Abstract
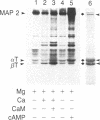
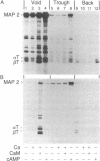
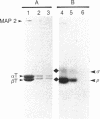
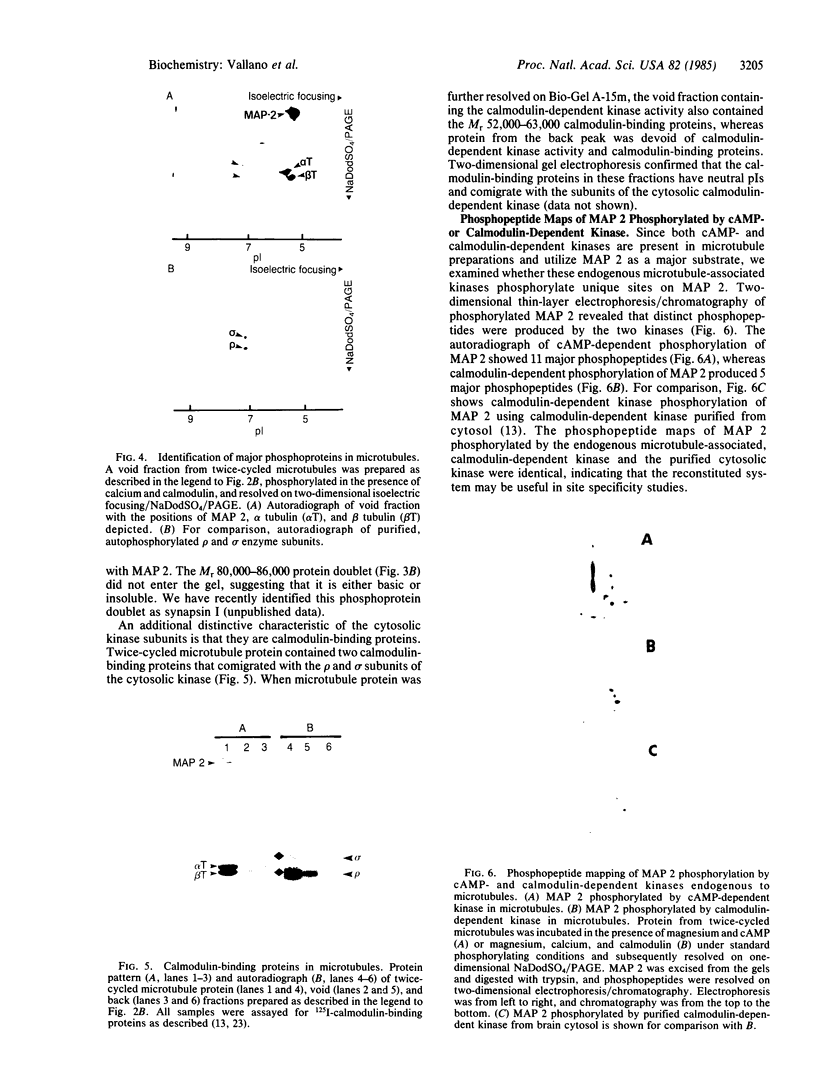
Both cAMP- and calmodulin-dependent kinases are proposed regulators of microtubule function by means of their ability to phosphorylate microtubule-associated protein 2(MAP 2). A cAMP-dependent kinase/MAP 2 complex is endogenous to microtubules. In this report, we demonstrate that an endogenous calmodulin-dependent kinase that phosphorylates MAP 2 as a major substrate is also present in microtubules prepared under conditions that preserve kinase activity. This enzyme is identical to a calmodulin-dependent kinase purified previously from rat brain cytosol. A fraction containing calmodulin-dependent kinase and MAP 2 was separated from the cAMP-dependent kinase/MAP 2 complex by gel filtration chromatography of microtubule protein in high ionic strength buffer. All of the recovered calmodulin-dependent kinase activity in microtubules eluted in a single protein peak. The specific activity of the enzyme for MAP 2 was enriched 31-fold in this fraction compared to cytosol. Two-dimensional tryptic phosphopeptide mapping revealed that the endogenous cAMP- and calmodulin-dependent kinases phosphorylated distinct sites on MAP 2. These data demonstrate that both kinases are present in microtubule preparations and that they may differentially regulate MAP 2 function by phosphorylating separate sites on MAP 2.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett M. K., Erondu N. E., Kennedy M. B. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that is highly concentrated in brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12735–12744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B. E., DeLorenzo R. J. Ca2+- and calmodulin-stimulated endogenous phosphorylation of neurotubulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):991–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin R. K., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Function of a calmodulin in postsynaptic densities. III. Calmodulin-binding proteins of the postsynaptic density. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):449–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J. Calmodulin in neurotransmitter release and synaptic function. Fed Proc. 1982 May;41(7):2265–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J., Emple G. P., Glaser G. H. Regulation of the level of endogenous phosphorylation of specific brain proteins by diphenylhydantoin. J Neurochem. 1977 Jan;28(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deery W. J., Means A. R., Brinkley B. R. Calmodulin-microtubule association in cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):904–910. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., Gonzalez B., McGuire J. S., Jr, DeLorenzo R. J. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent kinase from rat brain cytosol able to phosphorylate tubulin and microtubule-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12632–12640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson L., Frey T., Zeeberg B., Dalldorf F., Caplow M. Inhibition of microtubule assembly by phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2472–2479. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job D., Rauch C. T., Fischer E. H., Margolis R. L. Regulation of microtubule cold stability by calmodulin-dependent and -independent phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith C., DiPaola M., Maxfield F. R., Shelanski M. L. Microinjection of Ca++-calmodulin causes a localized depolymerization of microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1918–1924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Kumagai H., Ohtsuki I., Sakai H. The interactions between calcium-dependent regulator protein of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and microtubule proteins. I. Effect of calcium-dependent regulator protein on the calcium sensitivity of microtubule assembly. J Biochem. 1979 May;85(5):1257–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H. Differential phosphorylation of MAP-2 stimulated by calcium-calmodulin and cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1175–1178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloboda R. D., Rudolph S. A., Rosenbaum J. L., Greengard P. Cyclic AMP-dependent endogenous phosphorylation of a microtubule-associated protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):177–181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue K., Fujita M., Muramoto Y., Kakiuchi S. The calmodulin-binding protein in microtubules is tau factor. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 14;132(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80447-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Bloom G. S., Theurkauf W. E. Microtubule-associated proteins: subunits of the cytomatrix. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):38s–44s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.38s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Borisy G. G. The non-tubulin component of microtubule protein oligomers. Effect on self-association and hydrodynamic properties. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2834–2845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Suter M. M., Littman D. R., Kirschner M. W. Properties of the depolymerization products of microtubules from mammalian brain. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5529–5537. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Tubulin and calmodulin. Effects of microtubule and microfilament inhibitors on localization in the mitotic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):624–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Fukunaga K., Tanaka E., Miyamoto E. Ca2+- and calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein 2 and tau factor, and inhibition of microtubule assembly. J Neurochem. 1983 Oct;41(4):1119–1125. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb09060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]