Abstract
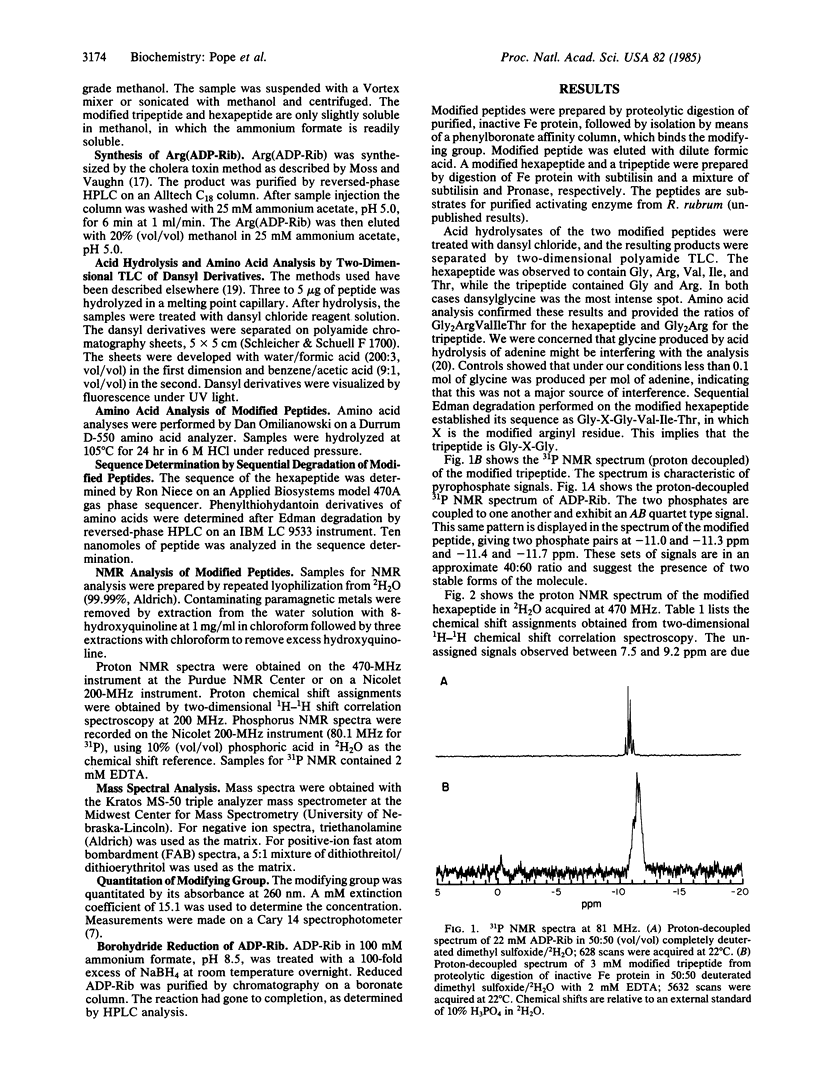
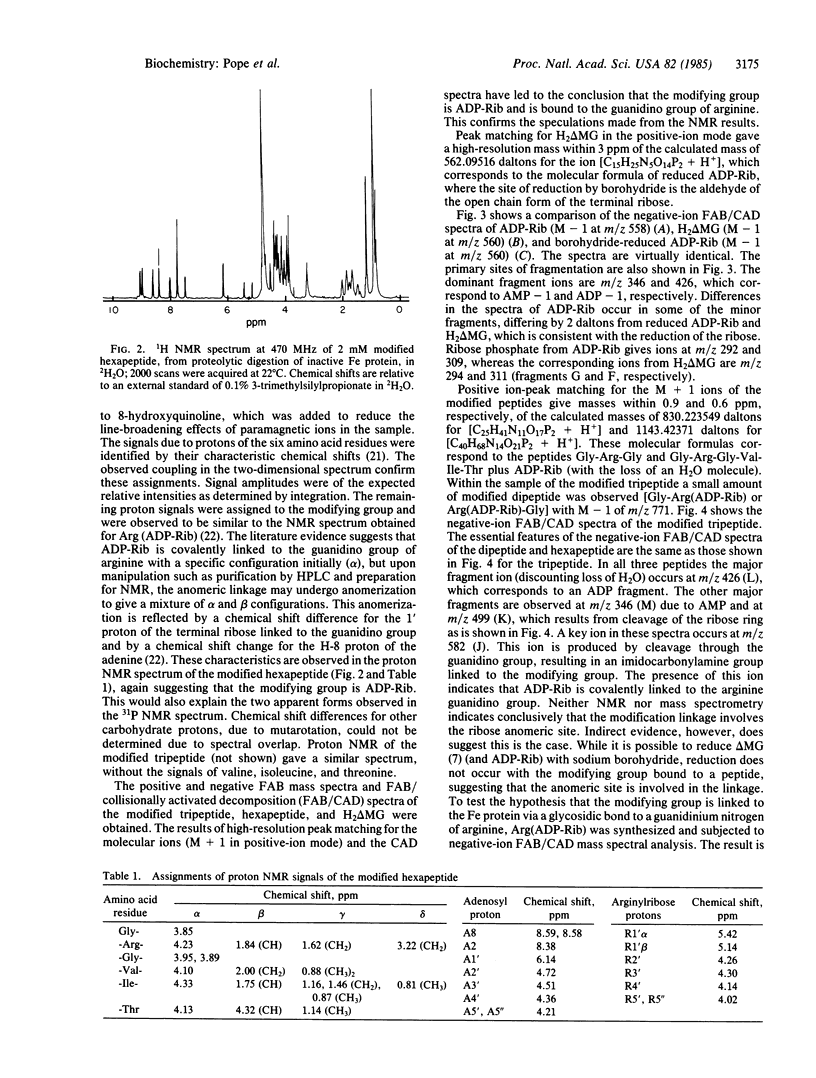
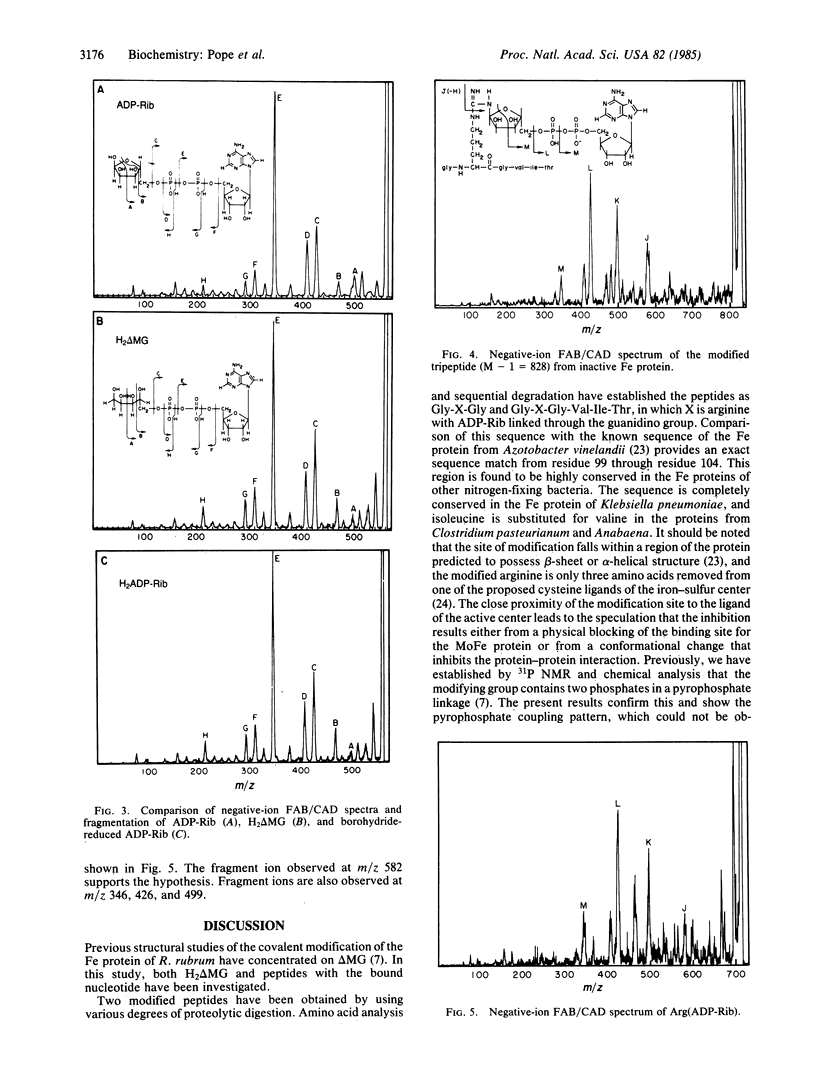
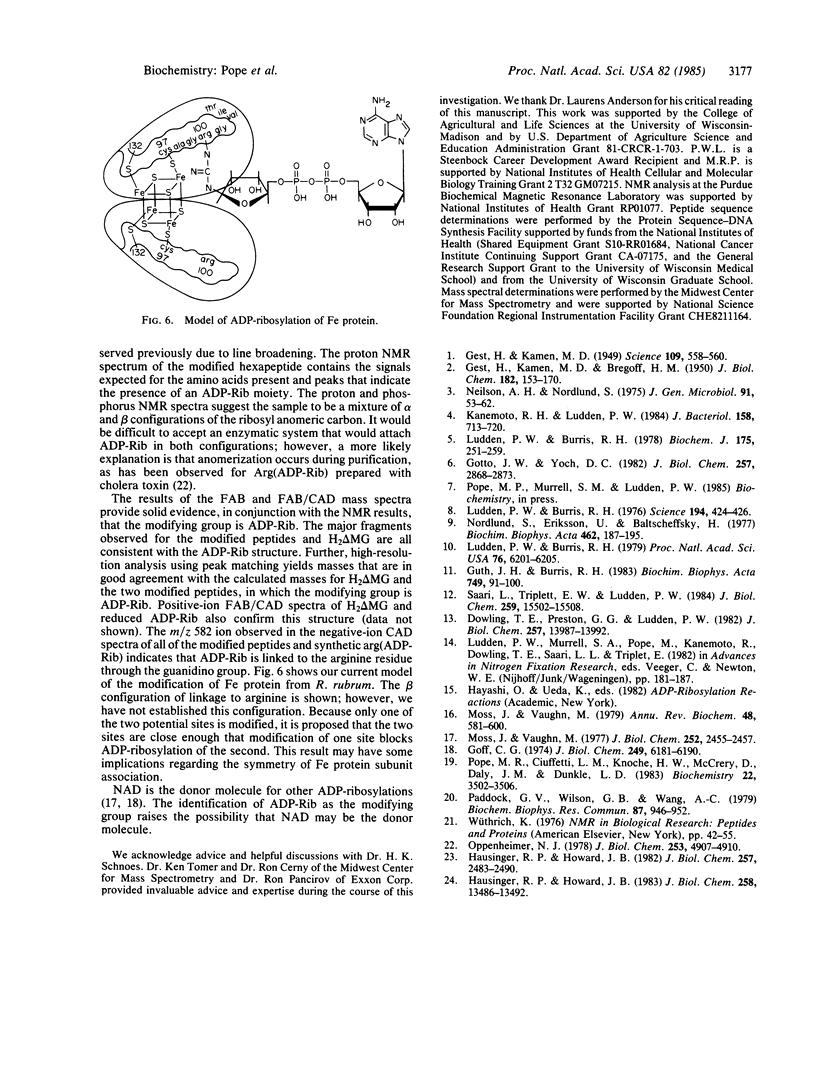
Nitrogenase in Rhodospirillum rubrum is inactivated in vivo by the covalent modification of the Fe protein with a nucleotide. The preparation of two modified peptides derived from proteolytic digestion of the inactive Fe protein is described. The modifying group is shown to be adenosine diphosphoribose, linked through the terminal ribose to a guanidino nitrogen of arginine. The structural features were established by using proton and phosphorus NMR, positive- and negative-ion fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry, and fast atom bombardment/collisionally activated decomposition mass spectrometry. Spectral methods along with chromatographic analysis and sequential degradation established the sequence of the modification site of Fe protein as Gly-Arg(ADR-ribose)-Gly-Val-Ile-Thr. This corresponds to the sequence in the Fe protein from Azotobacter vinelandii for amino acid residues 99 to 104.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dowling T. E., Preston G. G., Ludden P. W. Heat activation of the Fe protein of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13987–13992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G. Chemical structure of a modification of the Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase alpha polypeptides induced by bacteriophage T4 infection. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6181–6190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto J. W., Yoch D. C. Regulation of Rhodospirillum rubrum nitrogenase activity. Properties and interconversion of active and inactive Fe protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2868–2873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P., Howard J. B. The amino acid sequence of the nitrogenase iron protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2483–2490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P., Howard J. B. Thiol reactivity of the nitrogenase Fe-protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13486–13492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen M. D., Gest H. Evidence for a Nitrogenase System in the Photosynthetic Bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. Science. 1949 Jun 3;109(2840):560–560. doi: 10.1126/science.109.2840.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto R. H., Ludden P. W. Effect of ammonia, darkness, and phenazine methosulfate on whole-cell nitrogenase activity and Fe protein modification in Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):713–720. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.713-720.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Activating factor for the iron protein of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Science. 1976 Oct 22;194(4263):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.824729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum, and evidence for phosphate, ribose and an adenine-like unit covalently bound to the iron protein. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):251–259. doi: 10.1042/bj1750251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Removal of an adenine-like molecule during activation of dinitrogenase reductase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6201–6205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Activation of adenylate cyclase by choleragen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:581–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity with arginine as an acceptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2455–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson A. H., Nordlund S. Regulation of nitrogenase synthesis in intact cells of Rhodospirillum rubrum: inactivation of nitrogen fixation by ammonia, L-glutamine and L-asparagine. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Nov;91(1):53–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund S., Eriksson U., Baltscheffsky H. Necessity of a membrane component for nitrogenase activity in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 12;462(1):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer N. J. Structural determination and stereospecificity of the choleragen-catalyzed reaction of NAD+ with guanidines. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4907–4910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddock G. V., Wilson G. B., Wang A. C. Contribution of hydrolyzed nucleic acids and their constituents to the apparent amino acid composition of biological compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):946–952. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saari L. L., Triplett E. W., Ludden P. W. Purification and properties of the activating enzyme for iron protein of nitrogenase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15502–15508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



