Abstract
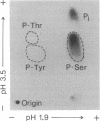
The phosphorylation of Drosophila melanogaster DNA topoisomerase II by purified casein kinase II was characterized in vitro. Under the conditions used, the kinase incorporated a maximum of 2-3 molecules of phosphate per homodimer of topoisomerase II. No autophosphorylation of the topoisomerase was observed. The only amino acid residue modified by casein kinase II was serine. Apparent Km and Vmax values for the phosphorylation reaction were 0.4 microM topoisomerase II and 3.3 mumol of phosphate incorporated per min per mg of kinase, respectively. Phosphorylation stimulated the DNA relaxation activity of topoisomerase II by 3-fold over that of the dephosphorylated enzyme, and the effects of modification could be reversed by treatment with alkaline phosphatase. Therefore, this study demonstrates that post-translational enzymatic modifications can be used to modulate the interaction between topoisomerase II and DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENDER M. L., KEZDY J. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF PROTEOLYTIC ENZYMES. Annu Rev Biochem. 1965;34:49–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.34.070165.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Cozzarelli N. R. A sign inversion mechanism for enzymatic supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1081–1083. doi: 10.1126/science.227059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castora F. J., Vissering F. F., Simpson M. V. The effect of bacterial DNA gyrase inhibitors on DNA synthesis in mammalian mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 9;740(4):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. DNA topoisomerases. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90341-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNardo S., Voelkel K., Sternglanz R. DNA topoisomerase II mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: topoisomerase II is required for segregation of daughter molecules at the termination of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguet M., Lavenot C., Harper F., Mirambeau G., De Recondo A. M. DNA topoisomerases from rat liver: physiological variations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1059–1075. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durban E., Mills J. S., Roll D., Busch H. Phosphorylation of purified Novikoff hepatoma topoisomerase I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):897–905. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durban E., Roll D., Beckner G., Busch H. Purification and characterization of a nuclear DNA-binding phosphoprotein in fetal and tumor tissues. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):537–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T., Hajduk S. L., Marini J. C. The molecular biology of trypanosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro A. M., Higgins N. P., Olivera B. M. Poly(ADP-ribosylation) of a DNA topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6000–6003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro A. M., Olivera B. M. Poly(ADP-ribosylation) of DNA topoisomerase I from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):547–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Berrios M., Blobel G. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous subnuclear fraction composed of nuclear matrix, peripheral lamina, and nuclear pore complexes from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):674–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. Nuclear lamina and the structural organization of the nuclear envelope. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):967–978. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V., Shelton E. R., Brutlag D. L. Purification and characterization of a type II casein kinase from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3258–3265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto T., Wang J. C. Yeast DNA topoisomerase II is encoded by a single-copy, essential gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinases--multipotential protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1982;21:101–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra-Bilen J., Ittel M. E., Niedergang C., Vosberg H. P., Mandel P. DNA topoisomerase I from calf thymus is inhibited in vitro by poly(ADP-ribosylation). Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 2;136(2):391–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. Type II DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that can unknot a topologically knotted DNA molecule via a reversible double-strand break. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):697–707. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern M. R., Painter R. B. Dependence of mammalian DNA replication on DNA supercoiling. II. Effects of novobiocin on DNA synthesis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 26;563(2):306–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern M. R., Paone R. F., Day R. S., 3rd Eukaryotic DNA repair is blocked at different steps by inhibitors of DNA topoisomerases and of DNA polymerases alpha and beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 26;697(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. S., Busch H., Durban E. Purification of a protein kinase from human Namalwa cells that phosphorylates topoisomerase I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1222–1227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91907-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins R., Miskimins W. K., Bernstein H., Shimizu N. Epidermal growth factor-induced topoisomerase(s). Intracellular translocation and relation to DNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jun;146(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Fisher L. M., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. DNA gyrase action involves the introduction of transient double-strand breaks into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1847–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio A., Uyeki E. M. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in permeabilized L cells by novobiocin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1448–1455. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Shelton E. R., Brutlag D. L. DNA topoisomerase II from Drosophila melanogaster. Relaxation of supercoiled DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9536–9543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. Double strand DNA cleavage by type II DNA topoisomerase from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8421–8428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Nolan J. M., Hsieh T. A protein kinase activity tightly associated with Drosophila type II DNA topoisomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6938–6942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E. R., Osheroff N., Brutlag D. L. DNA topoisomerase II from Drosophila melanogaster. Purification and physical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9530–9535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomai J., Zadok A. Reversible decatenation of kinetoplast DNA by a DNA topoisomerase from trypanosomatids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4019–4034. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck W. T., Rosenkranz P. G., Rosenkranz H. S. Inhibition of DNA synthesis accompanied by stimulation of protein synthesis in novobiocin-treated developing sea urchins. Mutat Res. 1982 Apr;104(1-3):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(82)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Arrest of segregation leads to accumulation of highly intertwined catenated dimers: dissection of the final stages of SV40 DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taudou G., Mirambeau G., Lavenot C., der Garabedian A., Vermeersch J., Duguet M. DNA topoisomerase activities in concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):431–435. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse-Dinh Y. C., Wong T. W., Goldberg A. R. Virus- and cell-encoded tyrosine protein kinases inactivate DNA topoisomerases in vitro. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):785–786. doi: 10.1038/312785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Yanagida M. Isolation of type I and II DNA topoisomerase mutants from fission yeast: single and double mutants show different phenotypes in cell growth and chromatin organization. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1737–1744. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]