Abstract
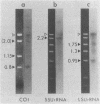
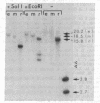
We have used heterologous hybridization and DNA sequence analysis to determine whether the 16-kilobase-pair (kbp) DNA from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mitochondria is the functional equivalent of mtDNA in other eukaryotes. Restriction fragments corresponding to a continuous internal stretch spanning 75% of the 16-kbp DNA have been cloned and mapped, and regions hybridizing with probes specific for the cytochrome oxidase subunit I [CytOx I (acronym COI)] and apocytochrome b (Cyt b) genes of yeast and the mitochondrial 26S and 18S rRNA genes of wheat have been identified. Sequence analysis has verified the presence of CytOx I and the large and small subunit rRNA genes in the C. reinhardtii 16-kbp DNA. In the region of the 16-kbp DNA corresponding to exon 4 in the yeast CytOx I gene, the derived amino acid sequence is 61% and 63% identical with the CytOx I amino acid sequences of yeast and human mitochondria, respectively. Notably, tryptophan is specified by TGG rather than by TGA in this section of the C. reinhardtii CytOx I gene. A probe from the CytOx I region of the 16-kbp DNA hybridizes only with this 16-kbp DNA in Southern blots of total cellular DNA from C. reinhardtii but with a larger DNA species in the total cellular DNA of C. moewusii and C. eugametos--two species that lack a 16-kbp DNA. These observations provide evidence that C. reinhardtii 16-kbp DNA comprises at least part of the mitochondrial genome of this organism and that a homologous DNA exists in other species of Chlamydomonas.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonen L., Gray M. W. Organization and expression of the mitochondrial genome of plants I. The genes for wheat mitochondrial ribosomal and transfer RNA: evidence for an unusual arrangement. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):319–335. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonitz S. G., Coruzzi G., Thalenfeld B. E., Tzagoloff A., Macino G. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Structure and nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for subunit 1 of yeast cytochrme oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11927–11941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast 16S rRNA gene and its surrounding regions of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7609–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconet D., Lejeune B., Quetier F., Gray M. W. Evidence for homologous recombination between repeated sequences containing 18S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in wheat mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):297–302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D., Chiang K. S. Physical mapping and characterization of Chlamydomonas mitochondrial DNA molecules: their unique ends, sequence homogeneity, and conservation. Plasmid. 1980 Jul;4(1):82–96. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Has the endosymbiont hypothesis been proven? Microbiol Rev. 1982 Mar;46(1):1–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.1.1-42.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. Mitochondrial genome diversity and the evolution of mitochondrial DNA. Can J Biochem. 1982 Mar;60(3):157–171. doi: 10.1139/o82-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Sankoff D., Cedergren R. J. On the evolutionary descent of organisms and organelles: a global phylogeny based on a highly conserved structural core in small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5837–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Arnberg A. C., Roosendaal E., van der Horst G., van der Veen R., van Ommen G. J., Grivell L. A. Variation, transcription and circular RNAs of the mitochondrial gene for subunit I of cytochrome c oxidase. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):35–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huysmans E., Dams E., Vandenberghe A., De Wachter R. The nucleotide sequences of the 5S rRNAs of four mushrooms and their use in studying the phylogenetic position of basidiomycetes among the eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2871–2880. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Piechulla B., Hahn U. Consensus structure and evolution of 5S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):893–900. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambach A., Hogness D. S. Translation of Drosophila melanogaster sequences in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R., Grant D., Chiang K. S., Swift H. Isolation and characterization of mitochondrial DNA from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3268–3272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Fukuhara H. Séquence nucléotidique du gène de l'ARN ribosomique 15S mitochondrial de la levure. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1980 Dec 8;291(12):933–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. F., Schnare M. N., Gray M. W. Pronounced structural similarities between the small subunit ribosomal RNA genes of wheat mitochondria and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]