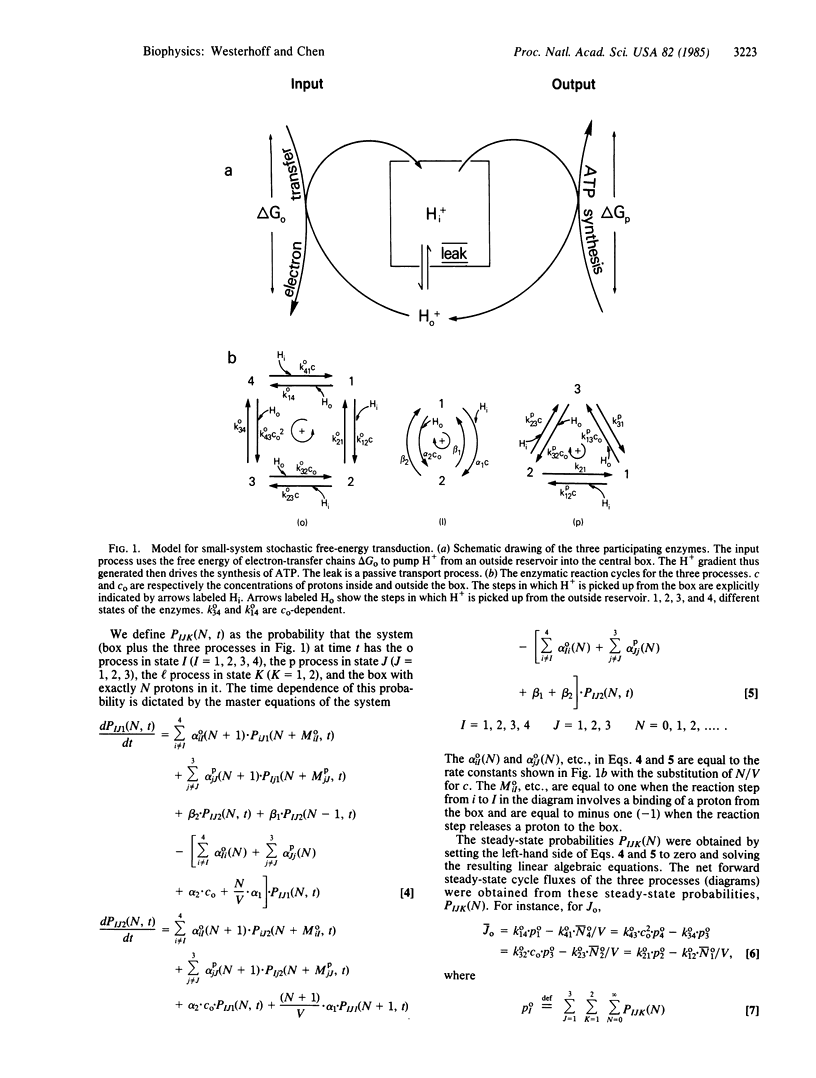
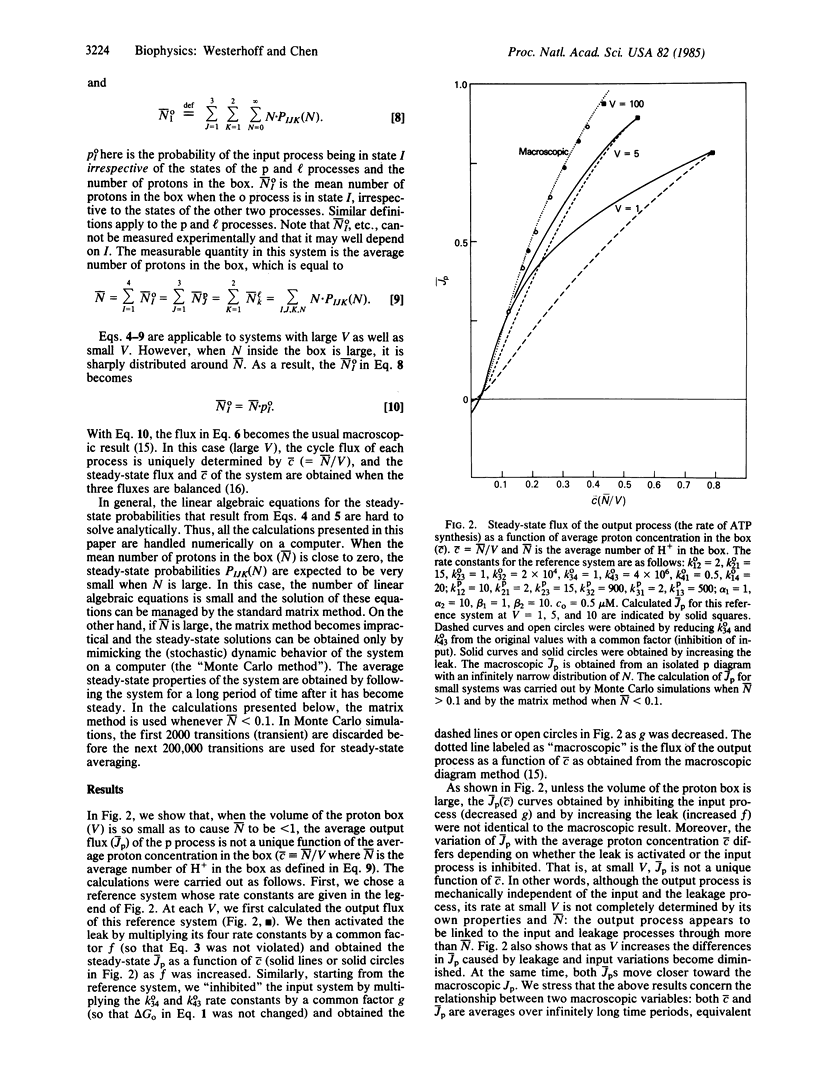
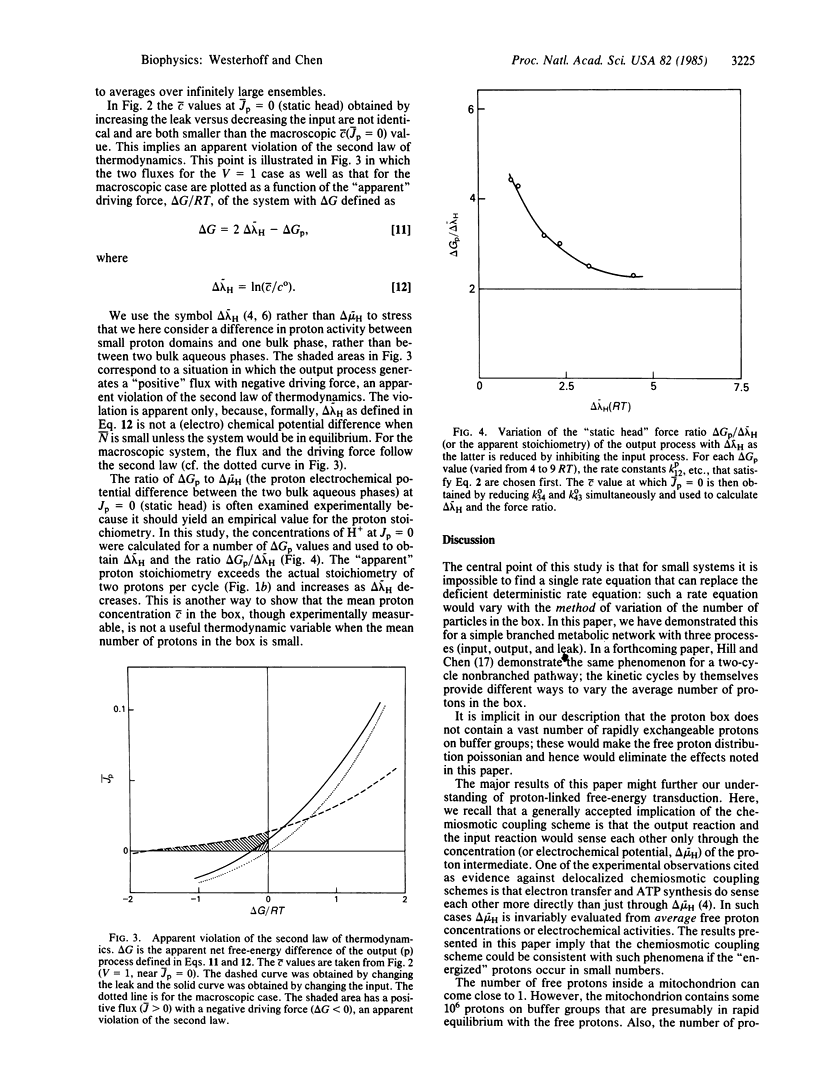
Abstract
Theoretical free-energy coupling systems in which the free energy coupling intermediate (e.g., the proton) occurs only in small numbers of molecules per coupling unit are shown to exhibit a number of peculiar properties: (i) the reactions involving the intermediates do not follow conventional kinetic (or nonequilibrium thermodynamic) rate laws in terms of the average concentration or chemical potential of the intermediate, (ii) the variation of the output reaction rate with the average intermediate concentration (or apparent chemical potential) is not unequivocal but depends on whether the input reaction or the leak is varied to alter that concentration, and (iii) when the apparent free energy contained in the average concentration of the intermediate is compared with the average free energy recovered in the output reaction, apparent violations of the second law of thermodynamics can occur. These phenomena are reminiscent of experimental observations in proton-linked free-energy transducing systems that suggest a more direct coupling between electron transfer chains and H+-ATPases than only through a bulk proton gradient, delta muH. Consequently, the chemiosmotic coupling theory can account for those observations if it limits the number of free energy coupling protons per chemiosmotic coupling unit to small values.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azzone G. F., Massari S., Pozzan T. The generation of the proton electrochemical potential and its role in energy transduction. Mol Cell Biochem. 1977 Sep 9;17(2):101–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01743433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L. Coupled enzyme systems in a vesicular membrane: oxidative phosphorylation as an example. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):232–235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kell D. B. On the functional proton current pathway of electron transport phosphorylation. An electrodic view. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 3;549(1):55–99. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClare C. W. Chemical machines, Maxwell's demon and living organisms. J Theor Biol. 1971 Jan;30(1):1–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melandri B. A., Venturoli G., de Santis A., Baccarini-Melandri A. The induction kinetics of bacterial photophosphorylation. Threshold effects by the phosphate potential and correlation with the amplitude of the carotenoid absorption band shift. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 5;592(1):38–52. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulachev V. P. The localized delta muH+ problem. The possible role of the local electric field in ATP synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80692-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. C. Mechanism of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:1015–1026. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.005055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam K., Woelders H., Colen A., Westerhoff H. V. A structural basis for mosaic protonic energy coupling. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Jun;12(3):401–402. doi: 10.1042/bst0120401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhoff H. V., Colen A. M., van Dam K. Metabolic control by pump slippage and proton leakage in 'delocalized' and more localized chemiosmotic energy-coupling schemes. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Jan;11(1):81–85. doi: 10.1042/bst0110081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhoff H. V., Melandri B. A., Venturoli G., Azzone G. F., Kell D. B. A minimal hypothesis for membrane-linked free-energy transduction. The role of independent, small coupling units. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 17;768(3-4):257–292. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerhoff H. V., Melandri B. A., Venturoli G., Azzone G. F., Kell D. B. Mosaic protonic coupling hypothesis for free energy transduction. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 2;165(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


