C. albicans results are presented separately in Fig. 1 for clarity of the Results section. For simplicity, the results from wild-type BMDMs and those from casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs are presented in separate graphs. The experiments were performed 3 independent times (for the med31∆/∆ mutant) or 4 independent times (for the srb9∆/∆ mutant). The means and SEM for percentages of dead macrophages are shown. Graphs are for means and SEM for individual time points with statistical significance. All numerical P values for the differences between wild-type and mutant strains are shown in Fig. S2 in the supplemental material. P values are indicated as follows: *, <0.05; **, <0.01; ***, <0.001; ****, <0.0001. Videos of mutant Candida are shown in Videos S4 and S5.
The C. albicans mutant lacking the SRB9 subunit from the kinase domain of Mediator infected and formed filaments in BMDMs similarly to wild-type C. albicans (Fig. 2A to C; see also Video S5 in the supplemental material). The srb9Δ/Δ mutant survived and multiplied normally during the infection period (Fig. S2D). Surprisingly, although it formed hyphal filaments, the srb9∆/∆ mutant was deficient in early escape from macrophages (Fig. 2D) and showed increased association with Lamp1-positive compartments (Fig. 2E). Consistent with fewer hyphae escaping, loss of SRB9 resulted in reduced macrophage killing in the first 4 h post-infection compared to wild-type C. albicans results (Fig. 3A). For example, at 3 h, the mutant caused approximately 40% less macrophage cell death than the wild type (mutant/wild-type ratio, 0.63 ± 0.098 standard deviation [SD]). The srb9∆/∆ mutant killed at the same rate as wild-type C. albicans in the second phase of cell death, and the kinetics of macrophage killing was restored to wild-type levels after re-expression of SRB9 (Fig. 3A). Therefore, while hyphal formation is important to induce macrophage death, factors additional to hyphal morphology are important for efficient killing and escape from macrophages, particularly early following phagocytosis. Both Mediator mutants were less virulent in the mouse tail vein systemic candidiasis model (Fig. S2).
We next combined the wild type and the Mediator mutants of C. albicans with wild-type and casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs to address whether the reduced ability of Mediator mutants to cause macrophage cell death was due to defective activation of pyroptosis. If this were the case, then we would expect that the difference in macrophage killing between wild-type and mutant C. albicans would be abrogated in the absence of pyroptosis in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs. As shown in Fig. 3B, in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs there was no statistically significant difference between wild-type C. albicans and the Mediator mutants in the ability to cause macrophage cell death in phase 1 (P values of <0.05 were considered to be significant; for all P values see Fig. S3). This result supports the notion that the Mediator mutants are defective in triggering pyroptosis. That there was no significant difference between wild-type hyphae and the morphogenesis-impaired med31Δ/Δ mutant in causing death of casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs early postphagocytosis suggests that an important function of hyphal filaments in macrophage killing in phase 1 is to trigger pyroptosis. The two Mediator mutants showed a reduced ability to cause IL-1β secretion in the supernatant of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-primed macrophages at 2 and 3 h post-phagocytosis, suggesting they were impaired in the ability to activate caspase-1 (Fig. 4; the IL-1β concentrations in pg/ml obtained in the individual experiments are shown in Fig. S4). In our system, IL-1β secretion was abrogated by >97% in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs (Fig. 4; see also Fig. S4). In casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs, there was a statistically significant reduction in the residual IL-1β secretion induced by Mediator mutant Candida as compared to the wild type at 3 h (but not at 2 h), and heat-killed and live wild-type C. albicans cells at both 2 and 3 h. This could have been caused by differences in the priming or processing signals for IL-1β secretion by this very minor caspase-1/caspase-11-independent mechanism or by differences in macrophage cell death between the fungal strains, as macrophage lysis releases IL-1β into the supernatant used for its measurement.
FIG 4 .
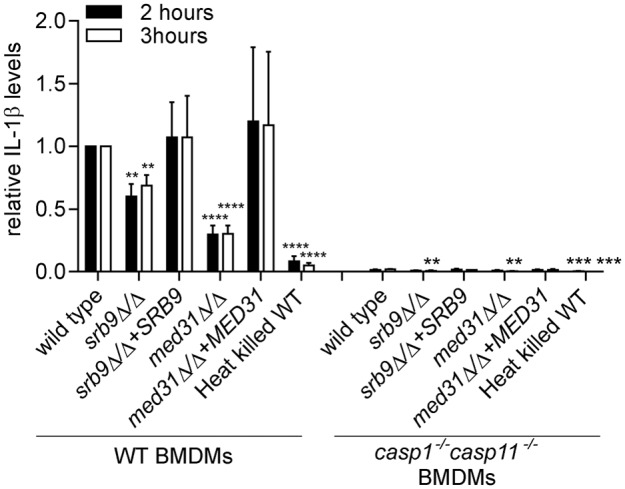
Effects of Mediator subunits on IL-1β secretion from macrophages. BMDMs were pretreated with LPS and infected with C. albicans, and IL-1β levels were determined from supernatants after 2 or 3 h after the 1 h coincubation as described in Materials and Methods. The experiment was performed 3 independent times (4 for the srb9Δ/Δ mutant), and fold differences were calculated, with IL-1β levels induced by wild-type C. albicans in wild-type BMDMs set to 1. Averages and SEM of the results of the independent experiments are shown. The individual experiments with IL-1β concentrations in supernatants (pg/ml) are shown in Fig. S4 in the supplemental material. Figure S4 also shows rescaled relative levels for IL-1β in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs for ease of comparison. P values were calculated for the comparisons between wild-type and mutant C. albicans and between wild-type and heat-killed C. albicans in either WT BMDMs (left side of the graph) or casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs (right side). **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001.
While the difference was not statistically significant, wild-type hyphae were able to induce more macrophage death than the Mediator mutants in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs (Fig. 3B), although this difference was smaller than in wild-type BMDMs (compare Fig. 3A to B). Also, all live strains (the wild type and both mutants) were inducing substantially more macrophage death than heat-killed yeast cells not only in wild-type BMDMs but also in the absence of pyroptosis in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs (Fig. 3). These results suggest that while pyroptosis is an important function of hyphal structures in causing early macrophage cell death, functions of hyphae additional to activation of pyroptosis also contribute.
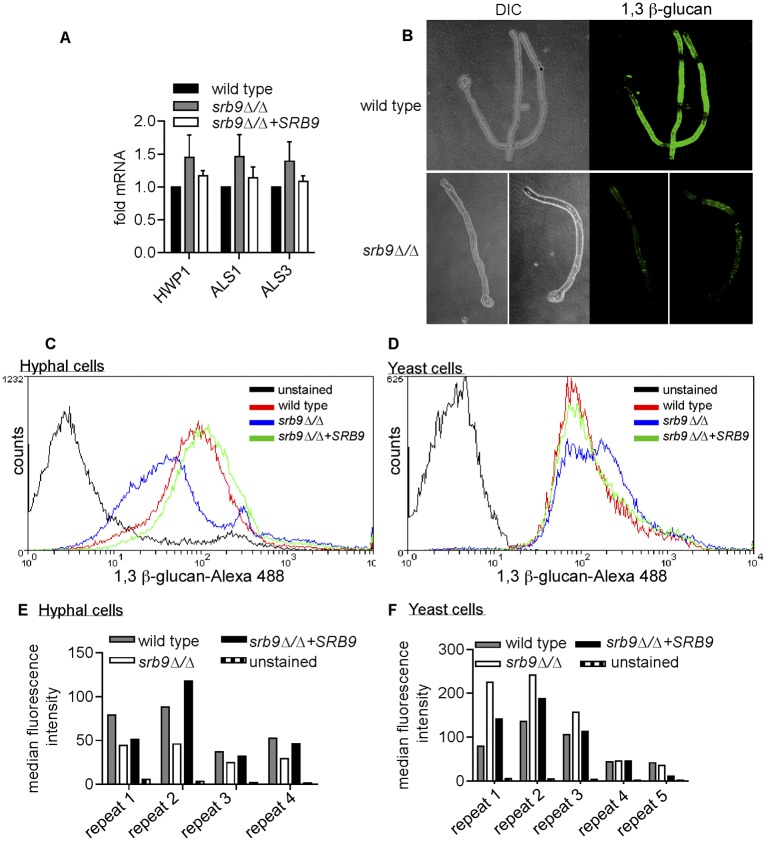
Breakdown of surface architecture and reduced 1,3 β-glucan in srb9∆/∆ hyphae.
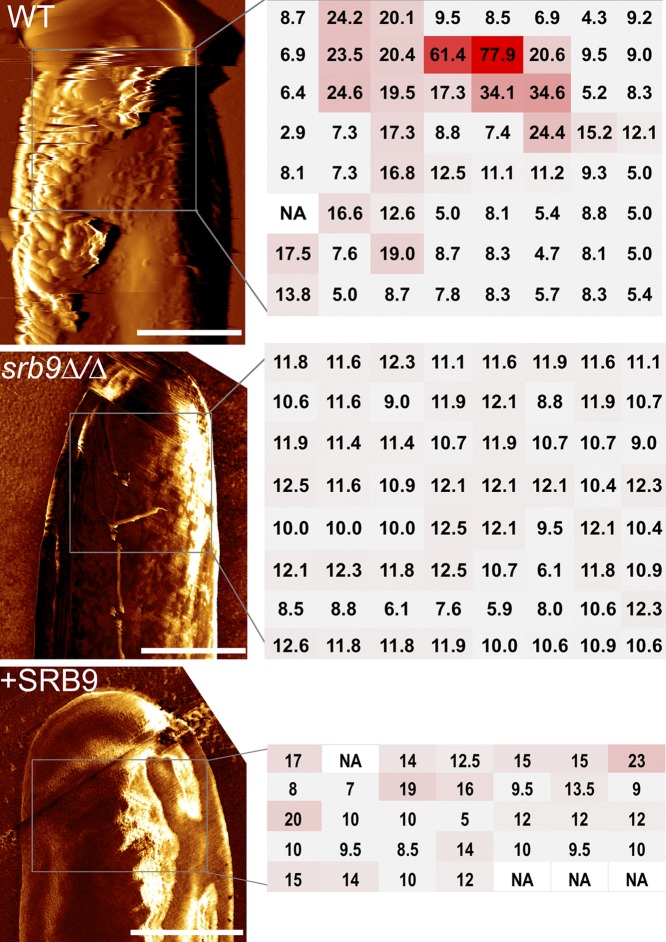
We next used the srb9∆/∆ mutant to examine additional determinants, besides filamentous morphology, which contribute to macrophage killing by C. albicans. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) showed that the srb9∆/∆ mutant hyphae displayed a breakdown of cell surface architecture; the surface of mutant hyphae appeared smoother than that of wild-type filaments as shown in surface topography images (Fig. 5). In addition, force mapping demonstrated that wild-type hyphae contain areas of high adhesion forces, which were absent on srb9∆/∆ hyphae (Fig. 5). The complemented srb9∆/∆+SRB9 strain had an intermediate phenotype (Fig. 5). We have previously found that the srb9∆/∆ mutant displays lower levels of some hypha-specific cell wall genes in vitro (28). However, in macrophages, the expression of the hyphal cell wall adhesins did not depend on Srb9 (Fig. 6A). Instead, srb9∆/∆ hyphae displayed reduced exposed 1,3 β-glucan levels compared to the wild type which appeared as punctate staining by confocal microscopy (Fig. 6B). Flow cytometry confirmed this result (Fig. 6C and E). Yeast forms of srb9∆/∆ did not display reduced 1,3 β-glucan exposure (in contrast, 1,3 β-glucan exposure was slightly higher in the mutant in some experiments; Fig. 6D and F). Taken together, these results show that Srb9 regulates morphogenesis-dependent cell surface exposure of 1,3 β-glucan but also the overall cell wall architecture.
FIG 5 .
srb9∆/∆ mutant hyphae display a breakdown of cell surface architecture. AFM (atomic force microscopy) was performed on hyphae grown in vitro under conditions that mimic those of the macrophage experiments (RPMI media, 37°C). Deflection images of hyphal tips from wild-type and srb9∆/∆ mutant hyphae are presented on the left and force measurements on the right. The regions in which force measurements were done were squares of the following sizes: 1.7 µm-by-1.7 µm for the wild type, 1.2 µm-by-1.2 µm for srb9∆/∆, and 1.5 µm-by-1 µm for the complemented strain). The adhesion forces, extracted from force-distance curves, were measured in an 8-by-8-matrix for the wild-type and mutant strains, or a 7-by-5 matrix for the complemented strain, as shown in the figure (the unit of adhesion force is nN). The measurements are color coded from gray (low intensity) to red (high intensity). Multiple hyphae were measured for each of the strains and gave equivalent results. The scale bar is 1 µm.
FIG 6 .
Srb9 regulates 1,3 β-glucan exposure on the cell surface of hyphae. (A) Quantitative PCR of the expression levels of the cell wall adhesins ALS1, ALS3, and HWP1 after phagocytosis by macrophages in wild-type, srb9∆/∆ mutant, and SRB9 complemented C. albicans strains. The experiment was performed on 3 separate occasions. 18S rRNA was used for normalization. Averages and SEM of the results from the 3 biological repeats are shown. (B) Wild-type and mutant hyphae stained with the 1,3 β-glucan antibody were visualized by confocal microscopy. Image stacks were used to create 3D renditions of wild-type and srb9∆/∆ mutant hyphae grown in vitro under conditions that mimicked the macrophage experiments (RPMI media, 37°C). (C to F) Hyphal growth of wild-type, srb9∆/∆ mutant, and complemented strains was induced in Spider media at 37°C for 3 h. Yeast cells were grown in YPD at 30° C. Exposed 1,3 β-glucan was stained using the 1,3 β-glucan antibody. Flow cytometry experiments were performed with several independent biological repeats, assayed on separate occasions. The flow cytometry curves (C and D) are from one representative experiment, and the bar graphs (E and F) show the median fluorescence obtained for the individual biological repeats.
DISCUSSION
The interaction of C. albicans with macrophages has most commonly been studied by sampling at defined time points where the events that occur before, after, or between the selected time points are missed (5, 6, 29). To dissect this process in greater detail, we followed C. albicans-macrophage intracellular interactions in real time using live-cell imaging. With our new assay, we show that macrophage killing by C. albicans occurs in two distinct phases: phase 1 (first 6 to 8 h) and phase 2 (8 to 10 h to 18 to 24 h post-phagocytosis). Both phases depend on the presence of wild-type hyphae but are distinguished by the requirement for activation of host responses by C. albicans. Phase 1 requires the activity of the pyroptotic caspases, caspase-1 and caspase-11. Wild-type C. albicans hyphae cause 40% to 50% less macrophage cell death in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs than in wild-type BMDMs in the first 8 h following uptake (Fig. 1). Caspase-1 and caspase-11 induce pyroptosis and are not known to cause any other form of programmed cell death. Therefore, these results show that C. albicans hyphae trigger pyroptotic macrophage cell death in phase 1. That wild-type C. albicans filaments fail to induce normal death rates in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs and also in RAW macrophages, where almost no host cell death is observed for the first 9 h, suggests that mechanical piercing by hyphae, which is currently considered to be a major contributor to macrophage killing (3–5), is not among the main mechanisms of early host cell death upon phagocytosis. Caspase-1 and caspase-11 can independently induce pyroptosis (18, 27). However, caspase-11 is primarily activated by Gram-negative bacteria and LPS (30, 31), suggesting that caspase-1 is the main pyroptotic caspase activated by C. albicans hyphae. Our conclusions are supported by a report published while the present manuscript was under review that showed that C. albicans hyphae induce macrophage pyroptosis that depends on caspase-1 and the inflammasome subunits NLRP3 and ASC (32). Consistent with our data, the same study showed that pyroptosis is the predominant mechanism of macrophage cell death when fungal cell numbers are low, such as early upon phagocytosis. It has to be noted that mechanisms additional to pyroptosis also operate in phase 1. First, wild-type C. albicans induces more macrophage cell death than heat-killed cells in the absence of pyroptosis in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs. Second, wild-type filaments caused higher cell death rates than the morphogenesis-impaired med31∆/∆ mutant not only in wild-type BMDMs, but also in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs. Moreover, phase 2 of killing requires wild-type hyphae, but the mechanism is distinct from pyroptosis, as this phase occurs normally in casp1−/− casp11−/− BMDMs. The additional macrophage cell death mechanism in phase 1, as well as the phase 2 death that occurs when C. albicans hyphae are abundant, could depend on mechanical destruction of macrophages by hyphae. Alternatively, another host cell death pathway could be triggered. C. albicans has been shown to induce apoptosis in peritoneal macrophages (33) and in the J774 macrophage-like cell line (34). However, we found no activation of apoptotic caspase 3 in BMDMs early upon phagocytosis (Fig. 1), and our results are supported by recent experiments using the RAW 267.4 cell line (23). Moreover, a study of macrophage-Candida interactions in vivo in kidneys of mice found that there is no activated caspase 3 in wild-type macrophages at day 6 following infection with Candida (35). Recently, extracellular C. albicans have been shown to activate a caspase-8-containing inflammasome in dendritic cells (14), but a previous study using RAW 267.4 macrophages showed no or minimal activation of caspase 8 and caspase 9 in response to C. albicans infection and the authors concluded that apoptosis does not play a major role in macrophage cell death induced by C. albicans (36). In addition to apoptosis, another possibility is that C. albicans triggers the caspase-independent programmed form of necrosis termed necroptosis (37). Ongoing studies in our laboratories are focused on elucidating the mechanistic features of pyroptosis-independent macrophage cell death caused by C. albicans.
We have shown that several aspects of macrophage-C. albicans interactions, including morphogenesis, hyphal architecture, and virulence factors of the cell wall, are controlled by the transcriptional regulator Mediator. We have also shown that Mediator subunits Med31 and Srb9 are necessary for wild-type virulence in the mouse systemic model. Med31, which is in the so-called Middle domain of the core Mediator complex, impacts on hyphal morphogenesis (28). In contrast, the Srb9 subunit from the kinase domain does not appear to have an impact on morphogenesis in macrophages, but it controls the formation of proper hyphal cell surface architecture (as demonstrated by AFM). The srb9Δ/Δ mutant hyphae display reduced 1,3 β–glucan exposure, while the expression of several hyphal adhesins did not differ from that seen with the wild type. C. albicans transcription factor mutants upc2 and ahr1 have macrophage-killing phenotypes similar to those of our srb9Δ/Δ mutant, but do not display lower levels of surface-exposed 1,3 β–glucan in yeast morphology (32). However, it is possible that hyphal forms of these mutants have a different cell wall 1,3 β–glucan phenotype, as is the case for the srb9Δ/Δ mutant, which shows reduced 1,3 β–glucan only in hyphae and not during yeast growth (Fig. 6). Several possible explanations can be envisaged to account for how the changes in cell wall structure in srb9Δ/Δ mutant hyphae affect macrophage cell death. First, proper cell wall structure might be important for the escape of hyphae from the phagolysosome. Phagolysosomal rupture by hyphal filaments has been proposed as a trigger for activation of caspase-1 inflammasomes (38). Second, it is possible that 1,3 β-glucan is sensed directly by host receptors. Increased exposure of 1,3 β–glucan on the cell surface of C. albicans induces higher levels of IL-1β (12), and the β–glucan preparation curdlan can activate caspase-1/NLRP3/Asc-containing inflammasomes (39, 40). It is also possible that the srb9Δ/Δ mutant displays changes to other components of the cell wall that impact on the activation of immune responses. Also, compromised hyphal cell wall structure impacts mechanical features of the hyphae that could mediate the ability to cause macrophage cell death.
In conclusion, our data show that the interplay between developmental transitions and survival strategies of C. albicans and the activation of host immune pathways is more sophisticated than previously appreciated. It is currently not clear what the consequence of Candida-triggered pyroptosis is for disease. Caspase-1 is known to protect against C. albicans infections (11, 13, 41), and it is thus possible that pyroptosis has a protective role by increasing inflammatory responses, as is the case for bacterial pathogens. While mice deficient in caspase-1 and the IL-1 receptor are highly susceptibility to disseminated candidiasis, casp1−/− casp11−/− mice show normal fungal burdens during the first few days in kidneys in the systemic infection model, and at the site of infection, on tongues, in the oral model (11, 41). The PRR dectin-1 is required for activation of caspase-1 by Candida in response to some fungal strains (14), and it will be interesting to determine how a possible role for dectin-1 in pyroptosis contributes to the roles of this PRR in disease caused by C. albicans (16, 42, 43). We suggest that pyroptosis might promote evasion of the innate immune response by C. albicans by providing an escape route for the pathogen (as shown, for example, by reduced escape of srb9Δ/Δ mutant hyphae). In other words, the same molecular event—activation of caspase-1 by fungal hyphae—can cause both protective immunity and fungal escape. The outcome of infection likely depends on a balance between these paradoxical consequences of the interactions between Candida hyphae and the innate immune response.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Detailed experimental procedures are provided in the supplemental material.
Ethics statement.
Animal experiments were performed in accordance with the National Health and Medical Research Council Australian Code of Practice for the Care and Use of Animals and approved by the Monash University Animal Ethics Committee (approval number SOBS/M/2010/49) or under conditions approved by the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute Animal Ethics Committee.
Statistical analysis.
For statistical analysis, the unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test was performed using GraphPad Prism software, and P values of <0.05 were considered to be significant. For the animal infection model (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material), statistical analysis was performed with Minitab version 16 statistical software. Differences in survival rates were estimated with the nonparametric Kaplan-Meier method using the log-rank test and survival curves plotted. Means of organ burdens were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).
Yeast strains and growth conditions.
The C. albicans strains are derivatives of BWP17 and described in reference 28. The strains were propagated at 30°C in yeast extract-peptone-dextrose (YPD) media with the addition of 80 µg/ml uridine. All experiments involving hyphal growth were performed in either RPMI or Spider media at 37°C.
Animal infections and isolation of bone marrow-derived macrophages.
Bone marrow from 6-to-8-week-old C57Bl/6 wild-type or casp1−/−/casp11−/−mice was isolated and macrophages were differentiated essentially as described in reference 44. For assaying virulence, 6-to-8-week-old BALB/c mice were infected using the mouse tail vein systemic candidiasis model as described previously with minor modifications (see reference 45 and the procedures described in the supplemental material).
Live-cell imaging and quantification of macrophage killing by C. albicans.
Macrophages were challenged with C. albicans at a MOI of 1:6 (macrophage:Candida). After 1 h of coincubation, nonphagocytosed fungal cells were removed by washing with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). PI was added to the wells for monitoring macrophage cell death. Experiments were performed on a Leica AF6000 LX live-cell imaging system with an inverted, fully motorized microscope driven by Leica Advanced Suite Application software. Time-lapse images were acquired with bright-field and TxRed filters every 15 min for up to 24 h using a 20×/0.8-A objective. Fluorescent (PI) images were converted into binary images with ImageJ software using the same signal threshold for all samples, and total PI signal was measured for each of the images. The time point where maximum macrophage death occurred was determined by assessing the time-lapse images and maximum percentage of dead macrophages calculated by manually counting PI-positive and total macrophages in fluorescent (PI) and bright-field images, respectively. This was used to calculate percentage death at earlier time points from the same sample based on total PI signal. Calculations were done using Microsoft Excel and data analyzed with GraphPad Prism software. Representative movies were made by merging the bright and fluorescent fields, and images were compressed and brightness and contrast adjusted evenly for the entire movie for ease of viewing using ImageJ. For methods to determine C. albicans survival in macrophages (see Fig. S2), please see the procedures described in the supplemental material.
Quantification of IL-1β production and caspase-3 activation.
For IL-1β production experiments, macrophages were pretreated with LPS (50 ng/ml for 3.5 h) and infected with C. albicans wild-type or Mediator mutant strains at a MOI of 1:6 (macrophages:Candida). IL-1β levels were determined from supernatants at 2 and 3 h after the 1-h coincubation period using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), as described in reference 44. Cleaved caspase-3 was detected in whole-cell extracts after coincubation of BMDMs with wild-type C. albicans or heat-killed yeast cells, or treatment with cycloheximide for 3 h, by probing with an antibody that recognizes cleaved caspase-3 (Asp175; Cell Signaling).
Gene expression analysis.
Analysis of adhesin gene expression was performed after 3 h of coincubation of C. albicans and wild-type BMDMs, using a 1:6 multiplicity of infection (macrophages:Candida). The levels of the adhesins were determined by quantitative PCR as described in the experimental procedures section of the supplemental material.
Microscopy and quantification of 1,3 β-glucan exposure by flow cytometry.
The phagocytosis data in Fig. 2A (percentage of infected macrophages and number of Candida cells/100 macrophages) were determined using the images from the live-cell microscopy experiments presented in Fig. 1B and 3 at 30 min after the 1 h coincubation period. The MOI was 1 macrophage to 6 Candida. The cell morphology of wild-type Candida in the various macrophages in Fig. 1C was determined from the live-cell microscopy experiments as described for phagocytosis above. For determining cell morphology, escape and phagolysosome association of the C. albicans wild type or the Mediator mutants (Fig. 2B to E), BMDMs were infected at a MOI of 1:2 (macrophage:Candida), followed by 1 h coincubation and washing. For monitoring escape, fungal cells were stained with calcofluor white (5 µg/ml, 10 min). Immunofluorescence experiments with the glucan antibody and for monitoring association with the phagosomal marker Lamp1 are described in detail in the experimental procedures section of the supplemental material. Imaging was done on an Olympus IX81 or a NikonC1 confocal microscope. Representative images were selected and cropped and brightness and contrast adjusted in CorelDRAW evenly for the entire image. For Fig. 6, fluorescent images of β-glucan in wild-type and mutant hyphae were taken with the same exposure and camera settings, and contrast and brightness adjusted evenly only for the bright-field images using CorelDRAW (the fluorescent images were not altered). Confocal stack images were used to construct three-dimensional (3D) images of representative hyphal cells, using ImageJ software with the 3D project function. AFM was performed on hyphae grown in vitro in RPMI media at 37°C. AFM measurements were performed at room temperature under dry conditions using the NanoWizard II AFM system at the Melbourne Centre for Nanofabrication. AFM contact-mode images were obtained using Si3N4 cantilevers (MSNL-10; Bruker, Santa Barbara, CA). Deflection images were simultaneously acquired and analyzed with JPK data software (JPK Instruments AG, Germany). Force-distance measurements were collected on single C. albicans hyphae, and several hyphae/strain were measured. Wild-type C. albicans and the srb9∆/∆ mutant were assayed on several separate occasions, while the complemented srb9∆/∆+SRB9 strain was analyzed on one occasion (5 independent hyphae).
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Supplemental procedures. Download
Lamp1 association of the wild type and the Mediator mutants of C. albicans. Images relate to the quantification of Lamp1 association of wild-type C. albicans and Mediator mutants presented in Fig. 2E. The multiplicity of infection was 2:1 (Candida:macrophages). Images were obtained at the 2-h time point following the 1-h coincubation using a NikonC1 confocal microscope. Representative images showing Lamp1 association were selected using ImageJ software. Brightness and contrast were adjusted using CorelDRAW. For clarity, single slices from the stack of images collected are presented here. Download
Mediator subunits Med31 and Srb9 are important for virulence of C. albicans. (A) Mice were infected with 3 × 105 CFU of wild-type C. albicans, Mediator mutants, or complemented strains and survival was monitored over time as described in the experimental procedures section. An estimation of differences in survival (log-rank test) using the Kaplan-Meier method was performed, and a P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant (**, P ≤ 0.001; P values are for comparisons of the indicated mutant or complemented strains to wild-type C. albicans). Although mice infected with the srb9Δ/Δ+SRB9 complemented strain exhibited higher survival rates than mice infected with the wild type, the complemented srb9Δ/Δ+SRB9 strain caused statistically significant higher mortality than the srb9Δ/Δ mutant (P = 0.013). (B) Kidney organ burdens were tested at day 1 post-infection by determining numbers of colony-forming units (CFUs) per gram of tissue (n = 3). Both mutants displayed lower kidney burden than wild-type C. albicans (**, P <0.001 [one-way ANOVA]). Similarly to the survival assay described for panel A, the srb9Δ/Δ+SRB9 complemented strain showed an intermediate phenotype, but the rescue of the mutant was significant at P = 0.052. Rescue of the med31Δ/Δ mutant by its respective complemented strain was significant at P <0.001. (C) Kidney histopathology was performed at day 1 post-infection, using an inoculum of C. albicans of 1.5 × 106 CFU. C. albicans cells were visualized by periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining using an Olympus Provis Ax70 microscope (400×). (D) Numbers of CFUs for the indicated strains were determined at time 13.5 h relative to time 0 h, which corresponds to the time just after the 1-h coincubation. The fold change in CFUs is shown. The experiment was performed on 3 (med31∆∆, med31∆∆+MED31) and 5 (wild type, srb9∆∆, and srb9∆∆+SRB9) separate occasions. The MOI was 1:2 (macrophage:Candida). Averages and SEM of results from the biological repeats are shown. **, P <0.01. Download
Graphical representation of the macrophage cell death data. These graphs are the same as those presented in Fig. 3 but with all numerical P values shown for differences between wild-type and Mediator mutant C. albicans at the selected time points. The stars represent P values as follows: *, <0.05; **, <0.01; ***, <0.001; ****, <0.0001. Download
Induction of IL-1β secretion by C. albicans Mediator mutants. (A) A time course of IL-1β secretion comparing wild-type and srb9∆/∆ mutant C. albicans. The multiplicity of infection was 1:6 (macrophage:Candida). Averages and SD of the results of two technical repeats are shown. (B) Results of the individual experiments used to create the graphs in Fig. 4 with absolute values of secreted IL-1β (pg/ml). For the srb9∆/∆ mutant, data from the experiment described for panel A and the experiments described for panel B were combined for the graph in Fig. 4. (C) Levels of secreted IL-1β induced by Mediator mutants of C. albicans in casp-1−/− casp-11−/− BMDMs were expressed relative to the levels induced by wild-type C. albicans. **, <0.01. ***, <0.001. Download
Wild-type C. albicans was used to infect wild-type BMDMs. For each experiment, 4 microscopy fields were monitored over time. A representative field is shown here. The video was made by merging bright images with fluorescent (propidium iodide) images to show death of macrophages over time. Brightness and contrast were adjusted by even application to the whole field using ImageJ. The original files were compressed in JPG file format and saved in AVI file format. Download
Wild-type C. albicans was used to infect RAW 264.7 macrophages. The video was processed as described for Video S1. Download
Wild-type C. albicans was used to infect casp1-/-casp11−/− BMDMs. The video was obtained and processed as described for Video S1. Download
The C. albicans Mediator mutant med31Δ/Δ was used to infect wild-type BMDMs. The video was obtained and processed as described for Video S1. Download
The C. albicans Mediator mutant srb9Δ/Δ was used to infect wild-type BMDMs. The video was obtained and processed as described for Video S1. Download
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Trevor Lithgow and Jamie Rossjohn for comments on the manuscript and acknowledge the technical support from the Monash University MicroImaging facility. We further thank Gilu Abraham for technical assistance.
A.T., T.N., J.E.V., and S.L.M. are supported by grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NH&MRC). Y.Q. and H.-H.S. are Australian Research Council (ARC) SuperScience Fellows. J.E.V. is an NH&MRC Career Development Fellow.
Footnotes
Citation Uwamahoro N, Verma-Gaur J, Shen H-H, Qu Y, Lewis R, Lu J, Bambery K, Masters SL, Vince JE, Naderer T, Traven A. 2014. The pathogen Candida albicans hijacks pyroptosis for escape from macrophages. mBio 5(2):e00003-14. doi:10.1128/mBio.00003-14.
REFERENCES
- 1. Brown GD, Denning DW, Gow NA, Levitz SM, Netea MG, White TC. 2012. Hidden killers: human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:165rv113. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Gow NA, van de Veerdonk FL, Brown AJ, Netea MG. 2012. Candida albicans morphogenesis and host defence: discriminating invasion from colonization. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10:112–122. 10.1038/nrmicro2711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Miramón P, Kasper L, Hube B. 2013. Thriving within the host: Candida spp. interactions with phagocytic cells. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 202:183–195. 10.1007/s00430-013-0288-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Lo HJ, Köhler JR, DiDomenico B, Loebenberg D, Cacciapuoti A, Fink GR. 1997. Nonfilamentous C. albicans mutants are avirulent. Cell 90:939–949. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80358-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. McKenzie CG, Koser U, Lewis LE, Bain JM, Mora-Montes HM, Barker RN, Gow NA, Erwig LP. 2010. Contribution of Candida albicans cell wall components to recognition by and escape from murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 78:1650–1658. 10.1128/IAI.00001-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wellington M, Koselny K, Krysan DJ. 2012. Candida albicans morphogenesis is not required for macrophage interleukin 1beta production. mBio 4:e00433-12. 10.1128/mBio.00433-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gow NA, Hube B. 2012. Importance of the Candida albicans cell wall during commensalism and infection. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 15:406–412. 10.1016/j.mib.2012.04.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Carlisle PL, Kadosh D. 2013. A genome-wide transcriptional analysis of morphology determination in Candida albicans. Mol. Biol. Cell 24:246–260. 10.1091/mbc.E12-01-0065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Heilmann CJ, Sorgo AG, Siliakus AR, Dekker HL, Brul S, de Koster CG, de Koning LJ, Klis FM. 2011. Hyphal induction in the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans reveals a characteristic wall protein profile. Microbiology 157:2297–2307. 10.1099/mic.0.049395-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Gantner BN, Simmons RM, Underhill DM. 2005. Dectin-1 mediates macrophage recognition of Candida albicans yeast but not filaments. EMBO J. 24:1277–1286. 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600594 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hise AG, Tomalka J, Ganesan S, Patel K, Hall BA, Brown GD, Fitzgerald KA. 2009. An essential role for the NLRP3 inflammasome in host defense against the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Cell Host Microbe 5:487–497. 10.1016/j.chom.2009.05.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Cheng SC, van de Veerdonk FL, Lenardon M, Stoffels M, Plantinga T, Smeekens S, Rizzetto L, Mukaremera L, Preechasuth K, Cavalieri D, Kanneganti TD, van der Meer JW, Kullberg BJ, Joosten LA, Gow NA, Netea MG. 2011. The dectin-1/inflammasome pathway is responsible for the induction of protective T-helper 17 responses that discriminate between yeasts and hyphae of Candida albicans. J. Leukoc. Biol. 90:357–366. 10.1189/jlb.1210702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Gross O, Poeck H, Bscheider M, Dostert C, Hannesschläger N, Endres S, Hartmann G, Tardivel A, Schweighoffer E, Tybulewicz V, Mocsai A, Tschopp J, Ruland J. 2009. Syk kinase signalling couples to the Nlrp3 inflammasome for anti-fungal host defence. Nature 459:433–436. 10.1038/nature07965 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Gringhuis SI, Kaptein TM, Wevers BA, Theelen B, van der Vlist M, Boekhout T, Geijtenbeek TB. 2012. Dectin-1 is an extracellular pathogen sensor for the induction and processing of IL-1beta via a noncanonical caspase-8 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 13:246–254. 10.1038/ni.2222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Joly S, Ma N, Sadler JJ, Soll DR, Cassel SL, Sutterwala FS. 2009. Cutting edge: Candida albicans hyphae formation triggers activation of the Nlrp3 inflammasome. J. Immunol. 183:3578–3581. 10.4049/jimmunol.0901323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Marakalala MJ, Vautier S, Potrykus J, Walker LA, Shepardson KM, Hopke A, Mora-Montes HM, Kerrigan A, Netea MG, Murray GI, Maccallum DM, Wheeler R, Munro CA, Gow NA, Cramer RA, Brown AJ, Brown GD. 2013. Differential adaptation of Candida albicans in vivo modulates immune recognition by dectin-1. PLoS Pathog. 9:e1003315. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ashida H, Mimuro H, Ogawa M, Kobayashi T, Sanada T, Kim M, Sasakawa C. 2011. Cell death and infection: a double-edged sword for host and pathogen survival. J. Cell Biol. 195:931–942. 10.1083/jcb.201108081 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Miao EA, Leaf IA, Treuting PM, Mao DP, Dors M, Sarkar A, Warren SE, Wewers MD, Aderem A. 2010. Caspase-1-induced pyroptosis is an innate immune effector mechanism against intracellular bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 11:1136–1142. 10.1038/ni.1960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Martin CJ, Booty MG, Rosebrock TR, Nunes-Alves C, Desjardins DM, Keren I, Fortune SM, Remold HG, Behar SM. 2012. Efferocytosis is an innate antibacterial mechanism. Cell Host Microbe 12:289-300. 10.1016/j.chom.2012.06.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Robinson N, McComb S, Mulligan R, Dudani R, Krishnan L, Sad S. 2012. Type I interferon induces necroptosis in macrophages during infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Nat. Immunol. 13:954-962. 10.1038/ni.2397 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Brennan MA, Cookson BT. 2000. Salmonella induces macrophage death by caspase-1-dependent necrosis. Mol. Microbiol. 38:31-40. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02103.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Monack DM, Hersh D, Ghori N, Bouley D, Zychlinsky A, Falkow S. 2000. Salmonella exploits caspase-1 to colonize Peyer’s patches in a murine typhoid model. J. Exp. Med. 192:249–258. 10.1084/jem.192.2.249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Reales-Calderon JA, Sylvester M, Strijbis K, Jensen ON, Nombela C, Molero G, Gil C. 2013. Candida albicans induces pro-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic signals in macrophages as revealed by quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics. J. Proteomics 91:106–135. 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.06.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Fites JS, Ramsey JP, Holden WM, Collier SP, Sutherland DM, Reinert LK, Gayek AS, Dermody TS, Aune TM, Oswald-Richter K, Rollins-Smith LA. 2013. The invasive chytrid fungus of amphibians paralyzes lymphocyte responses. Science 342:366–369. 10.1126/science.1243316 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Rudkin FM, Bain JM, Walls C, Lewis LE, Gow NA, Erwig LP. 2013. Altered dynamics of Candida albicans phagocytosis by macrophages and PMNs when both phagocyte subsets are present. mBio 4:e00810-13. 10.1128/mBio.00810-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Pelegrin P, Barroso-Gutierrez C, Surprenant A. 2008. P2X7 receptor differentially couples to distinct release pathways for IL-1beta in mouse macrophage. J. Immunol. 180:7147-7157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Kayagaki N, Warming S, Lamkanfi M, Vande Walle L, Louie S, Dong J, Newton K, Qu Y, Liu J, Heldens S, Zhang J, Lee WP, Roose-Girma M, Dixit VM. 2011. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature 479:117–121. 10.1038/nature10558 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Uwamahoro N, Qu Y, Jelicic B, Lo TL, Beaurepaire C, Bantun F, Quenault T, Boag PR, Ramm G, Callaghan J, Beilharz TH, Nantel A, Peleg AY, Traven A. 2012. The functions of Mediator in Candida albicans support a role in shaping species-specific gene expression. PLoS Genet. 8:e1002613. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Fernández-Arenas E, Bleck CK, Nombela C, Gil C, Griffiths G, Diez-Orejas R. 2009. Candida albicans actively modulates intracellular membrane trafficking in mouse macrophage phagosomes. Cell. Microbiol. 11:560-589. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01274.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Kayagaki N, Wong MT, Stowe IB, Ramani SR, Gonzalez LC, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K, Zhang J, Lee WP, Muszyński A, Forsberg LS, Carlson RW, Dixit VM. 2013. Noncanonical inflammasome activation by intracellular LPS independent of TLR4. Science 341:1246–1249. 10.1126/science.1240248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Hagar JA, Powell DA, Aachoui Y, Ernst RK, Miao EA. 2013. Cytoplasmic LPS activates caspase-11: implications in TLR4-independent endotoxic shock. Science 341:1250–1253. 10.1126/science.1240988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Wellington M, Koselny K, Sutterwala FS, Krysan DJ. 2014. Candida albicans triggers NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in macrophages. Eukaryot. Cell 13:329-340. 10.1128/EC.00336-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Schröppel K, Kryk M, Herrmann M, Leberer E, Röllinghoff M, Bogdan C. 2001. Suppression of type 2 NO-synthase activity in macrophages by Candida albicans. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 290:659–668. 10.1016/S1438-4221(01)80003-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Ibata-Ombetta S, Idziorek T, Trinel PA, Poulain D, Jouault T. 2003. Candida albicans phospholipomannan promotes survival of phagocytosed yeasts through modulation of bad phosphorylation and macrophage apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 278:13086–13093. 10.1074/jbc.M210680200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lionakis MS, Netea MG. 2013. Candida and host determinants of susceptibility to invasive candidiasis. PLOS Pathog. 9:e1003079. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003079 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Marcil A, Harcus D, Thomas DY, Whiteway M. 2002. Candida albicans killing by RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cells: effects of Candida genotype, infection ratios, and gamma interferon treatment. Infect. Immun. 70:6319–6329. 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6319-6329.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Moriwaki K, Chan FK. 2013. RIP3: a molecular switch for necrosis and inflammation. Genes Dev. 27:1640–1649. 10.1101/gad.223321.113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Joly S, Sutterwala FS. 2010. Fungal pathogen recognition by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Virulence 1:276–280. 10.4161/viru.1.4.11482 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Kumar H, Kumagai Y, Tsuchida T, Koenig PA, Satoh T, Guo Z, Jang MH, Saitoh T, Akira S, Kawai T. 2009. Involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome in innate and humoral adaptive immune responses to fungal beta-glucan. J. Immunol. 183:8061–8067. 10.4049/jimmunol.0902477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Kankkunen P, Teirilä L, Rintahaka J, Alenius H, Wolff H, Matikainen S. 2010. (1,3)-beta-glucans activate both dectin-1 and NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages. J. Immunol. 184:6335–6342. 10.4049/jimmunol.0903019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. van de Veerdonk FL, Joosten LA, Shaw PJ, Smeekens SP, Malireddi RK, van der Meer JW, Kullberg BJ, Netea MG, Kanneganti TD. 2011. The inflammasome drives protective Th1 and Th17 cellular responses in disseminated candidiasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 41:2260–2268. 10.1002/eji.201041226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Ferwerda B, Ferwerda G, Plantinga TS, Willment JA, van Spriel AB, Venselaar H, Elbers CC, Johnson MD, Cambi A, Huysamen C, Jacobs L, Jansen T, Verheijen K, Masthoff L, Morré SA, Vriend G, Williams DL, Perfect JR, Joosten LA, Wijmenga C, van der Meer JW, Adema GJ, Kullberg BJ, Brown GD, Netea MG. 2009. Human dectin-1 deficiency and mucocutaneous fungal infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 361:1760–1767. 10.1056/NEJMoa0901053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Rosentul DC, Plantinga TS, Oosting M, Scott WK, Velez Edwards DR, Smith PB, Alexander BD, Yang JC, Laird GM, Joosten LA, van der Meer JW, Perfect JR, Kullberg BJ, Netea MG, Johnson MD. 2011. Genetic variation in the dectin-1/CARD9 recognition pathway and susceptibility to candidemia. J. Infect. Dis. 204:1138–1145. 10.1093/infdis/jir458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Vince JE, Wong WW, Gentle I, Lawlor KE, Allam R, O’Reilly L, Mason K, Gross O, Guarda G, Anderton H, Castillo R, Häcker G, Silke J, Tschopp J. 2012. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins limit RIP3 kinase-dependent interleukin-1 activation. Immunity 36:215–227. 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Dagley MJ, Gentle IE, Beilharz TH, Pettolino FA, Djordjevic JT, Lo TL, Uwamahoro N, Rupasinghe T, Tull DL, McConville M, Beaurepaire C, Nantel A, Lithgow T, Mitchell AP, Traven A. 2011. Cell wall integrity is linked to mitochondria and phospholipid homeostasis in Candida albicans through the activity of the post-transcriptional regulator Ccr4-Pop2. Mol. Microbiol. 79:968–989. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07503.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental procedures. Download
Lamp1 association of the wild type and the Mediator mutants of C. albicans. Images relate to the quantification of Lamp1 association of wild-type C. albicans and Mediator mutants presented in Fig. 2E. The multiplicity of infection was 2:1 (Candida:macrophages). Images were obtained at the 2-h time point following the 1-h coincubation using a NikonC1 confocal microscope. Representative images showing Lamp1 association were selected using ImageJ software. Brightness and contrast were adjusted using CorelDRAW. For clarity, single slices from the stack of images collected are presented here. Download
Mediator subunits Med31 and Srb9 are important for virulence of C. albicans. (A) Mice were infected with 3 × 105 CFU of wild-type C. albicans, Mediator mutants, or complemented strains and survival was monitored over time as described in the experimental procedures section. An estimation of differences in survival (log-rank test) using the Kaplan-Meier method was performed, and a P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant (**, P ≤ 0.001; P values are for comparisons of the indicated mutant or complemented strains to wild-type C. albicans). Although mice infected with the srb9Δ/Δ+SRB9 complemented strain exhibited higher survival rates than mice infected with the wild type, the complemented srb9Δ/Δ+SRB9 strain caused statistically significant higher mortality than the srb9Δ/Δ mutant (P = 0.013). (B) Kidney organ burdens were tested at day 1 post-infection by determining numbers of colony-forming units (CFUs) per gram of tissue (n = 3). Both mutants displayed lower kidney burden than wild-type C. albicans (**, P <0.001 [one-way ANOVA]). Similarly to the survival assay described for panel A, the srb9Δ/Δ+SRB9 complemented strain showed an intermediate phenotype, but the rescue of the mutant was significant at P = 0.052. Rescue of the med31Δ/Δ mutant by its respective complemented strain was significant at P <0.001. (C) Kidney histopathology was performed at day 1 post-infection, using an inoculum of C. albicans of 1.5 × 106 CFU. C. albicans cells were visualized by periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining using an Olympus Provis Ax70 microscope (400×). (D) Numbers of CFUs for the indicated strains were determined at time 13.5 h relative to time 0 h, which corresponds to the time just after the 1-h coincubation. The fold change in CFUs is shown. The experiment was performed on 3 (med31∆∆, med31∆∆+MED31) and 5 (wild type, srb9∆∆, and srb9∆∆+SRB9) separate occasions. The MOI was 1:2 (macrophage:Candida). Averages and SEM of results from the biological repeats are shown. **, P <0.01. Download
Graphical representation of the macrophage cell death data. These graphs are the same as those presented in Fig. 3 but with all numerical P values shown for differences between wild-type and Mediator mutant C. albicans at the selected time points. The stars represent P values as follows: *, <0.05; **, <0.01; ***, <0.001; ****, <0.0001. Download
Induction of IL-1β secretion by C. albicans Mediator mutants. (A) A time course of IL-1β secretion comparing wild-type and srb9∆/∆ mutant C. albicans. The multiplicity of infection was 1:6 (macrophage:Candida). Averages and SD of the results of two technical repeats are shown. (B) Results of the individual experiments used to create the graphs in Fig. 4 with absolute values of secreted IL-1β (pg/ml). For the srb9∆/∆ mutant, data from the experiment described for panel A and the experiments described for panel B were combined for the graph in Fig. 4. (C) Levels of secreted IL-1β induced by Mediator mutants of C. albicans in casp-1−/− casp-11−/− BMDMs were expressed relative to the levels induced by wild-type C. albicans. **, <0.01. ***, <0.001. Download
Wild-type C. albicans was used to infect wild-type BMDMs. For each experiment, 4 microscopy fields were monitored over time. A representative field is shown here. The video was made by merging bright images with fluorescent (propidium iodide) images to show death of macrophages over time. Brightness and contrast were adjusted by even application to the whole field using ImageJ. The original files were compressed in JPG file format and saved in AVI file format. Download
Wild-type C. albicans was used to infect RAW 264.7 macrophages. The video was processed as described for Video S1. Download
Wild-type C. albicans was used to infect casp1-/-casp11−/− BMDMs. The video was obtained and processed as described for Video S1. Download
The C. albicans Mediator mutant med31Δ/Δ was used to infect wild-type BMDMs. The video was obtained and processed as described for Video S1. Download
The C. albicans Mediator mutant srb9Δ/Δ was used to infect wild-type BMDMs. The video was obtained and processed as described for Video S1. Download